
ALB/NLB now supports Post-Quantum Key Exchange.
This page has been translated by machine translation. View original
In November 2025, there was an update to Application Load Balancer (ALB) and Network Load Balancer (NLB) that added support for Post-Quantum Key Exchange.
While practical quantum computers may still be some time away, there is a risk of HNDL (Harvest Now, Decrypt Later) / SNDL (Store Now, Decrypt Later) attacks, where encrypted communication data is intercepted and stored now to be decrypted later when high-performance quantum computers become available.
With ALB and NLB now supporting new cryptographic methods (post-quantum cryptography) that are difficult to decrypt even with quantum computers, it's possible to prepare for the risk of future data decryption.
I recently had the opportunity to create ALB and NLB with post-quantum cryptography support using CloudFormation and test their functionality with browser connections, which I'd like to share.
Test Environment
Architecture Diagram

ALB
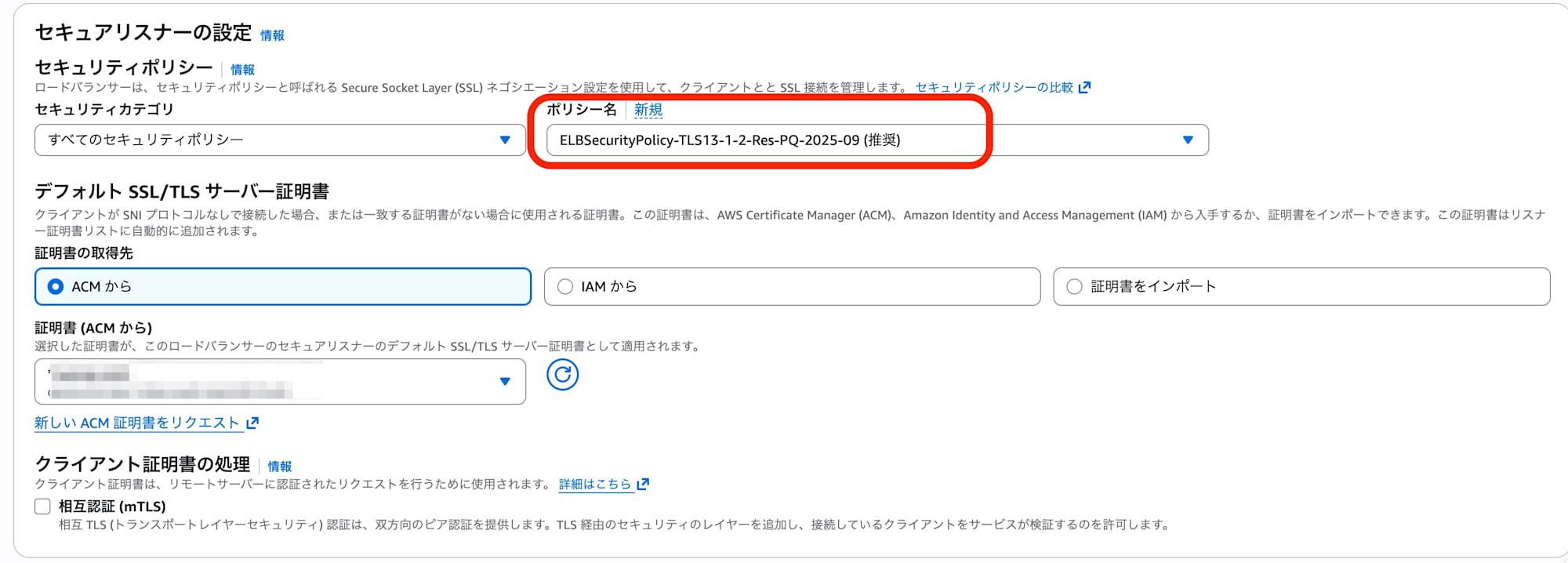
I configured the security policy "ELBSecurityPolicy-TLS13-1-2-Res-PQ-2025-09," which includes "PQ" indicating post-quantum cryptography support.
Listener:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::Listener
Properties:
LoadBalancerArn: !Ref LoadBalancer
Port: 443
Protocol: HTTPS
Certificates:
- CertificateArn: !Ref CertificateArn
SslPolicy: ELBSecurityPolicy-TLS13-1-2-Res-PQ-2025-09
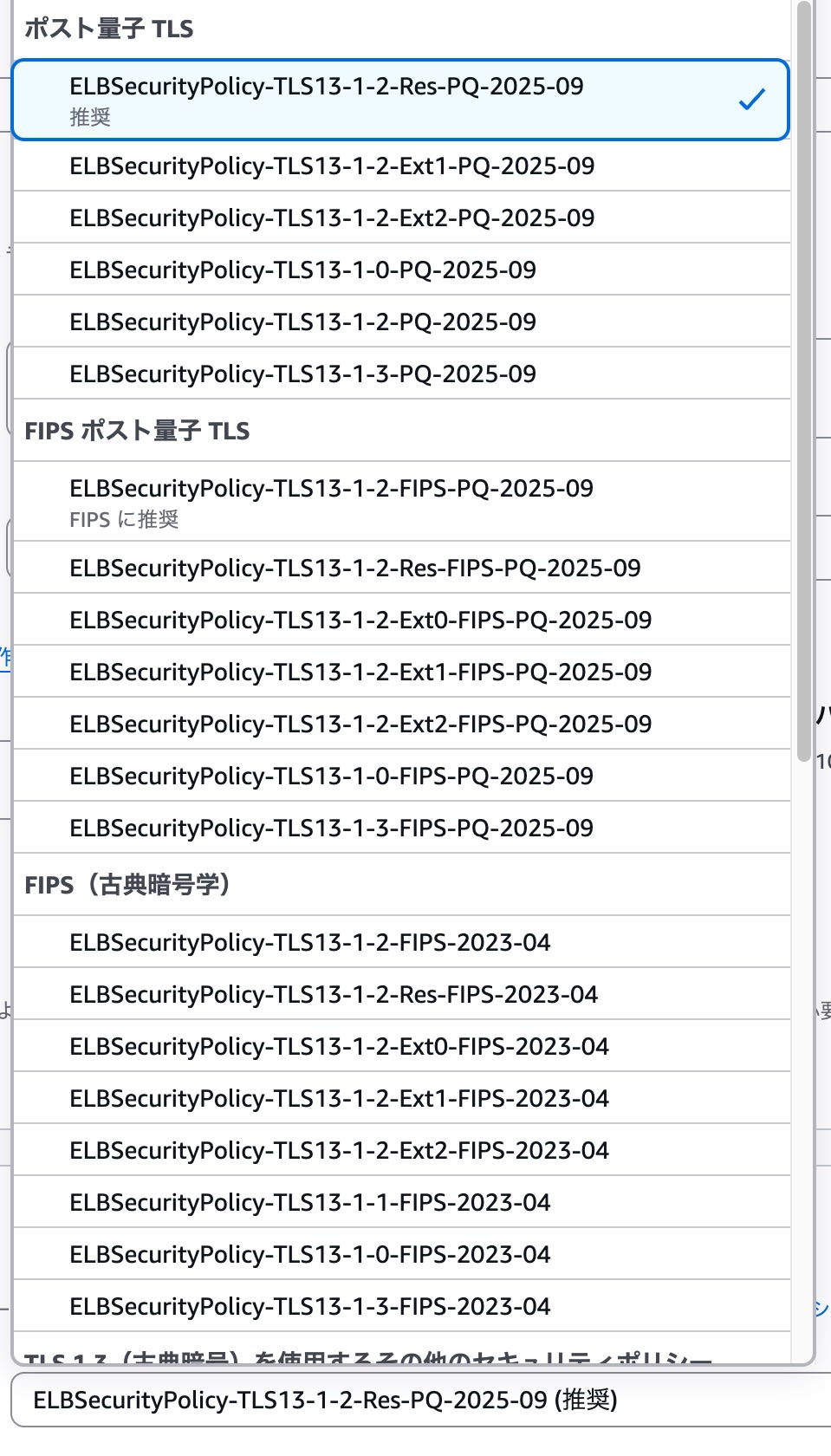
- In the management console, I used "ELBSecurityPolicy-TLS13-1-2-Res-PQ-2025-09" which was listed as recommended among the PQ-supported post-quantum TLS policies.
ACM (AWS Certificate Manager)
For the TLS/SSL certificate, I used one created with the key algorithm "ECDSA P 256".
CloudFormation
I used the following template to build the ALB and EC2 for testing.
Test Environment Creation Template (Click to expand)
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: 'ALB Post-Quantum TLS Test Environment (ARM64/T4g)'
Parameters:
VpcId:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPC::Id
Description: Default VPC ID
SubnetIds:
Type: List<AWS::EC2::Subnet::Id>
Description: Select at least 2 Public Subnets
CertificateArn:
Type: String
Description: ACM Certificate ARN for HTTPS Listener
Default: arn:aws:acm:ap-northeast-1:********:certificate/****-***-***-***-******
AllowedPattern: "arn:aws:acm:.*"
LatestAmiId:
Type: AWS::SSM::Parameter::Value<AWS::EC2::Image::Id>
Default: /aws/service/ami-amazon-linux-latest/al2023-ami-kernel-default-arm64
Resources:
# Security Group
ALBSecurityGroup:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupDescription: Allow HTTPS
VpcId: !Ref VpcId
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: 443
ToPort: 443
CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0
EC2SecurityGroup:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupDescription: Allow HTTP from ALB
VpcId: !Ref VpcId
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: 80
ToPort: 80
SourceSecurityGroupId: !Ref ALBSecurityGroup
# EC2 Instance
TargetInstance:
Type: AWS::EC2::Instance
Properties:
ImageId: !Ref LatestAmiId
InstanceType: t4g.nano
SecurityGroupIds:
- !Ref EC2SecurityGroup
SubnetId: !Select [0, !Ref SubnetIds]
UserData:
Fn::Base64: !Sub |
#!/bin/bash
yum update -y
yum install -y httpd
systemctl start httpd
systemctl enable httpd
echo "<h1>Post-Quantum TLS Test (ARM)</h1>" > /var/www/html/index.html
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: ALB-PQ-Target-ARM
# Target Group
TargetGroup:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::TargetGroup
Properties:
Name: alb-pq-test-tg
Port: 80
Protocol: HTTP
VpcId: !Ref VpcId
Targets:
- Id: !Ref TargetInstance
# ALB
LoadBalancer:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::LoadBalancer
Properties:
Name: alb-pq-test
Scheme: internet-facing
SecurityGroups:
- !Ref ALBSecurityGroup
Subnets: !Ref SubnetIds
# HTTPS Listener with PQ Policy
Listener:
Type: AWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::Listener
Properties:
LoadBalancerArn: !Ref LoadBalancer
Port: 443
Protocol: HTTPS
Certificates:
- CertificateArn: !Ref CertificateArn
SslPolicy: ELBSecurityPolicy-TLS13-1-2-Res-PQ-2025-09
DefaultActions:
- Type: forward
TargetGroupArn: !Ref TargetGroup
Connection Verification
Chrome
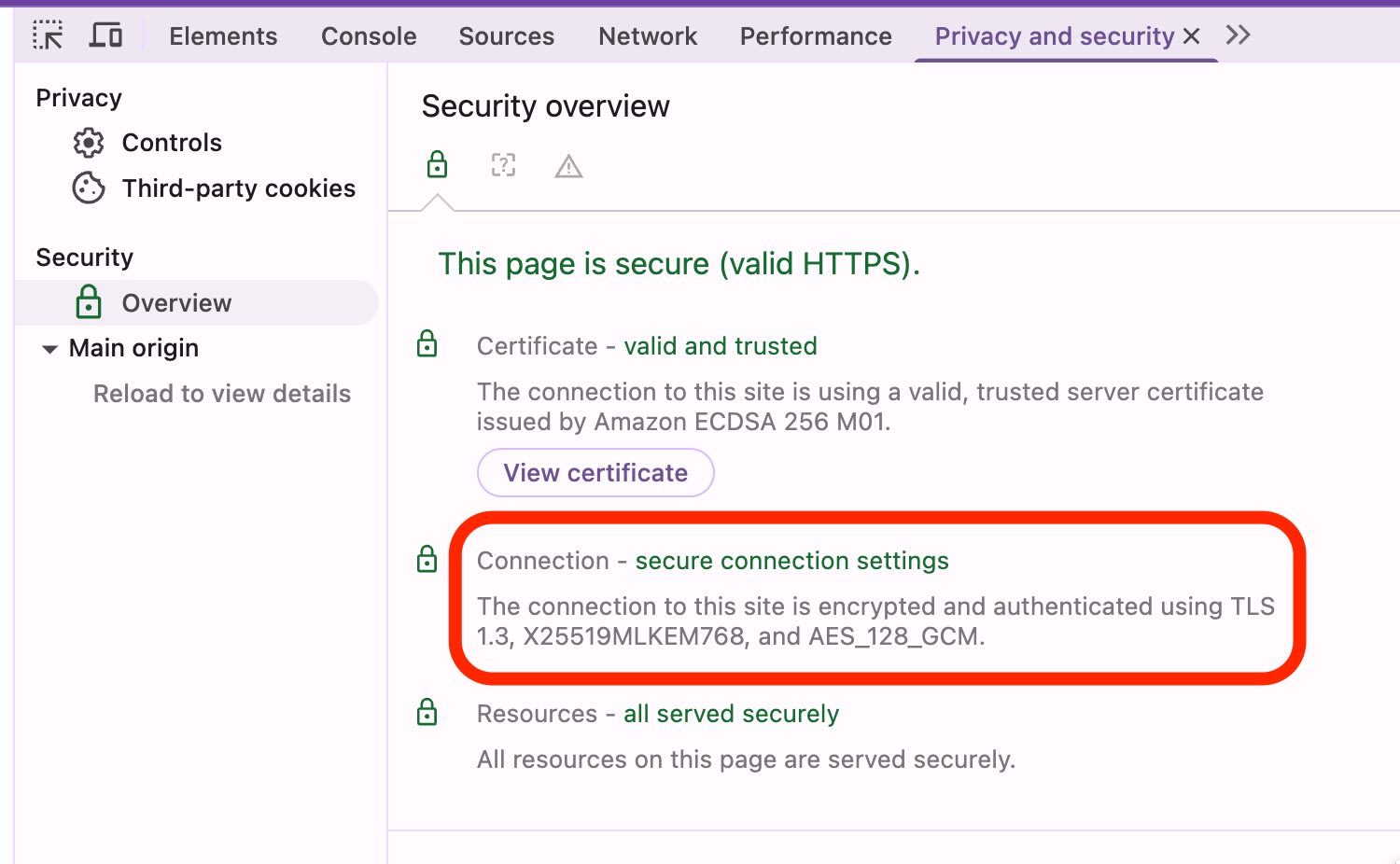
I attempted to verify using the developer tools in Google Chrome, version 142.0.7444.176 (Official Build) (arm64).
In the Connection - secure connection settings section, I confirmed the use of MLKEM768: a quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithm standardized by NIST (Module-Lattice-Based Key-Encapsulation Mechanism, formerly Kyber).
SSL Labs
I also attempted verification using SSL Labs' SSL Server Test.
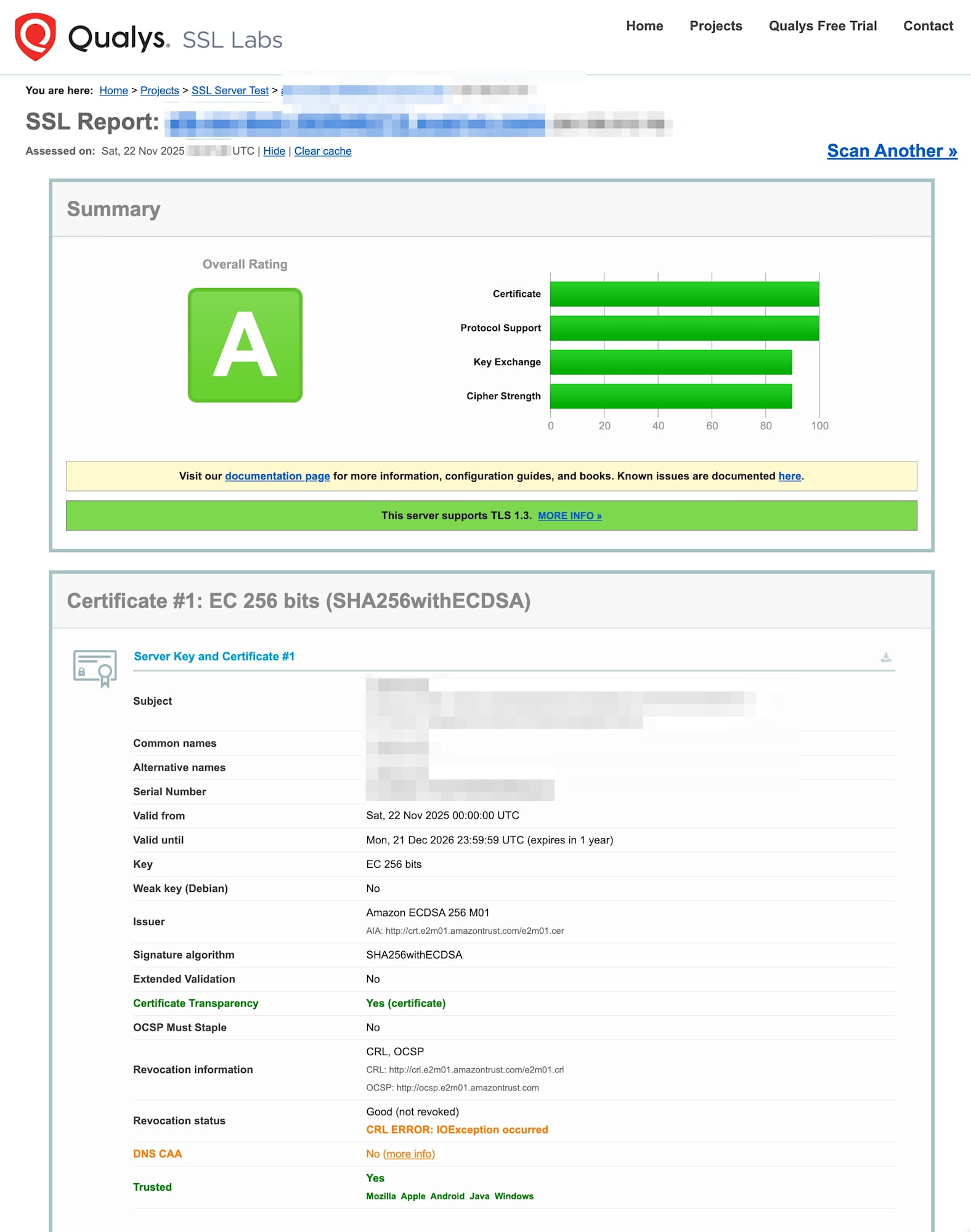
As of November 2025, the SSL Server Test does not support quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms (PQ), so PQ connections could not be verified.

However, connections using X25519 (traditional elliptic curve cryptography) were successful with an "A" rating, confirming that existing clients without PQ support can still access the system without issues.
Summary
By simply changing the security policy of ALB/NLB, it's now possible to protect against HNDL/SNDL attacks. For systems in finance, healthcare, public sectors, etc., where confidentiality must be maintained for years or decades, this implementation is worth considering.
The performance impact of using hybrid key exchange is limited to an increase in TLS handshake message size by about 1KB. The ML-KEM (lattice cryptography) used is actually much faster in computation compared to traditional RSA or elliptic curve cryptography, resulting in minimal impact on CPU resource consumption for ELBs and browsers.
In the future, if countermeasures against HNDL/SNDL attacks are required, please consider using the post-quantum key exchange (PQ) policy now supported by ALB/NLB.



