
Tried connecting Alexa and Bedrock using Lambda
This page has been translated by machine translation. View original
Introduction
Hello, I'm Shota Yamamoto.
This time, I've built a system that allows me to ask AI questions by voice by connecting Alexa, which I use at home, with Amazon Bedrock.
While Alexa's standard features can provide AI-powered answers to some extent, this time I'll implement more advanced AI responses using Bedrock.
1. Creating a Lambda Function and Setting Permissions
Creating the Function
First, let's create a Lambda function to execute the processing.
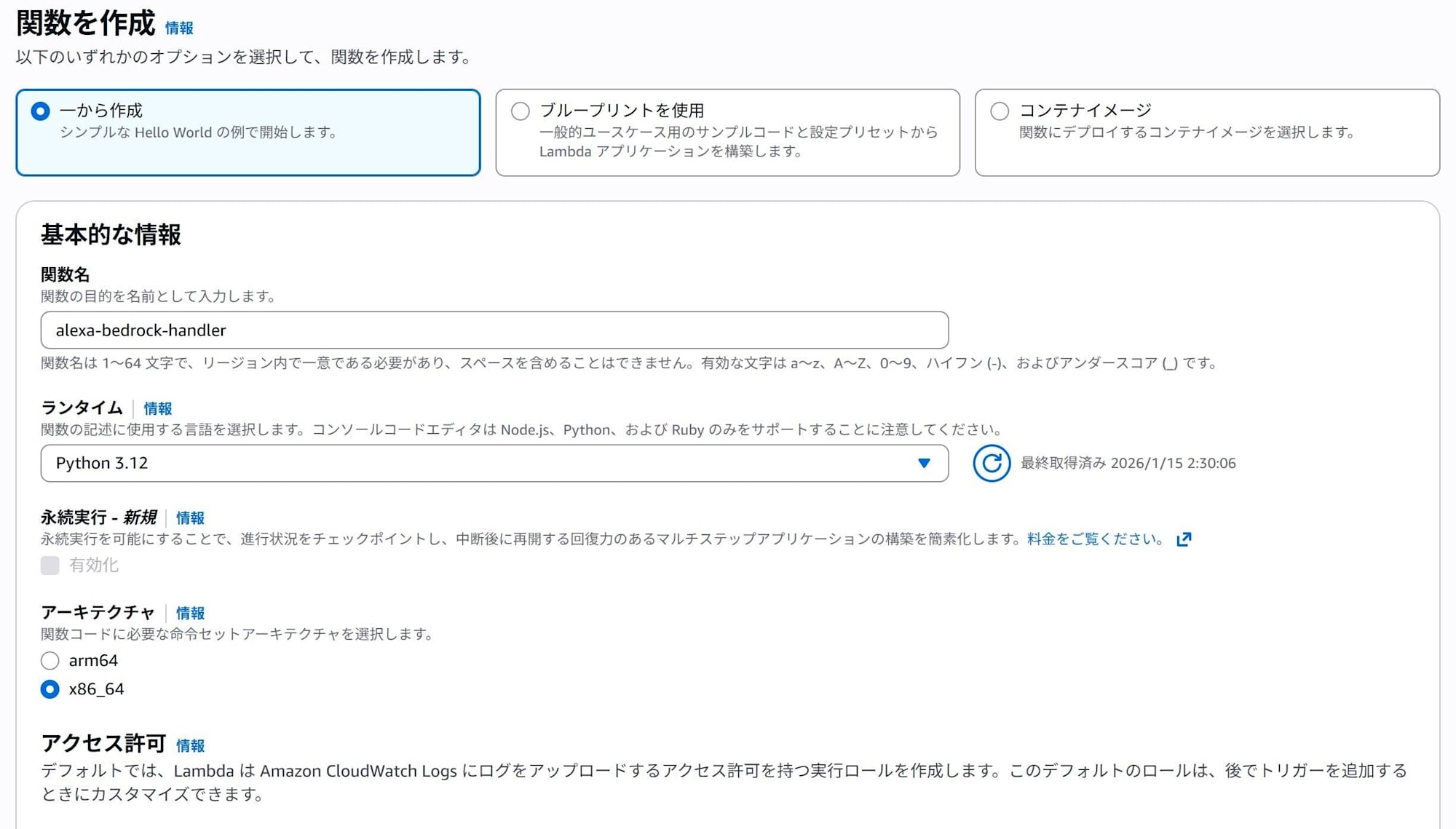
In the Lambda console, click "Create function" and create a function with the following settings.
- Function name: alexa-bedrock-handler (arbitrary)
- Runtime: Python 3.12
- Architecture: x86_64
- Change default execution role → Leave as "Create a new role with basic Lambda permissions".
Setting Permissions and Timeout
Next, set up the policy for Lambda to access Bedrock.
From the Configuration tab, go to Permissions → click on the Role name to navigate to the IAM console.
Add permissions → Attach policies, then search for and attach AmazonBedrockFullAccess.
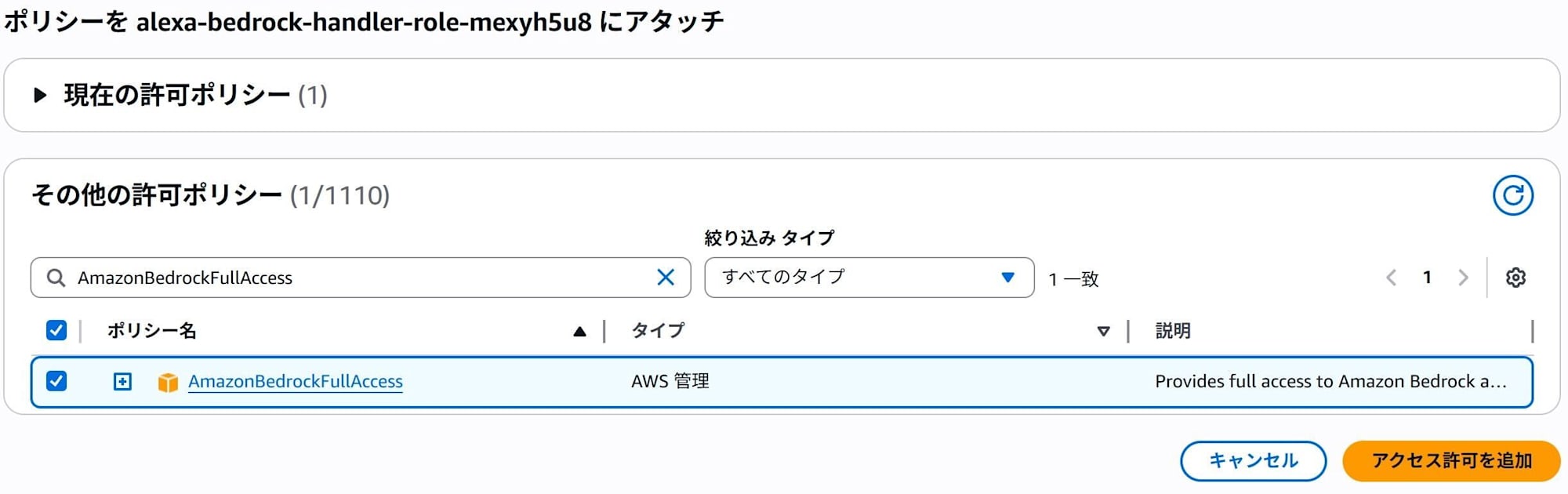
※ This article uses AmazonBedrockFullAccess for testing purposes, but
for production environments, following the principle of least privilege,
it's recommended to use custom policies that allow access only to necessary models.
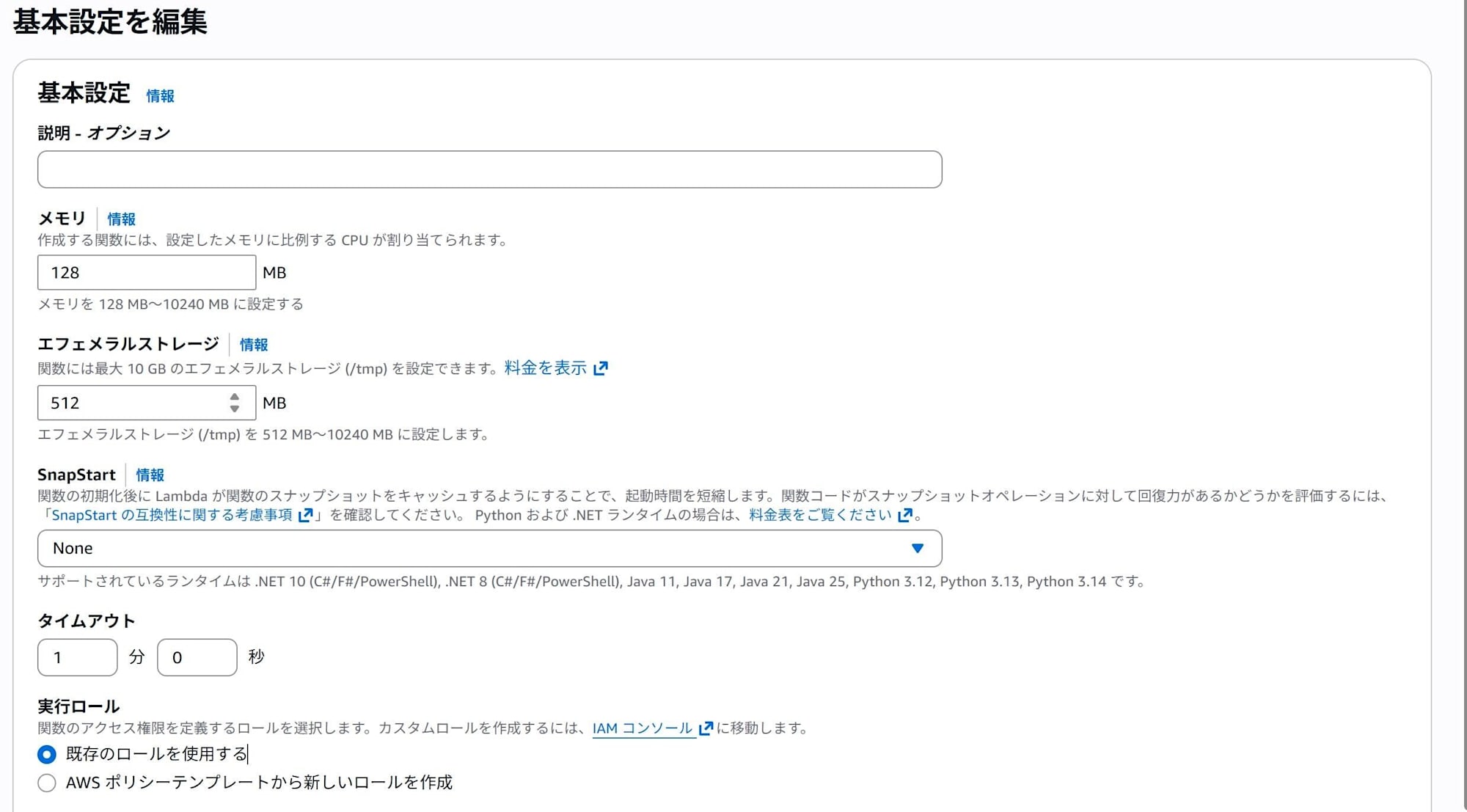
Next, since Lambda's default timeout is a bit short, let's extend it.
From the Configuration tab → General configuration → Edit, change the timeout to about 60 seconds.
Setting Up the Code
In the "Code" tab, write the following code.
The following code generates AI responses with Amazon Bedrock (Claude 3 Haiku) when speaking to Alexa.
import json
import boto3
import logging
# Logger setup
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# Bedrock client
bedrock = boto3.client(service_name='bedrock-runtime', region_name='ap-northeast-1') # Change according to your region
def lambda_handler(event, context):
logger.info(json.dumps(event))
request_type = event['request']['type']
# 1. At launch
if request_type == "LaunchRequest":
return build_response("Welcome to AI Chat. What would you like to talk about?", should_end_session=False)
# 2. When asking a question ("Tell me about ○○")
elif request_type == "IntentRequest":
intent_name = event['request']['intent']['name']
if intent_name == "ChatIntent":
# Get user's utterance from slots
slots = event['request']['intent']['slots']
user_input = slots['Query']['value']
# Call Bedrock
ai_response = call_bedrock(user_input)
# Respond and maintain the session
return build_response(ai_response, should_end_session=False)
elif intent_name == "AMAZON.StopIntent" or intent_name == "AMAZON.CancelIntent":
return build_response("Ending now.", should_end_session=True)
return build_response("Sorry, I didn't understand that.", should_end_session=False)
def call_bedrock(prompt):
try:
# Payload for Claude 3
body = json.dumps({
"anthropic_version": "bedrock-2023-05-31",
"max_tokens": 300,
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": f"Please answer in about 3 lines in an easy-to-understand way.\n\nUser's question: {prompt}"
}
]
})
response = bedrock.invoke_model(
modelId='anthropic.claude-3-haiku-20240307-v1:0', # Change according to the model you want to use
body=body
)
response_body = json.loads(response.get('body').read())
return response_body['content'][0]['text']
except Exception as e:
logger.error(e)
return "Failed to call the AI."
def build_response(output_speech, should_end_session):
return {
"version": "1.0",
"response": {
"outputSpeech": {
"type": "PlainText",
"text": output_speech
},
"shouldEndSession": should_end_session
}
}
2. Configuration in Alexa Developer Console
Creating a Skill
Next, let's set up the Alexa side.
Log in to the Alexa Developer Console with the account you use for Alexa.
Click "Create skill" and create a skill with the following settings.
- Skill name: AIChat
- Primary locale selection: Japanese
- Experience type: Other
- Model selection: Custom
- Hosting service: Your own provisioning
- Templates: Create from scratch

Setting the Invocation Name
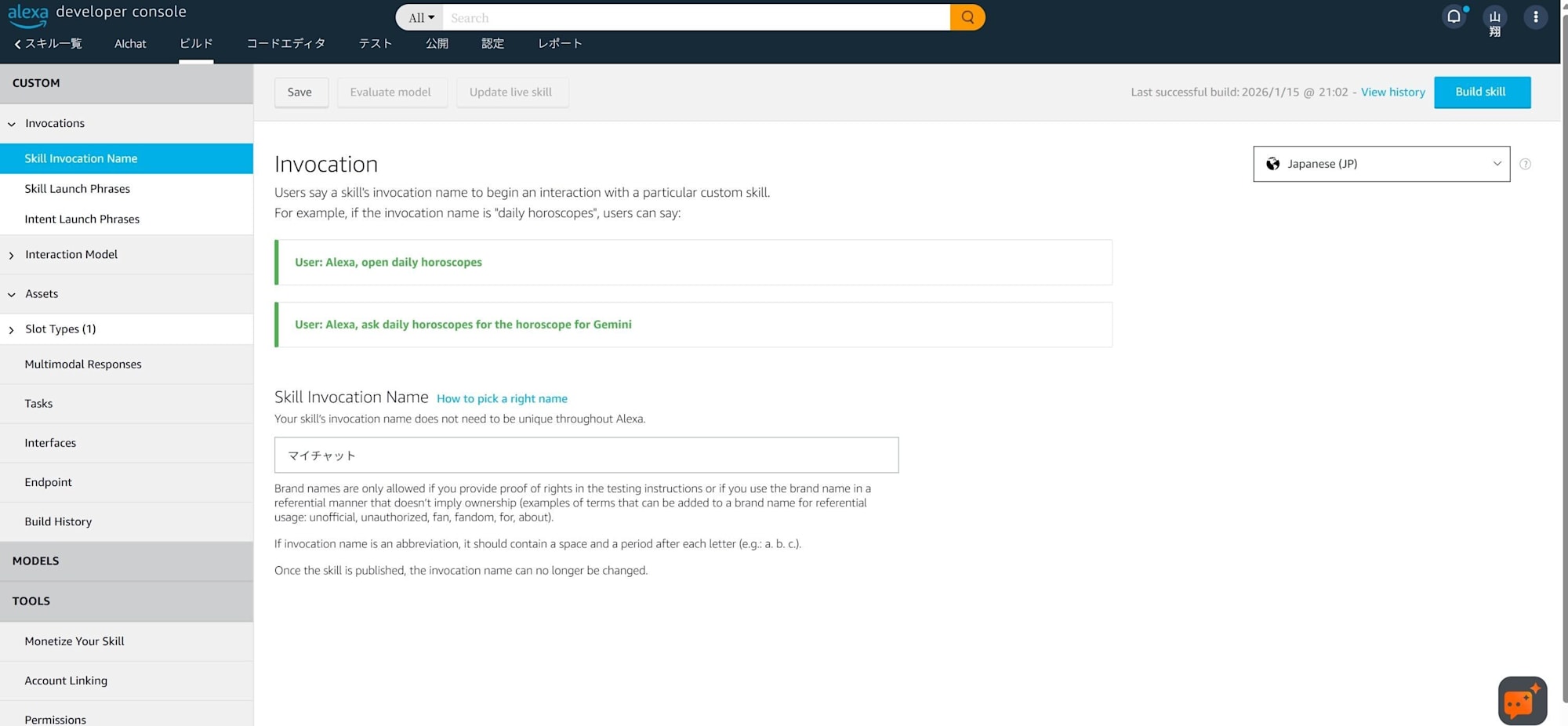
Next, set an invocation name to call the AI.
From the left menu, select Invocation and then Skill Invocation Name.
The invocation name can be set arbitrarily, but it's recommended to use a name that Alexa can easily recognize. When I initially set it to "AI Chat," it didn't work well, so I changed it to "My Chat."
Creating Intents
Next, let's create intents.
From the left menu, select Interaction Model and click on Intents.
A list of currently created intents will be displayed. Click "Add Intent".
Set the name to "ChatIntent" and create the intent.
Once created, create a slot with the following settings in Intent Slots:
- NAME: Query
- SLOT TYPE: AMAZON.SearchQuery
After creating the slot, set Sample Utterances.
Set it as follows:
{Query} 教えて
{Query} とは
{Query} して
{Query} やって

Setting the Skill Endpoint
Select Endpoint from the left menu.
Choose AWS Lambda ARN for Service Endpoint Type.
The Default Region is blank, so paste the Lambda ARN here. You can get the Lambda ARN from the management console by opening the Lambda and clicking "Copy ARN" in the top right.
Also, take note of the Skill ID displayed on this screen as you'll need it later.

Building the Model
After all settings are complete, press Build skill in the upper right.
3. Setting Up Lambda Trigger
Finally, let's set up the trigger.
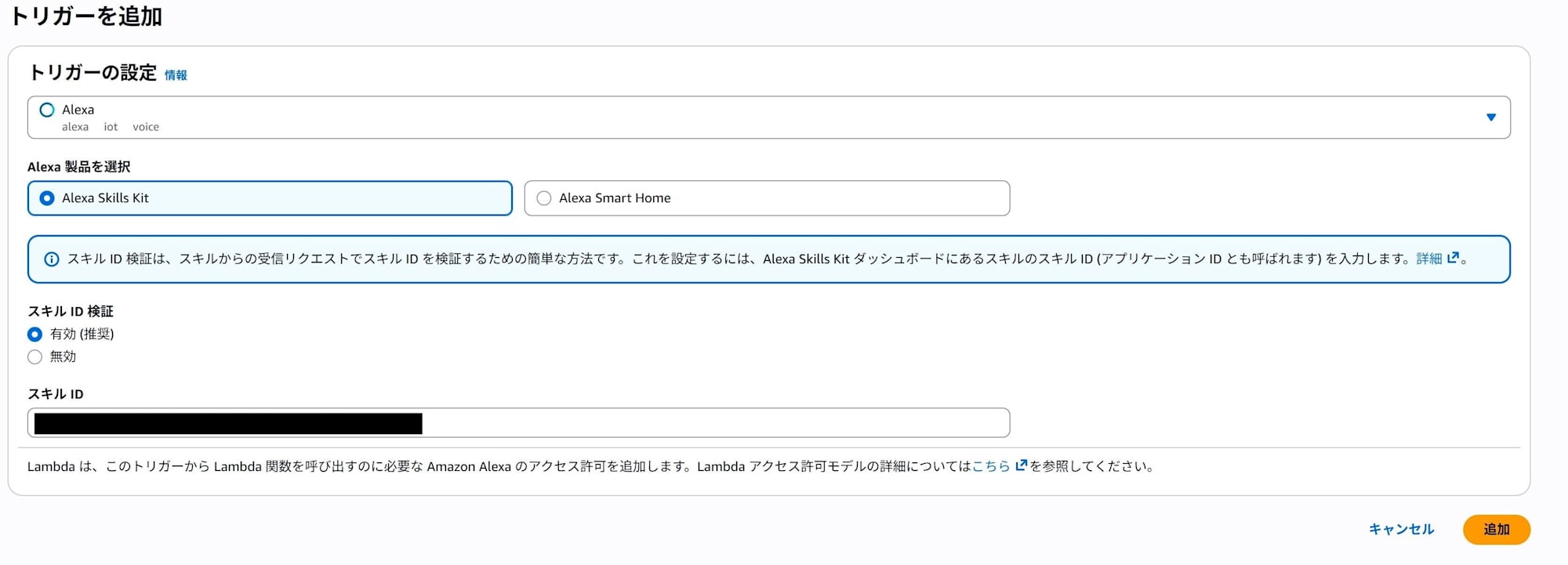
Open Lambda in the management console and select Alexa from Add trigger.
Next, select Alexa Skills kit and enable skill ID verification.
Enter the Skill ID you noted earlier when setting the endpoint.
4. Testing
Finally, let's test.
You can perform text-based testing on the Test tab of the Alexa Developer Console.
Change the stage where skill testing is enabled from "Private" to "Development".
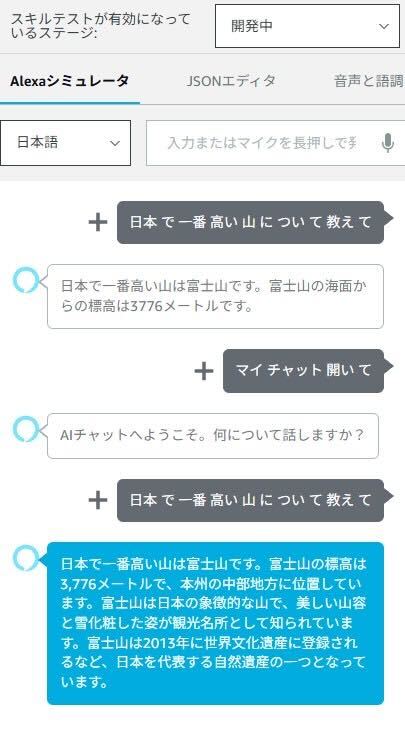
Since the invocation name was set to "My Chat," entering "Open My Chat" will return "Welcome to AI Chat. What would you like to talk about?"
After that, entering "Tell me about ○○" will return an AI-generated answer.
The image below compares the default response with the Bedrock-powered response.
5. Additional Information
Enabling Model Access
This time, I used Claude 3 Haiku.
When using Anthropic models in Bedrock, you need to submit details about your use case for the first time.
Go to Bedrock → Model catalog → Claude 3 Haiku → select Playground, and a form will be displayed. Please fill it out as appropriate.
How to Change Models and Prompts
You can change models by modifying the ID part in the code as follows:
modelId='anthropic.claude-3-haiku-20240307-v1:0',
Be aware of regional restrictions when changing models.
Also, you can change the prompt by modifying this part:
"content": f"Please answer in about 3 lines in an easy-to-understand way.\n\nUser's question: {prompt}"
How to Run on Echo Devices
To use it on Echo devices, you need to enable the skill in the Alexa app.
- Open the Alexa app and select "Skills & Games" from the 3-line menu
- Scroll to the bottom and select My Skills
- Select the skill you created from the Development tab and enable it
In my environment, it was enabled by default, but it didn't work properly, so I had to disable it once and then enable it again to make it functional.
Conclusion
This time, I built a system that connects Alexa with Amazon Bedrock to ask AI questions by voice.
This article used the affordable and fast Claude 3 Haiku, but you can change to other models depending on your needs. Feel free to customize with your preferred model.
Also, the implementation this time is a simple question-and-answer format, but you can make it conversational by changing the code. Feel free to try it if you're interested.
References
About Classmethod Operations, Inc.
We are the operations company of the Classmethod Group.
We are a group of experts with specialized teams in operations, maintenance development, support, information systems, and back office, providing everything from business outsourcing to problem-solving and high value-added services through "mechanisms" that fully utilize IT and AI.
We are recruiting members for various positions.
If you are interested in our culture, systems, and work style that realize both "Operational Excellence" and "Work and live like yourself," please visit the Classmethod Operations, Inc. Corporate Site. ※Changed company name from Annotation Inc. in January 2026



