
Getting Started with Amazon MemoryDB for Valkey - A Managed Database with Redis Compatibility that Reduces Costs by 30%
This page has been translated by machine translation. View original
Introduction
In this article, I'll explain Amazon MemoryDB for Valkey in detail. I'll cover Valkey's features, comparison with MemoryDB for Redis, actual migration procedures, and basic command examples.
What is MemoryDB
Amazon MemoryDB is a Redis-compatible fully-managed in-memory database service. Since data is persistently stored, it can be used as a primary database.
Difference from ElastiCache
The main differences between Amazon MemoryDB and Amazon ElastiCache are in data persistence and architecture.
- ElastiCache is a service for caching purposes, so data retention is temporary. While backup via snapshots is possible, persistence is not performed.
- MemoryDB persists all writes. Even if a node fails, data integrity is maintained, allowing it to be used as a primary database.
What is Valkey
Valkey is a project started in 2024 under the Linux Foundation as an open source fork of Redis. It was launched after Redis Labs changed the Redis license. Valkey is based on Redis 7.2 and continues to be developed under an open source license (BSD 3-Clause License) while maintaining high compatibility with Redis.
What is MemoryDB for Valkey
MemoryDB for Valkey is a service that allows you to use Valkey with Amazon MemoryDB. You can enjoy almost the same functionality as traditional MemoryDB for Redis at a lower price. AWS also provides procedures for easily migrating existing Redis environments to Valkey (described later).
Target Audience
This article is intended for:
- Developers and infrastructure engineers currently using Redis or ElastiCache who are considering migrating to Valkey
- Those considering implementing MemoryDB but unsure whether to choose Redis or Valkey
References
- https://aws.amazon.com/jp/memorydb/
- https://aws.amazon.com/jp/elasticache/
- https://aws.amazon.com/jp/blogs/news/get-started-with-amazon-memorydb-for-valkey/
- https://aws.amazon.com/jp/memorydb/pricing/
- https://valkey.io/
- https://redis.io/blog/redis-adopts-dual-source-available-licensing/
- https://redis.io/blog/agplv3/
Comparison with MemoryDB for Redis
There are no major differences in architecture or functionality between MemoryDB for Valkey and MemoryDB for Redis. Both run on the MemoryDB platform and offer features such as data persistence, Multi-AZ configuration, and automatic failover.
Functionality
Currently, the functional differences between MemoryDB for Valkey and MemoryDB for Redis are limited. Both support the following features:
- Redis-compatible command set
- Data persistence and transaction logs
- Multi-AZ configuration for high availability
- Automatic backups and point-in-time recovery
- Secure communication within VPC
- Encryption (at rest and in transit)
However, since Valkey is based on Redis 7.2, it may not support the latest Redis features.
Price Comparison
Amazon MemoryDB for Valkey pricing is 30% lower than MemoryDB for Redis OSS. (As of July 2025)
Specific price examples (Asia Pacific (Tokyo) region, db.r7g.large):
- MemoryDB for Redis: $0.371/hour
- MemoryDB for Valkey: $0.2597/hour
Migration Procedure
Redis → Valkey migration can be easily executed from the AWS console. It's possible to change engines without downtime.
Preparation
Before migrating, perform the following checks:
- Confirm that Redis commands used by your application are supported in Valkey
- Verify that the cluster to be migrated is operating normally
- Take backups in advance if necessary
Migrating from MemoryDB for Redis to MemoryDB for Valkey
Here's how to migrate an existing MemoryDB for Redis cluster to Valkey:
- Access the MemoryDB console, and select the target cluster from the "Clusters" menu in the left pane.
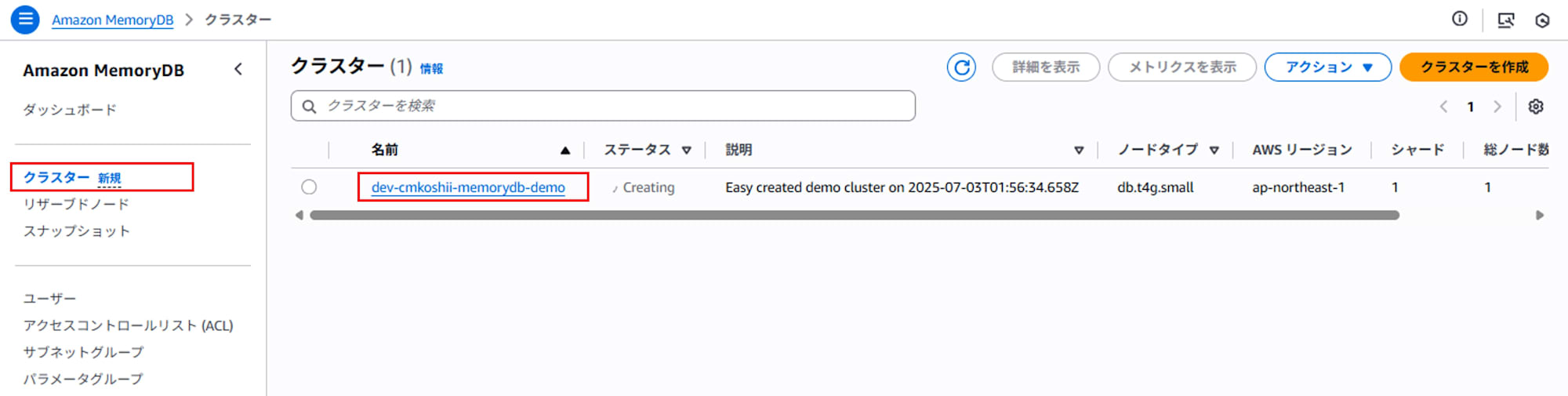
- Click the "Modify" button.
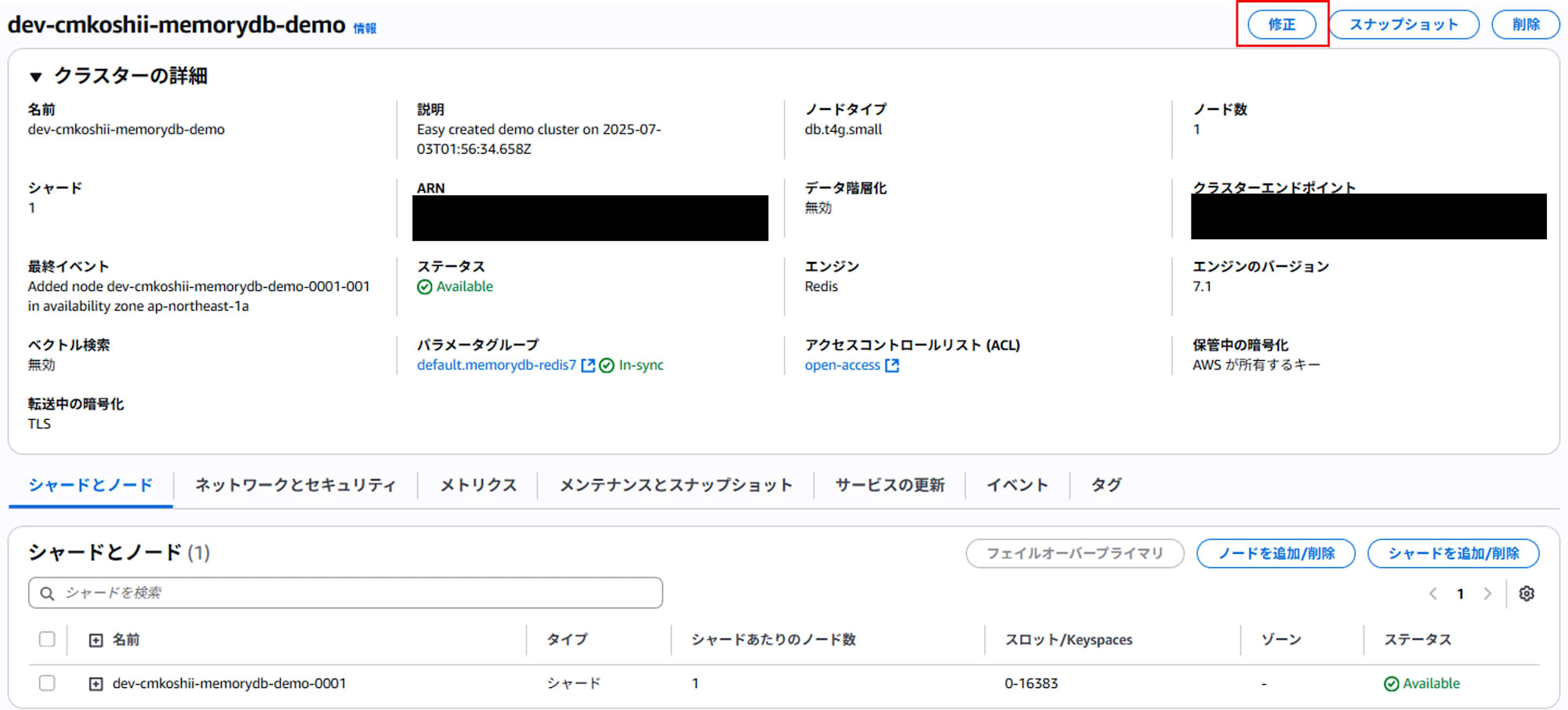
- Under "Cluster settings > Engine", select Valkey.
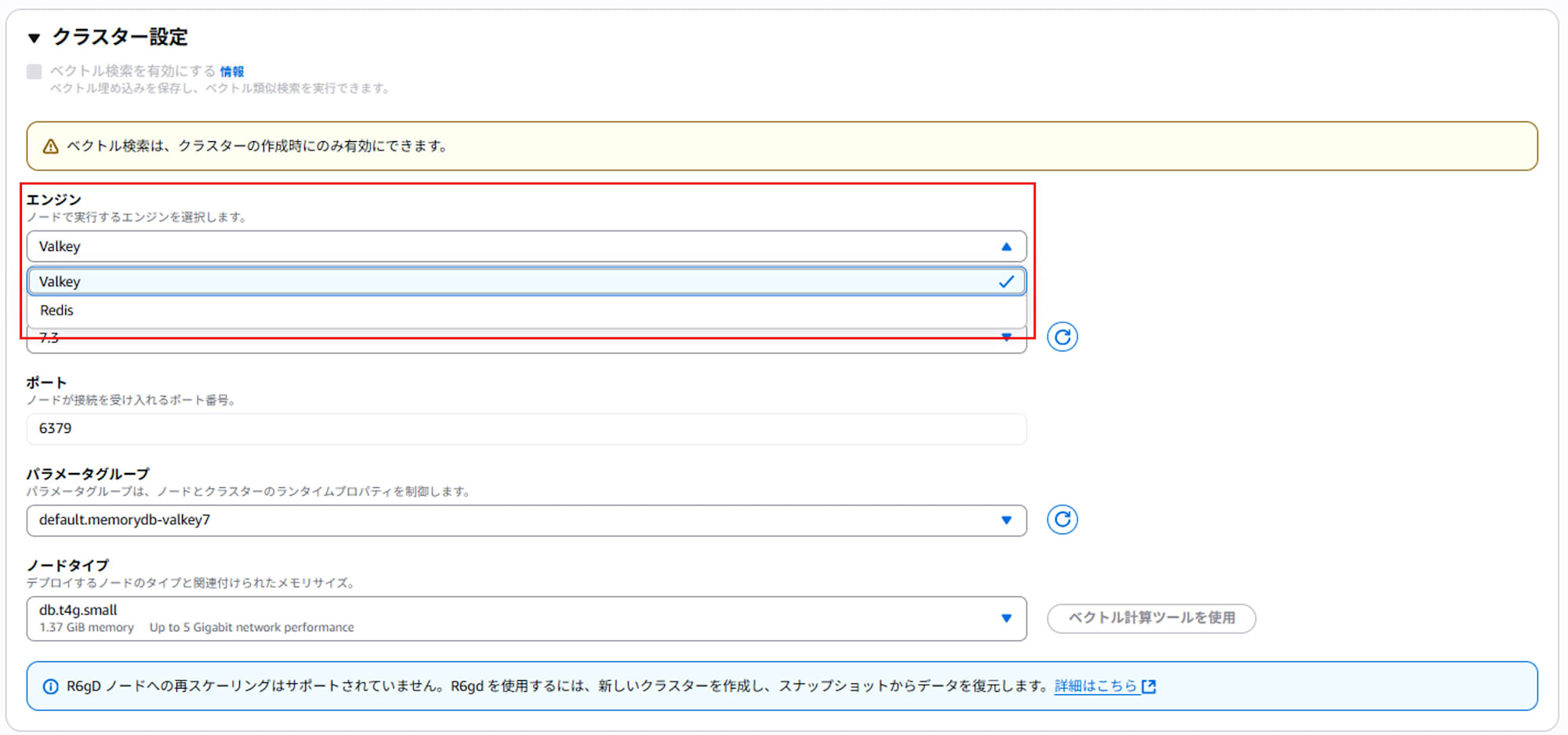
- "Preview changes" and check the content. If there are no issues, select "Save changes" to execute the engine change.
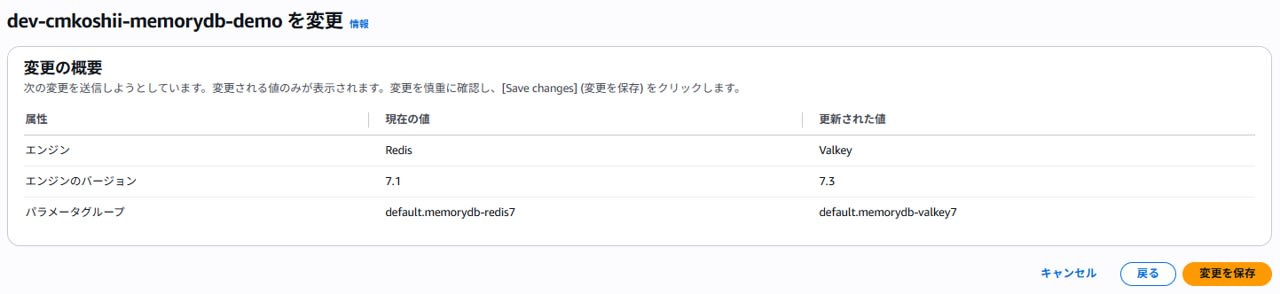
- Confirm that the cluster status changes to "Updating".
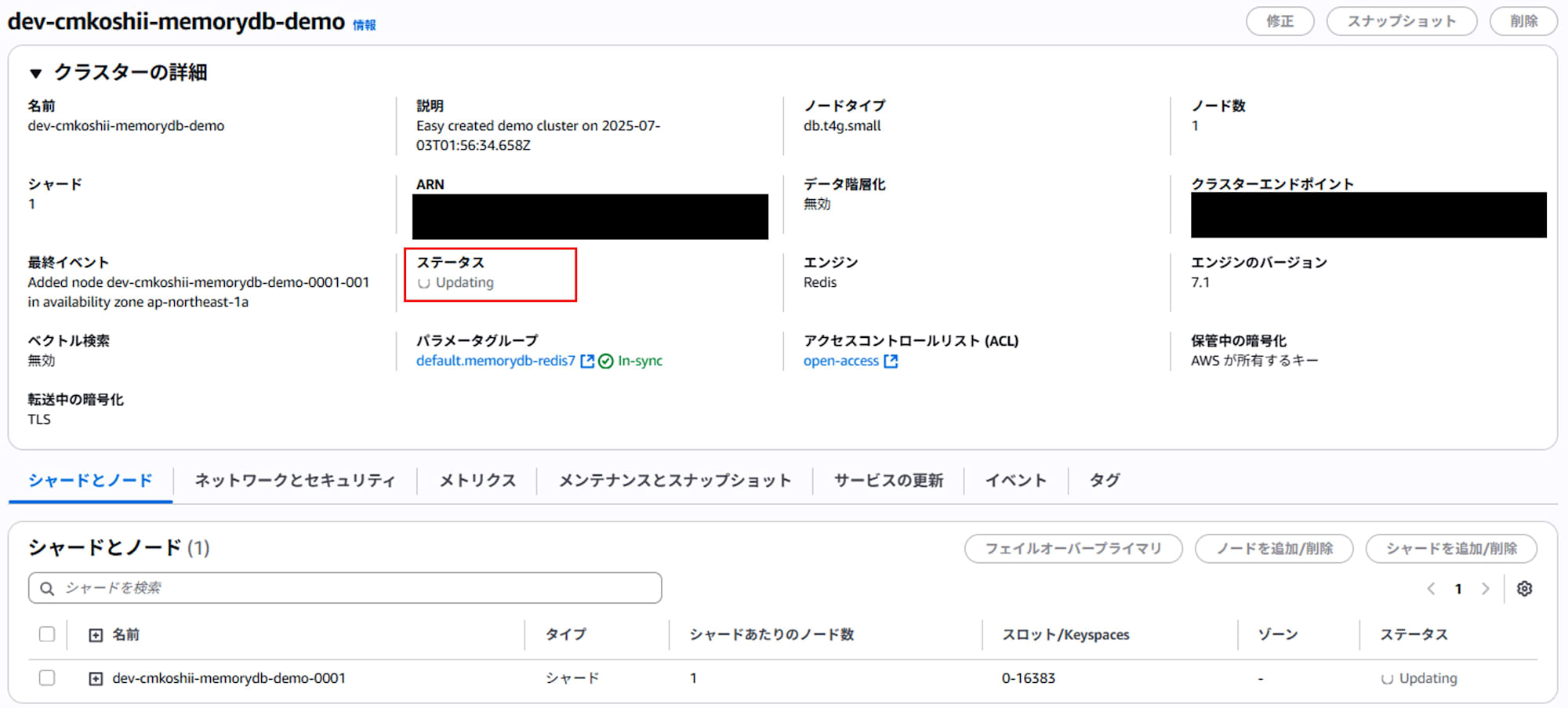
- When the status changes from "Updating" to "Available" and the engine type displays "Valkey", the migration is complete.
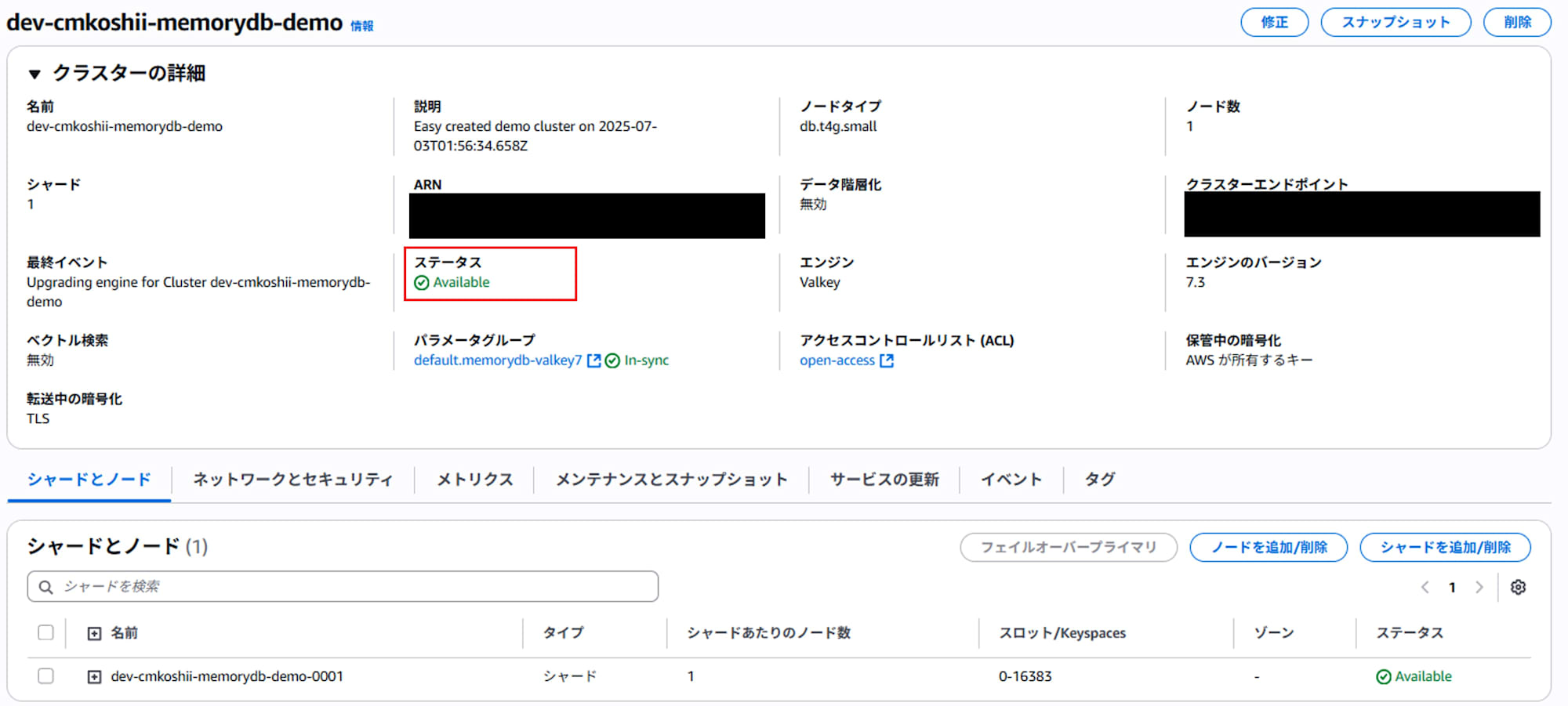
Post-Migration Checks
After migration is complete, perform operational verification using the following steps:
Installing Valkey CLI
Install valkey-cli on an EC2 instance in the same VPC.
# For Amazon Linux
sudo yum install valkey
# For Ubuntu
sudo apt update
sudo apt install valkey
Connecting to MemoryDB for Valkey
# Access with TLS connection
valkey-cli --tls -h your-memorydb-cluster-endpoint.memorydb.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com -p 6379
Operational Verification
# Connection check
> PING
PONG
# Check existing data
> KEYS *
# Basic operation test
> SET test "hello valkey"
OK
> GET test
"hello valkey"
Basic Command Examples
MemoryDB for Valkey is Redis-compatible, so you can use existing Redis commands as they are.
Basic CRUD Operations
Writing Data (SET)
# Storing strings
SET user:1001 "John Doe"
SET user:1002 "Jane Smith"
# Storing numbers
SET counter 100
# Storing with TTL (auto-delete after 60 seconds)
SETEX session:abc123 60 "user_session_data"
Reading Data (GET)
# Getting a single key
GET user:1001
# Batch retrieval of multiple keys
MGET user:1001 user:1002 counter
Deleting Data (DEL)
# Deleting a single key
DEL user:1001
# Deleting multiple keys
DEL user:1001 user:1002 counter
List Operations
# Adding elements to a list
LPUSH tasks "task1" "task2" "task3"
# Getting elements from a list
LRANGE tasks 0 -1
# Removing elements from a list
LPOP tasks
Hash Operations
# Setting hash fields
HSET user:profile:1001 name "John Doe" age 30 email "john@example.com"
# Getting hash fields
HGET user:profile:1001 name
HGETALL user:profile:1001
# Deleting hash fields
HDEL user:profile:1001 age
Performance Test Examples
You can run performance tests using the valkey-benchmark tool.
# Basic benchmark (100,000 requests, 50 concurrent connections)
valkey-benchmark --tls -h your-memorydb-cluster-endpoint.memorydb.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com -p 6379 -n 100000 -c 50
# SET command only benchmark
valkey-benchmark --tls -h your-memorydb-cluster-endpoint.memorydb.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com -p 6379 -n 100000 -c 50 -t set
# GET command only benchmark
valkey-benchmark --tls -h your-memorydb-cluster-endpoint.memorydb.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com -p 6379 -n 100000 -c 50 -t get
# Benchmark with pipeline
valkey-benchmark --tls -h your-memorydb-cluster-endpoint.memorydb.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com -p 6379 -n 100000 -c 50 -P 10
Output example
====== PING_INLINE ======
1 requests completed in 0.00 seconds
1 parallel clients
3 bytes payload
keep alive: 1
multi-thread: no
Latency by percentile distribution:
0.000% <= 3.455 milliseconds (cumulative count 1)
100.000% <= 3.455 milliseconds (cumulative count 1)
Cumulative distribution of latencies:
0.000% <= 0.103 milliseconds (cumulative count 0)
100.000% <= 4.103 milliseconds (cumulative count 1)
Summary:
throughput summary: 250.00 requests per second
latency summary (msec):
avg min p50 p95 p99 max
3.452 3.448 3.455 3.455 3.455 3.455
Monitoring Setup
MemoryDB for Valkey monitoring is done through CloudWatch.
Key Metrics
- CPUUtilization: CPU usage
- DatabaseMemoryUsagePercentage: Memory usage
- NetworkBytesIn/Out: Network I/O
- CurrConnections: Current number of connections
- GetTypeCmds/SetTypeCmds: Number of GET/SET commands executed
Alarm Setting Example Using AWS CLI
aws cloudwatch put-metric-alarm \
--alarm-name "MemoryDB-HighCPU" \
--alarm-description "MemoryDB CPU usage is high" \
--metric-name CPUUtilization \
--namespace AWS/MemoryDB \
--statistic Average \
--period 300 \
--threshold 80 \
--comparison-operator GreaterThanThreshold \
--dimensions Name=ClusterName,Value=your-cluster-name \
--evaluation-periods 2
Summary
MemoryDB for Valkey is a service that maintains high compatibility with Redis while achieving a 30% cost reduction. Migration from existing MemoryDB for Redis can be easily executed without downtime. You can choose configurations suited to your needs by using MemoryDB for Valkey when persistence is required and ElastiCache for Valkey for caching purposes.



