
I want to automate or semi-automate the remediation of Security Hub CSPM controls
This page has been translated by machine translation. View original
Hello, I'm Maruto.
Are you all enabling Security Hub CSPM?
I think many of you have enabled it to improve the security of AWS resources.
While you don't need to address everything, there are many recommendations, so you might be finding it challenging to keep up.
Today I'd like to introduce an automation approach that is also mentioned in the AWS official documentation, as a reference.
What you can achieve with this article
- Inviting member accounts from the Security Hub administrator account
- Semi-automation and automation of Security Hub control remediation
Prerequisites
- AWS Config and AWS Security Hub are enabled in each account
- AWS Config is needed for detections related to global resources such as IAM.
Brief procedure
- Deploy the administrator stack in the Security Hub administrator account
- Deploy remediation roles in member accounts
- Deploy member account stacks
Let's try it (preparation)
Let's deploy the necessary stacks and make preparations.
Registration/invitation of member accounts from Security Hub administrator account
First, let's register and invite member accounts from the Security Hub administrator account.
In the Security Hub CSPM console sidebar, go to "Settings" to send invitations.
After opening settings, select Add accounts.
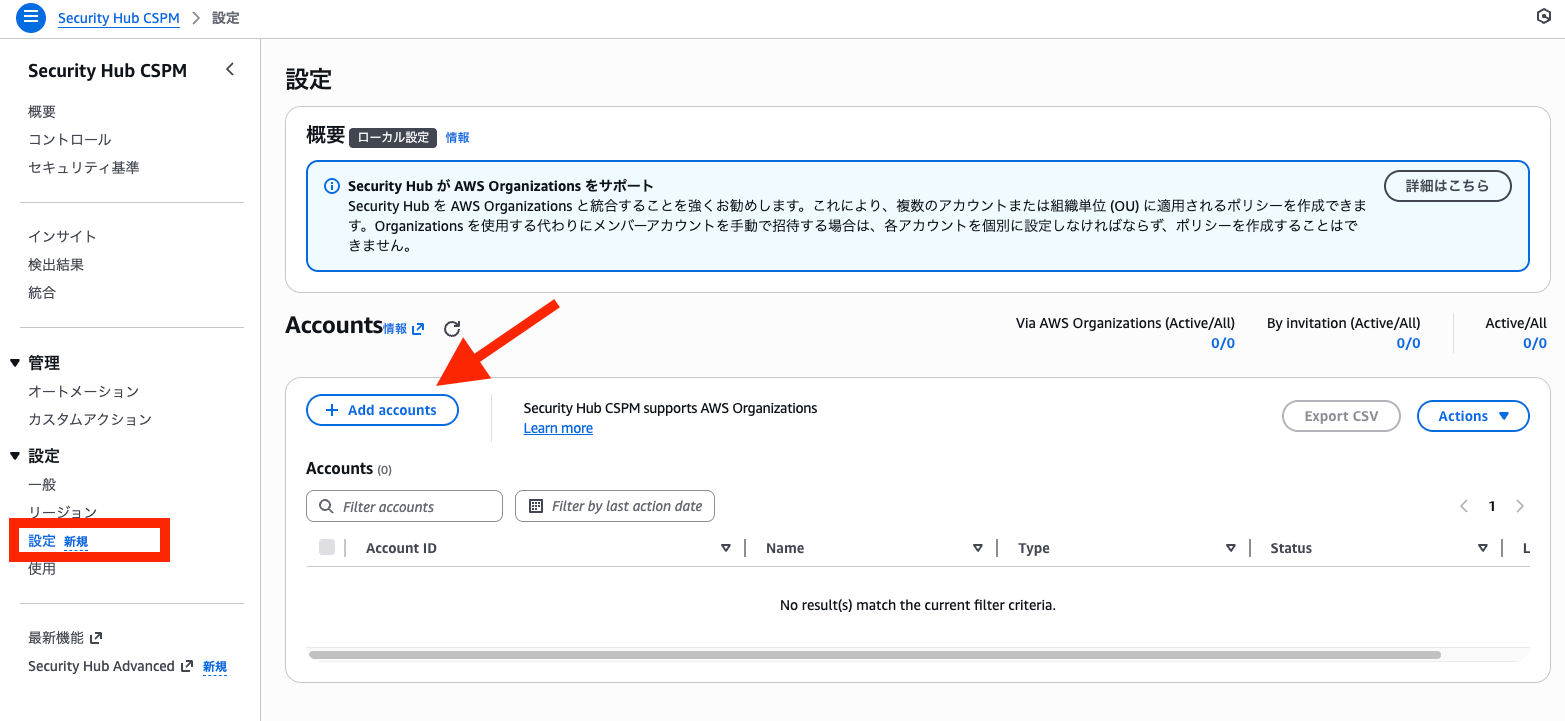
Next, enter the AWS account ID of the member account and select the Add button.
The entered AWS account ID will appear in the "Accounts to add" section, then select the Next button.
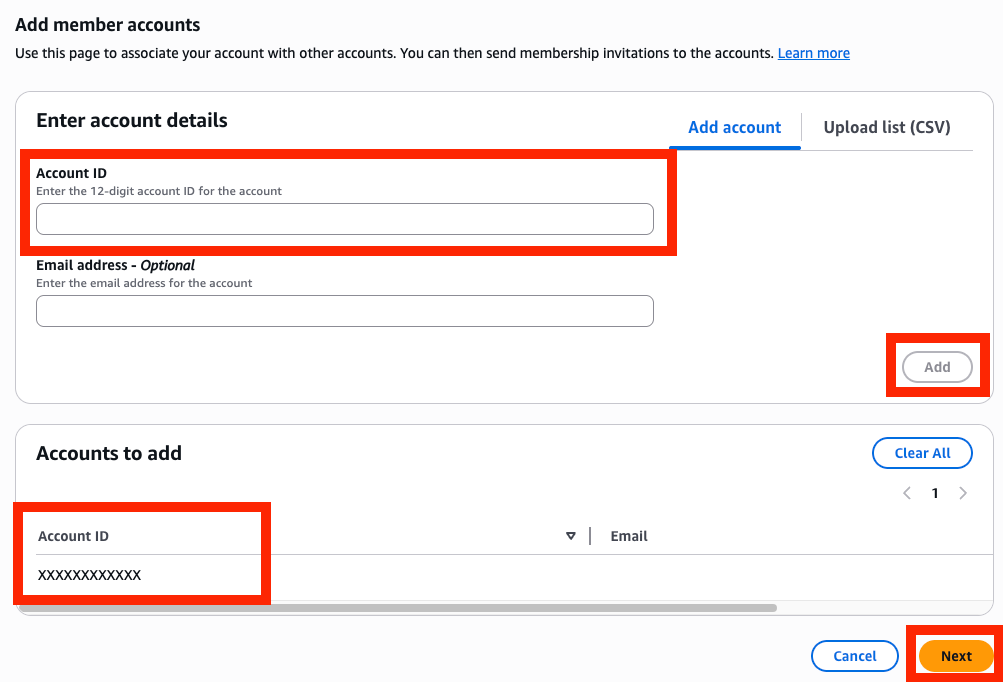
After that, the Status for the added member account will show as "Created", so click on invite next to it to complete the invitation to the member account.
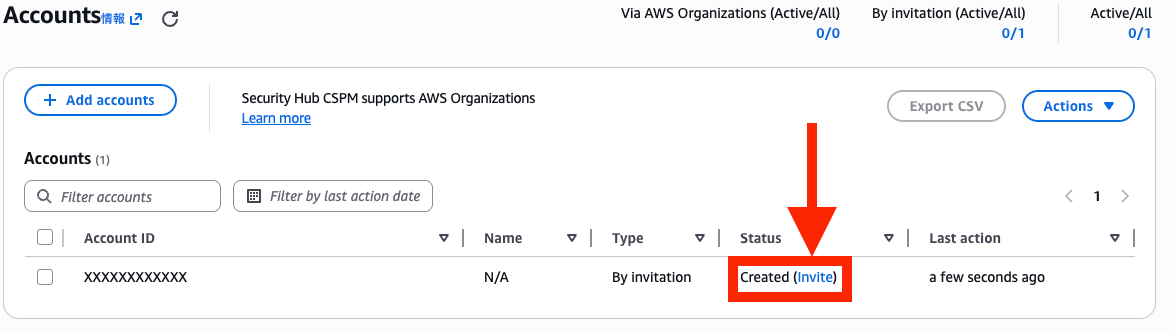
Next, log in to the member account.
After logging in, open the Security Hub CSPM settings, and you'll see the invitation in the Administrator account section.
Confirm it's the Security Hub administrator account ID, change the Accept toggle switch to on, and select Accept invitation to approve the invitation.
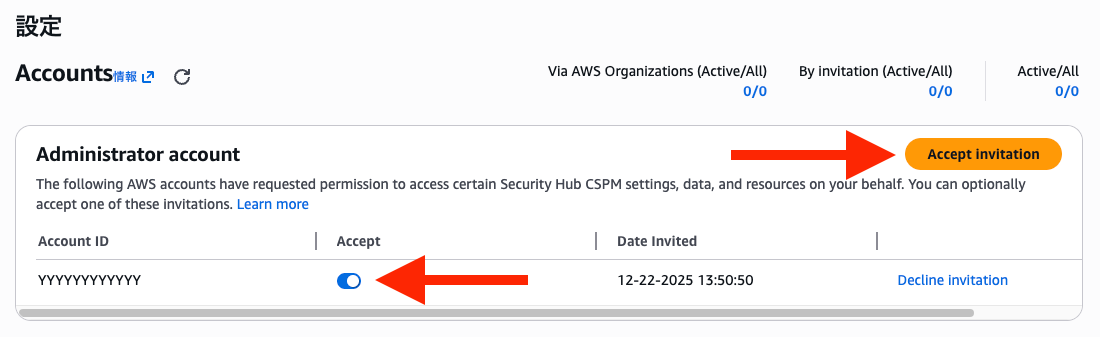
Log in to the Security Hub administrator account again, and if the Status has changed to Enabled, the member account invitation and registration is complete.
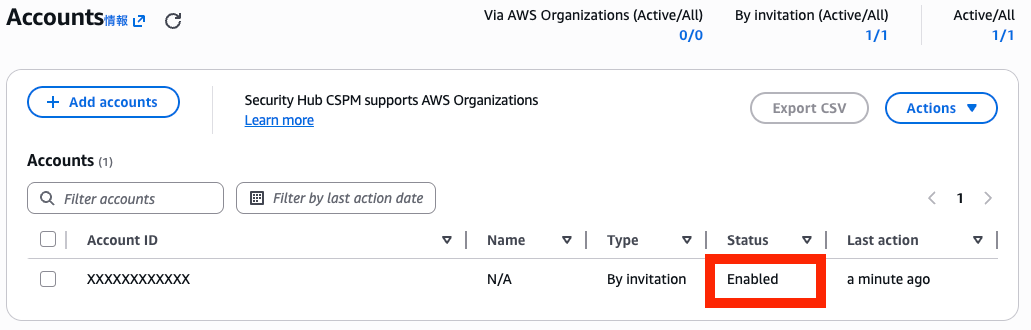
Deploy the administrator stack in the Security Hub administrator account
Next, deploy the administrator stack in the Security Hub administrator account.
We'll use the CloudFormation template linked in the AWS official documentation.
The template is available at the Launch solution button below.

After clicking the Launch solution button, it will try to create a stack in Northern Virginia (us-east-1), so change the region if needed.
(There aren't major differences between regions, but for this article, we'll verify in Asia Pacific (Tokyo) (ap-northeast-1).)
In the first step, all required fields are already filled in, so select Next without making any changes.
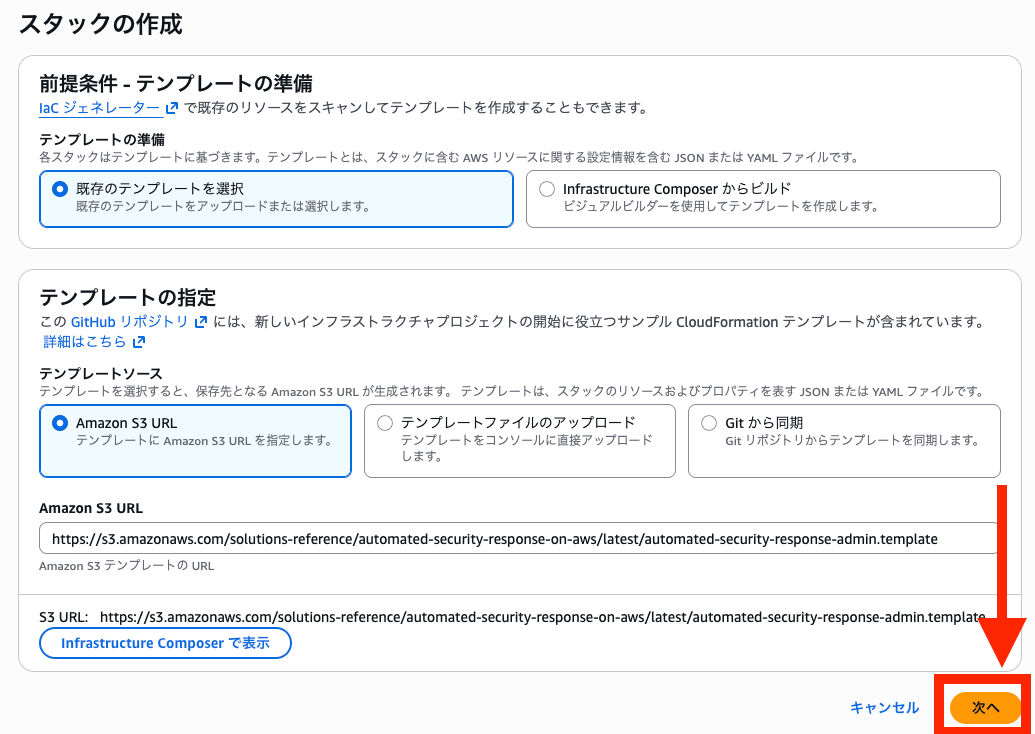
Next, set parameters on the specify stack details page.
For this verification, we'll test controls for AWS Foundational Security Best Practices v1.0.0.
Enter a stack name of your choice and set the parameters as follows:
| Parameter Name | Notes | Value in this article |
|---|---|---|
| LoadSCAdminStack | Install control auto-remediation components | yes |
| LoadAFSBPAdminStack | Install auto-remediation components for AWS Foundational Security Best Practices v1.0.0 | yes |
| LoadCIS120AdminStack | Install auto-remediation components for CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark v1.2.0 | no |
| LoadCIS140AdminStack | Install auto-remediation components for CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark v1.4.0 | no |
| LoadCIS300AdminStack | Install auto-remediation components for CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark v3.0.0 | no |
| LoadNIST80053AdminStack | Install auto-remediation components for NIST Special Publication 800-53 Revision 5 | no |
| LoadPCI321AdminStack | Install auto-remediation components for PCI DSS v3.2.1 | no |
| ReuseOrchestratorLogGroup | Whether to use existing Orchestrator Log Group ※For first deployment, set to no |
no |
| ShouldDeployWebUI | Whether to enable a dashboard WebUI separate from Security Hub | no |
| AdminUserEmail | Administrator email address for WebUI dashboard ※Can be left blank if WebUI dashboard is disabled |
blank |
| UseCloudWatchMetrics | Whether to monitor resources related to auto-remediation | no |
| UseCloudWatchMetricsAlarms | Whether to have CloudWatch Alarms for auto-remediation related resources | no |
| EnableEnhancedCloudWatchMetrics | Whether to create CloudWatch metrics individually for each control ID | no |
| RemediationFailureAlarmThreshold | Threshold for failure count per control ID | Default value (5) |
| TicketGenFunctionName | Lambda function name if integrating with ticket management system Not covered in this article. |
blank |
After entering parameters, proceed without changing any other settings.
You'll be asked to confirm that IAM resources and capabilities are required, so check the box and continue to deploy the CloudFormation stack.

If no errors occur and the CloudFormation stack status is CREATE_COMPLETE, this task is complete.

Deploy remediation roles in member accounts
Next, deploy the necessary roles in the member account to allow cross-account API calls from the administrator account.
As before, there's a link to the template in the AWS official documentation. (Don't forget to change the region)
There are two parameters to set:
| Parameter Name | Notes | Value in this article |
|---|---|---|
| Namespace | Suffix for IAM role ※Must be alphanumeric, max 9 characters |
shtest |
| SecHubAdminAccount | Security Hub administrator AWS account ID | <AWS Account ID> |
Deploy the CloudFormation stack without changing other settings.
Deploy member account stack
Finally, deploy resources to execute auto-remediation in the member account.
Click Launch solution at the link below to deploy. (Don't forget to change the region)
There are parameters similar to those for the administrator account:
| Parameter Name | Notes | Value in this article |
|---|---|---|
| LoadSCMemberStack | Install control auto-remediation components | yes |
| LoadAFSBPAdminStack | Install auto-remediation components for AWS Foundational Security Best Practices v1.0.0 | yes |
| LoadCIS120AdminStack | Install auto-remediation components for CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark v1.2.0 | no |
| LoadCIS140AdminStack | Install auto-remediation components for CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark v1.4.0 | no |
| LoadCIS300AdminStack | Install auto-remediation components for CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark v3.0.0 | no |
| LoadNIST80053AdminStack | Install auto-remediation components for NIST Special Publication 800-53 Revision 5 | no |
| LoadPCI321AdminStack | Install auto-remediation components for PCI DSS v3.2.1 | no |
| CreateS3BucketForRedshiftAuditLogging | Whether to create S3 bucket for remediating AWS Foundational Security Best Practices v1.0.0 Redshift.4 | no |
| SecHubAdminAccount | Security Hub administrator AWS account ID | <AWS Account ID> |
| Namespace | Namespace set when deploying remediation roles in member account | shtest |
| EnableCloudTrailForASRActionLog | Whether to monitor management events generated by CloudWatch dashboard mechanism ※Requires AWS Organization |
no |
Proceed with the deployment. Once completed, the preparations are finished.
Let's try it (remediation)
Now that preparations are complete, let's create and configure a resource that fails a Security Hub control and perform semi-automated remediation.
As a clear example, we'll test EC2.2 "VPC default security groups should not allow inbound and outbound traffic".
First, I added a rule to the default security group to allow access from 0.0.0.0/0 to all ports and protocols, causing the control to fail.
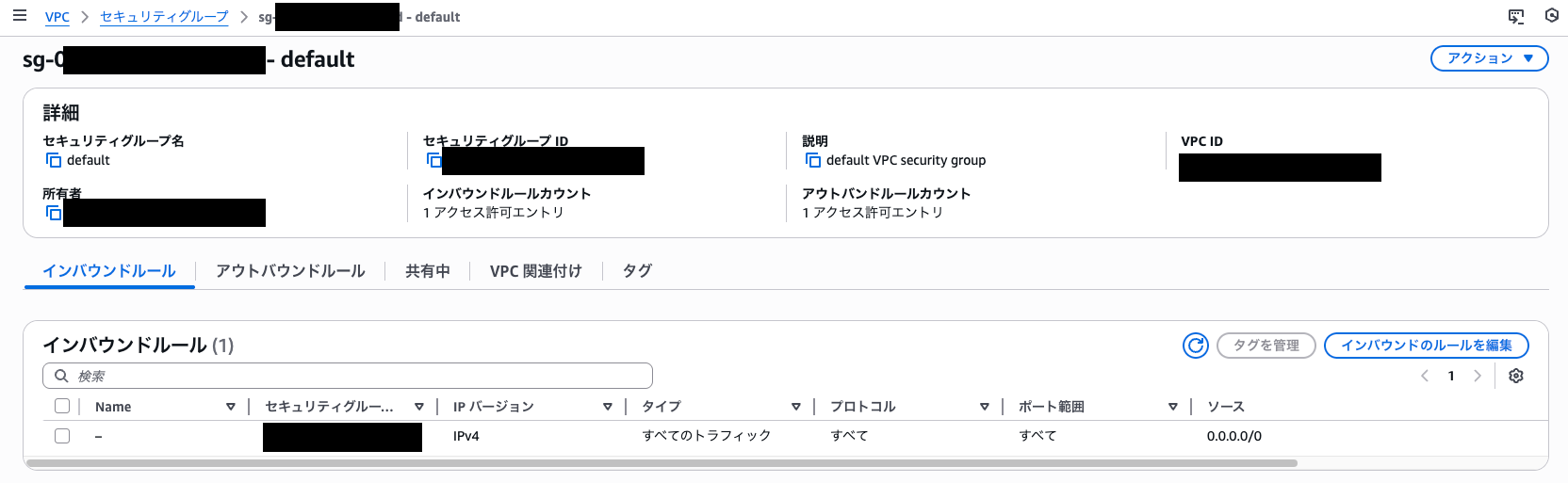
After a while, I confirmed that the EC2.2 control failed.

Now let's perform the auto-remediation.
To remediate, select the checkbox next to the resource with FAILED status, then select Actions > Remediate with ASR.

You'll see a message "Successfully sent finding to Amazon EventBridge", indicating that a resource remediation request has been made via EventBridge.

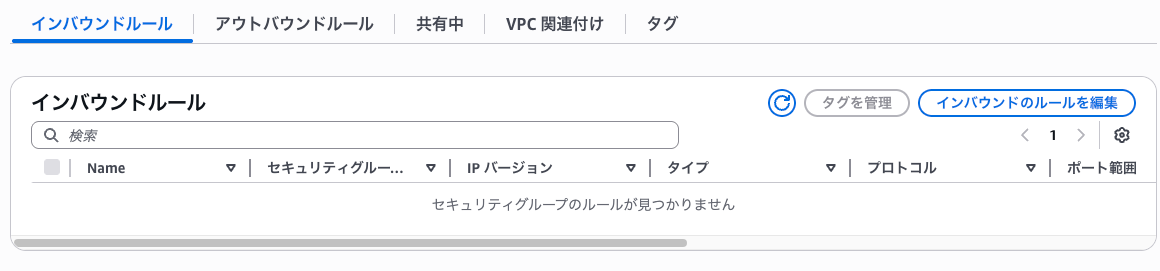
After a while, checking the security group again, all inbound and outbound traffic rules have been removed, and it's been fixed according to the control.
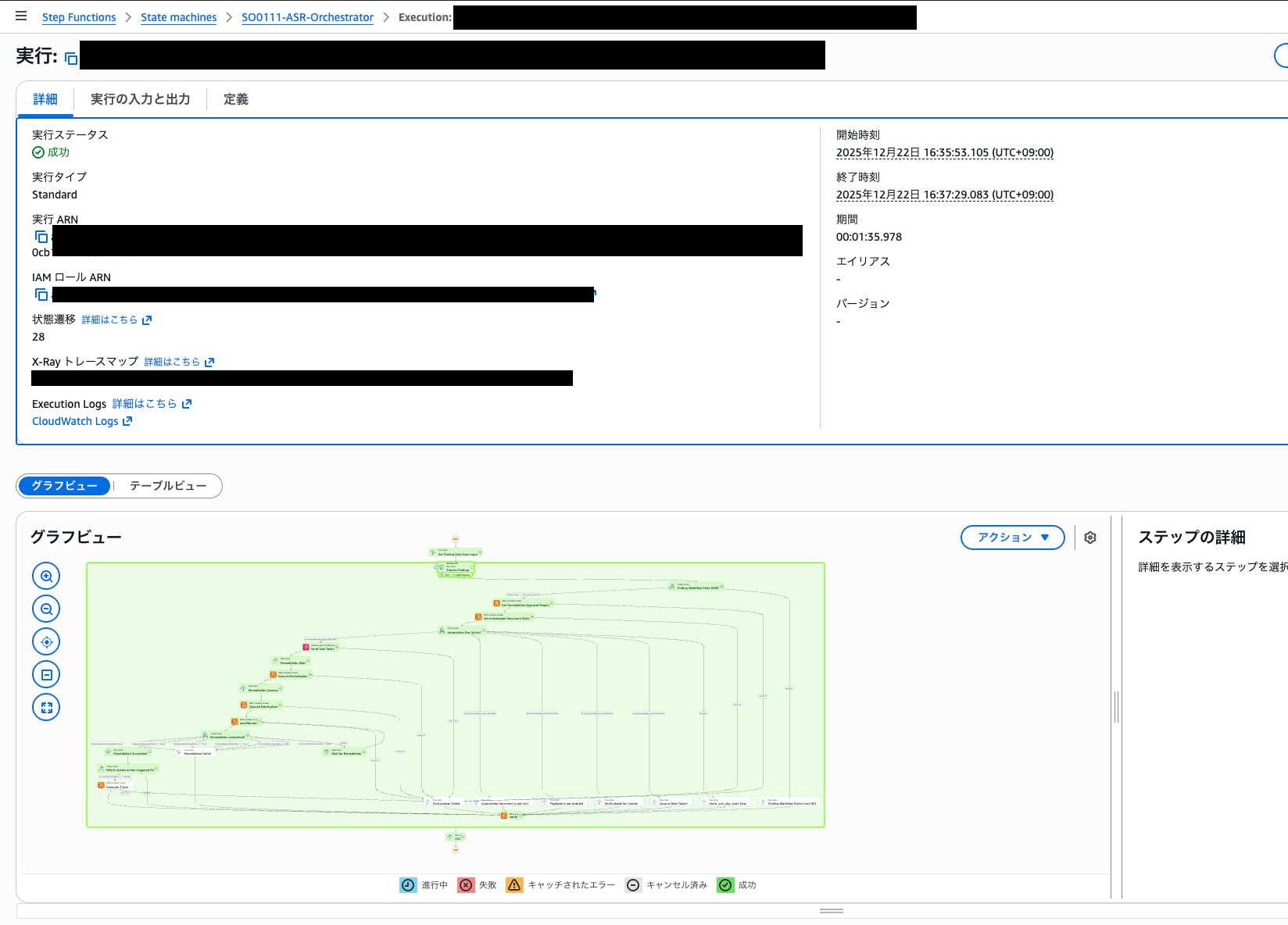
Behind the scenes, you can check the actual operation status in the "SO0111-ASR-Orchestrator" Step Functions.
Enable automatic remediation based on control failures
This time we manually requested auto-remediation from Security Hub, but you can also monitor control failures and perform automatic remediation.
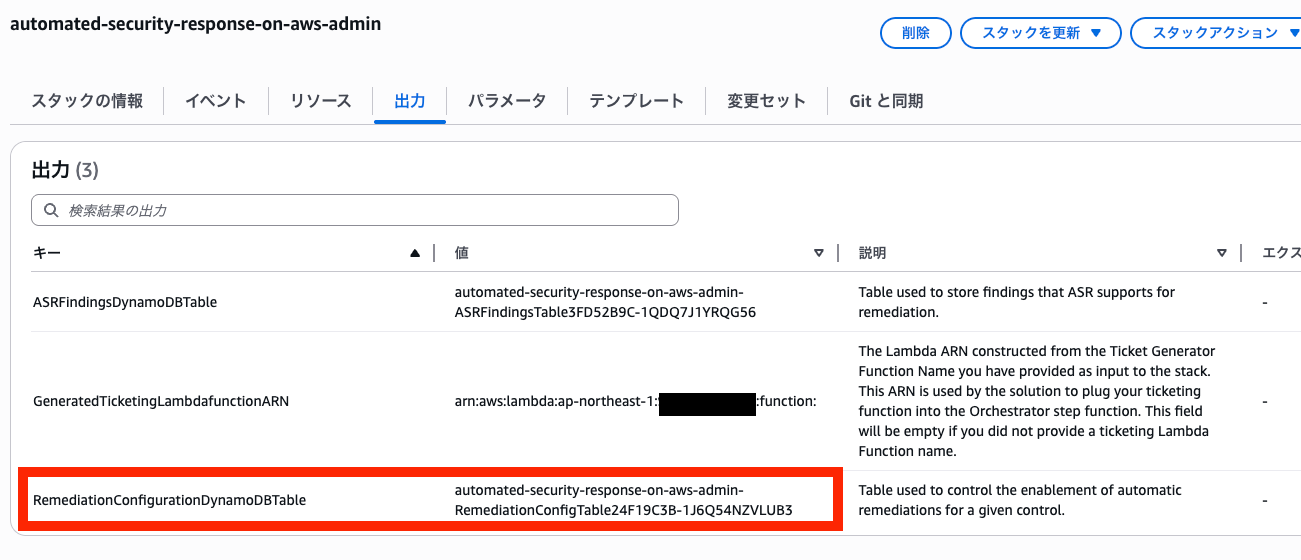
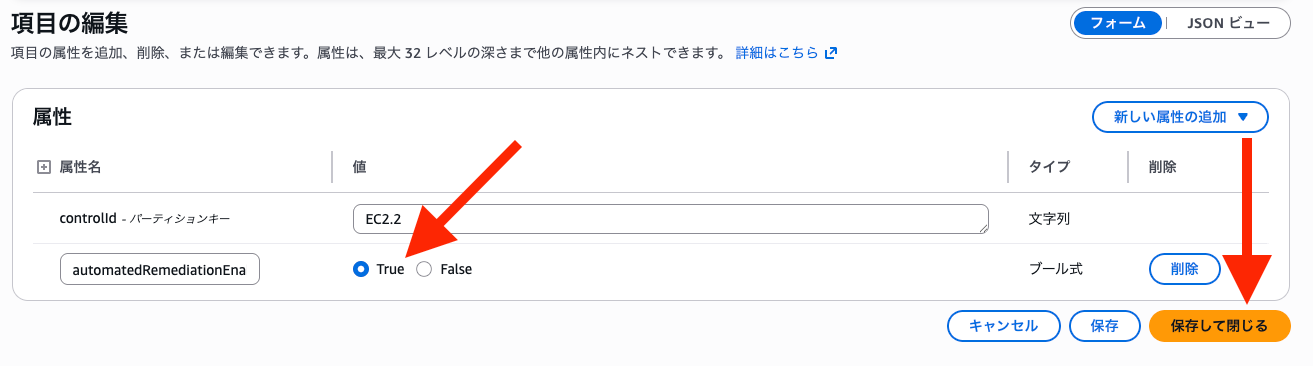
To enable this feature, you need to modify DynamoDB in the Security Hub administrator account.
The DynamoDB table name is listed in the Security Hub administrator CloudFormation stack output RemediationConfigurationDynamoDBTable.
When checking the table, you can see that automatedRemediationEnabled is set to true/false for each controlId. (Default is false for all)
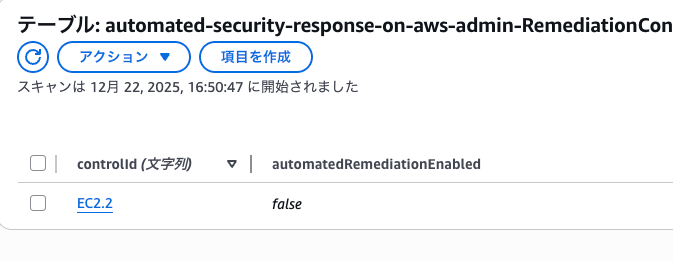
You can enable automation by setting automatedRemediationEnabled to true for the control IDs you want to automate.
Conclusion
Today we explored automating Security Hub CSPM control remediation.
While there are several settings involved, it makes it easier to return to recommended states, so I encourage you to try it out.
That's all from Maruto.



