![Tried deploying Strands Agents with Amazon Bedrock AgentCore L2 Construct [CDK]](https://images.ctfassets.net/ct0aopd36mqt/7qr9SuOUauNHt4mdfTe2zu/8f7d8575eed91c386015d09e022e604a/AgentCore.png?w=3840&fm=webp)
Tried deploying Strands Agents with Amazon Bedrock AgentCore L2 Construct [CDK]
This page has been translated by machine translation. View original
Introduction
Hello, I'm Kanno from the Consulting Department, and I'm a big fan of supermarkets.
Recently, AWS CDK v2.221.0 was released!
In this version, the L2 Construct for Amazon Bedrock AgentCore (hereinafter, AgentCore) has been added!
AgentCore was previously provided as an L1 Construct, but with the L2 Construct now available, deploying AI agents has become much easier.
Today, I'd like to share the steps I took to deploy a simple Strands Agent using the AgentCore L2 Construct!
The Benefits of L2 Constructs
Until now, there were several methods to deploy AgentCore Runtime:
- Starter Toolkit CLI: Deploy with
agentcore configure→agentcore launch- The specific deployment method is introduced in the article below.
- AWS CLI: Manually specifying detailed parameters
- CDK L1 Constructs: Direct mapping to CloudFormation
- Terraform: Recently added!
And now we have the L2 Construct!
The advantages of the L2 Construct are:
- ECR and IAM roles are automatically created
- Comprehensive default values, requiring minimal code to work
It's great that proper abstraction means we don't have to worry about many parameters.
While the Starter Toolkit is convenient, AgentCore had to be managed separately from IaC. This update is great news for those who want to manage AgentCore infrastructure as code!
Implementation
Now, let's proceed with the deployment.
Prerequisites
Here's the environment I used:
- Node.js v24.10.0
- npm v11.6.1
- Docker: v27.5.1
Project Structure
Here's the structure of the project we're creating.
We'll create it from the CDK template and write agent-related processes in the agent folder.
.
├── agent/
│ ├── agent.py # Python Agent
│ ├── requirements.txt # Python dependencies
│ ├── Dockerfile # Container definition
│ └── .dockerignore
├── lib/
│ └── sample-agentcore-l2-stack.ts # CDK Stack
├── bin/
│ └── sample-agentcore-l2.ts # CDK App
└── package.json
It's a simple code, but I've also published a sample in the repository below for reference if needed.
Create from CDK Template
Create a CDK template with the following command:
cdk init --language=typescript
Check CDK Dependencies
Check package.json. We're using version 2.221.0 for this project.
{
"dependencies": {
"aws-cdk-lib": "2.221.0",
"@aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-agentcore-alpha": "2.221.0-alpha.0",
"constructs": "^10.0.0"
}
}
If you're using a different version, let's update it.
npm install
Implementing Strands Agents
We use app.entrypoint to specify the entry point process.
We also use a simple weather-returning tool with the @tool designation.
"""
Simple Strands Agent for AgentCore Runtime
Uses BedrockAgentCoreApp for simplified deployment
"""
from strands import Agent, tool
from strands.models import BedrockModel
from bedrock_agentcore.runtime import BedrockAgentCoreApp
# Initialize the AgentCore app
app = BedrockAgentCoreApp()
@tool
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
"""
Get the current weather for a specified city.
Args:
city: The name of the city
Returns:
A string describing the weather
"""
# This is a dummy implementation for demonstration
# In a real application, you would call a weather API
weather_data = {
"Tokyo": "晴れ、気温25度",
"東京": "晴れ、気温25度",
"Osaka": "曇り、気温22度",
"大阪": "曇り、気温22度",
"New York": "Rainy, 18°C",
"London": "Foggy, 15°C",
}
return weather_data.get(city, f"{city}の天気情報は現在利用できません")
@app.entrypoint
async def entrypoint(payload):
"""
Main entrypoint for the agent.
This function is called when the agent is invoked.
Args:
payload: The input payload containing prompt and optional model config
Yields:
Streaming messages from the agent
"""
# Extract message and model configuration from payload
message = payload.get("prompt", "")
model_config = payload.get("model", {})
model_id = model_config.get("modelId", "anthropic.claude-3-5-haiku-20241022-v1:0")
# Initialize Bedrock model
model = BedrockModel(
model_id=model_id,
params={"max_tokens": 4096, "temperature": 0.7},
region="us-west-2"
)
# Create agent with the weather tool
agent = Agent(
model=model,
tools=[get_weather],
system_prompt="""あなたは親切なAIアシスタントです。
ユーザーの質問に丁寧に答えてください。
天気情報が必要な場合は、get_weatherツールを使用してください。"""
)
# Stream responses back to the caller
stream_messages = agent.stream_async(message)
async for msg in stream_messages:
if "event" in msg:
yield msg
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Run the app when executed directly
app.run()
List dependencies in requirements.txt. We'll only install the Strands Agents package and the AgentCore package.
strands-agents
bedrock-agentcore
Let's also write the Dockerfile.
I created this based on the automatically generated one from the Starter Toolkit.
# Dockerfile for AgentCore Runtime
# Must be ARM64 architecture for AgentCore Runtime
FROM ghcr.io/astral-sh/uv:python3.12-bookworm-slim
WORKDIR /app
# Configure UV for container environment
ENV UV_SYSTEM_PYTHON=1 \
UV_COMPILE_BYTECODE=1
# Copy requirements and install dependencies
COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt
RUN uv pip install -r requirements.txt
# Install OpenTelemetry for observability
RUN uv pip install aws-opentelemetry-distro>=0.10.1
# Set AWS region environment variables
ENV AWS_REGION=us-west-2 \
AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=us-west-2
# Signal that this is running in Docker
ENV DOCKER_CONTAINER=1
# Create non-root user for security
RUN useradd -m -u 1000 bedrock_agentcore
USER bedrock_agentcore
# Expose required ports
EXPOSE 8080
EXPOSE 8000
# Copy application code
COPY . .
# Run the application with OpenTelemetry instrumentation
CMD ["opentelemetry-instrument", "python", "-m", "agent"]
CDK Implementation
Now it's time to write the CDK code!
Let's implement it with a minimal configuration!
import * as cdk from "aws-cdk-lib";
import * as path from "path";
import { Construct } from "constructs";
import * as agentcore from "@aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-agentcore-alpha";
export class SampleAgentcoreL2Stack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
// Build local Docker image
const agentRuntimeArtifact = agentcore.AgentRuntimeArtifact.fromAsset(
path.join(__dirname, "../agent"),
);
// AgentCore Runtime (L2 Construct)
const runtime = new agentcore.Runtime(this, "StrandsAgentRuntime", {
runtimeName: "simpleStrandsAgent",
agentRuntimeArtifact: agentRuntimeArtifact,
description: "Simple Strands Agent with weather tool",
});
// Output
new cdk.CfnOutput(this, "RuntimeArn", {
value: runtime.agentRuntimeArn,
});
}
}
This is very simple! Just specify the path where the agent is implemented with AgentRuntimeArtifact.fromAsset and pass it to Runtime. It's convenient that building, auto-creating ECR, and pushing the image are all done automatically, and an IAM role is also created automatically if not specified.
It's as simple as the Starter Toolkit but with automatic creation, which is great.
Reference: L1 Notation
With L1, the notation would look like this, so by comparison, L2 is certainly simpler.
The nice thing is that ECR and IAM Role are automatically generated without having to specify them.
Full code
import * as path from 'node:path';
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import * as agentcore from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-bedrockagentcore';
import * as ecrAssets from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-ecr-assets';
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam';
import { Construct } from 'constructs';
export interface MastraAgentCoreStackProps extends cdk.StackProps {
readonly dockerAssetDirectory?: string;
readonly dockerfileName?: string;
readonly agentRuntimeName?: string;
readonly agentRuntimeEndpointName?: string;
}
export class CdkStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(
scope: Construct,
id: string,
props: MastraAgentCoreStackProps = {},
) {
super(scope, id, props);
const {
dockerAssetDirectory = path.join(__dirname, '..', '..'),
dockerfileName = 'Dockerfile.agentcore',
agentRuntimeName = 'MastraAgentRuntime',
agentRuntimeEndpointName = 'MastraAgentEndpoint',
} = props;
const dockerImageAsset = new ecrAssets.DockerImageAsset(
this,
'MastraAgentDockerAsset',
{
directory: dockerAssetDirectory,
file: dockerfileName,
platform: ecrAssets.Platform.LINUX_ARM64,
exclude: ['cdk', 'cdk.out', '.git', 'node_modules'],
},
);
const runtimeRole = new iam.Role(this, 'MastraAgentRuntimeRole', {
roleName: cdk.PhysicalName.GENERATE_IF_NEEDED,
assumedBy: new iam.ServicePrincipal('bedrock-agentcore.amazonaws.com'),
description: 'Execution role for Bedrock AgentCore runtime hosting Mastra agent',
});
const region = cdk.Stack.of(this).region;
const accountId = cdk.Stack.of(this).account;
runtimeRole.addToPolicy(
new iam.PolicyStatement({
sid: 'ECRImageAccess',
effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW,
actions: ['ecr:BatchGetImage', 'ecr:GetDownloadUrlForLayer'],
resources: [
`arn:aws:ecr:${region}:${accountId}:repository/${dockerImageAsset.repository.repositoryName}`,
],
}),
);
runtimeRole.addToPolicy(
new iam.PolicyStatement({
sid: 'ECRAuthToken',
effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW,
actions: ['ecr:GetAuthorizationToken'],
resources: ['*'],
}),
);
runtimeRole.addToPolicy(
new iam.PolicyStatement({
sid: 'CloudWatchLogsAccess',
effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW,
actions: [
'logs:CreateLogGroup',
'logs:CreateLogStream',
'logs:DescribeLogGroups',
'logs:DescribeLogStreams',
'logs:PutLogEvents',
],
resources: [
`arn:aws:logs:${region}:${accountId}:log-group:/aws/bedrock-agentcore/runtimes/*`,
`arn:aws:logs:${region}:${accountId}:log-group:/aws/bedrock-agentcore/runtimes/*:log-stream:*`,
`arn:aws:logs:${region}:${accountId}:log-group:/aws/bedrock-agentcore/runtimes/*:*`,
`arn:aws:logs:${region}:${accountId}:log-group:*`,
],
}),
);
runtimeRole.addToPolicy(
new iam.PolicyStatement({
sid: 'XRayTelemetry',
effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW,
actions: [
'xray:PutTraceSegments',
'xray:PutTelemetryRecords',
'xray:GetSamplingRules',
'xray:GetSamplingTargets',
],
resources: ['*'],
}),
);
runtimeRole.addToPolicy(
new iam.PolicyStatement({
sid: 'AgentWorkloadAccessToken',
effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW,
actions: [
'bedrock-agentcore:GetWorkloadAccessToken',
'bedrock-agentcore:GetWorkloadAccessTokenForJWT',
'bedrock-agentcore:GetWorkloadAccessTokenForUserId',
],
resources: [
`arn:aws:bedrock-agentcore:${region}:${accountId}:workload-identity-directory/default`,
`arn:aws:bedrock-agentcore:${region}:${accountId}:workload-identity-directory/default/workload-identity/*`,
],
}),
);
runtimeRole.addToPolicy(
new iam.PolicyStatement({
sid: 'BedrockModelInvocation',
effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW,
actions: ['bedrock:InvokeModel', 'bedrock:InvokeModelWithResponseStream'],
resources: [
'arn:aws:bedrock:*::foundation-model/*',
`arn:aws:bedrock:${region}:${accountId}:*`,
],
}),
);
runtimeRole.addToPolicy(
new iam.PolicyStatement({
sid: 'CloudWatchMetrics',
effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW,
actions: ['cloudwatch:PutMetricData'],
resources: ['*'],
conditions: {
StringEquals: {
'cloudwatch:namespace': 'bedrock-agentcore',
},
},
}),
);
// CloudWatch OTLP endpoint permissions
runtimeRole.addToPolicy(
new iam.PolicyStatement({
sid: 'CloudWatchOTLPEndpoints',
effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW,
actions: [
'xray:PutTraceSegments',
'xray:PutTelemetryRecords',
'logs:PutLogEvents',
'logs:CreateLogStream',
'logs:CreateLogGroup',
],
resources: ['*'],
}),
);
const runtime = new agentcore.CfnRuntime(this, 'MastraAgentRuntime', {
agentRuntimeName,
agentRuntimeArtifact: {
containerConfiguration: {
containerUri: dockerImageAsset.imageUri,
},
},
networkConfiguration: {
networkMode: 'PUBLIC',
},
roleArn: runtimeRole.roleArn,
protocolConfiguration: 'HTTP',
});
runtime.node.addDependency(runtimeRole);
}
}
Deployment
Now that the code is written, let's deploy it.
cdk deploy
Upon completion of the deployment, the Runtime ARN will be output.
✅ SampleAgentcoreL2Stack
✨ Deployment time: 37.77s
Outputs:
SampleAgentcoreL2Stack.RuntimeArn = arn:aws:bedrock-agentcore:us-west-2:123456789012:runtime/simpleStrandsAgent-XXXXX
SampleAgentcoreL2Stack.RuntimeId = simpleStrandsAgent-XXXXX
Stack ARN:
arn:aws:cloudformation:us-west-2:123456789012:stack/SampleAgentcoreL2Stack/xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx
✨ Total time: 42.09s
Testing
Now that the deployment has succeeded, let's try calling the agent!
From the AWS console, let's send a payload via the Test > Agent Sandbox tab.
{
"prompt": "こんにちは"
}
And then...
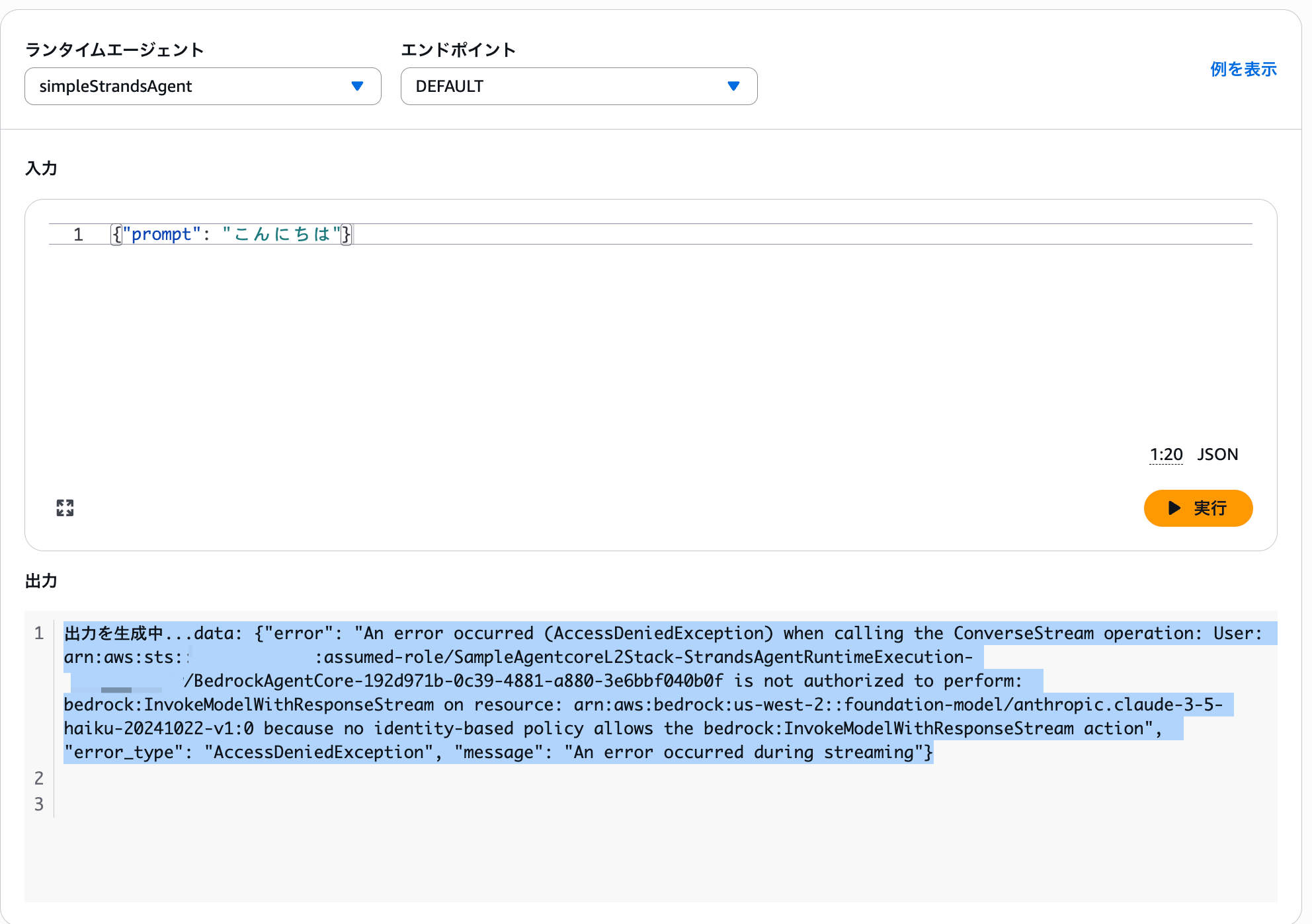
Generating output...data: {"error": "An error occurred (AccessDeniedException) when calling the ConverseStream operation: User: arn:aws:sts::123456789012:assumed-role/SampleAgentcoreL2Stack-StrandsAgentRuntimeExecution-XXXXX/BedrockAgentCore-xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx is not authorized to perform: bedrock:InvokeModelWithResponseStream on resource: arn:aws:bedrock:us-west-2::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-3-5-haiku-20241022-v1:0 because no identity-based policy allows the bedrock:InvokeModelWithResponseStream action", "error_type": "AccessDeniedException", "message": "An error occurred during streaming"}
Oops, an error occurred.
Looking at the error message, it seems we're missing permissions to invoke Bedrock models.
Indeed, checking the permissions of the auto-created IAM role, there are permissions for ECR and CloudWatch Logs, but none for Bedrock.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:DescribeLogStreams"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:logs:us-west-2:123456789012:log-group:/aws/bedrock-agentcore/runtimes/*",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Sid": "LogGroupAccess"
},
{
"Action": "logs:DescribeLogGroups",
"Resource": "arn:aws:logs:us-west-2:123456789012:log-group:*",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Sid": "DescribeLogGroups"
},
{
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:logs:us-west-2:123456789012:log-group:/aws/bedrock-agentcore/runtimes/*:log-stream:*",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Sid": "LogStreamAccess"
},
{
"Action": [
"xray:GetSamplingRules",
"xray:GetSamplingTargets",
"xray:PutTelemetryRecords",
"xray:PutTraceSegments"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Sid": "XRayAccess"
},
{
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"cloudwatch:namespace": "bedrock-agentcore"
}
},
"Action": "cloudwatch:PutMetricData",
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Sid": "CloudWatchMetrics"
},
{
"Action": [
"bedrock-agentcore:GetWorkloadAccessToken",
"bedrock-agentcore:GetWorkloadAccessTokenForJWT",
"bedrock-agentcore:GetWorkloadAccessTokenForUserId"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:bedrock-agentcore:us-west-2:123456789012:workload-identity-directory/default",
"arn:aws:bedrock-agentcore:us-west-2:123456789012:workload-identity-directory/default/workload-identity/*"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Sid": "GetAgentAccessToken"
},
{
"Action": [
"ecr:BatchCheckLayerAvailability",
"ecr:BatchGetImage",
"ecr:GetDownloadUrlForLayer"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:ecr:us-west-2:123456789012:repository/cdk-XXXXX-container-assets-123456789012-us-west-2",
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": "ecr:GetAuthorizationToken",
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
}
]
}
Adding Permissions
Let's add Bedrock permissions.
We can easily add permissions using the addToRolePolicy() method.
Let's modify lib/sample-agentcore-l2-stack.ts to allow invoking all Bedrock models.
import * as cdk from "aws-cdk-lib";
import * as path from "path";
import { Construct } from "constructs";
import * as agentcore from "@aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-agentcore-alpha";
import * as iam from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam";
export class SampleAgentcoreL2Stack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
const agentRuntimeArtifact = agentcore.AgentRuntimeArtifact.fromAsset(
path.join(__dirname, "../agent"),
);
const runtime = new agentcore.Runtime(this, "StrandsAgentRuntime", {
runtimeName: "simpleStrandsAgent",
agentRuntimeArtifact: agentRuntimeArtifact,
description: "Simple Strands Agent with weather tool",
});
// Add Bedrock invocation permissions!
runtime.addToRolePolicy(
new iam.PolicyStatement({
effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW,
actions: [
"bedrock:InvokeModel",
"bedrock:InvokeModelWithResponseStream",
],
resources: [
`arn:aws:bedrock:${this.region}::foundation-model/*`,
],
}),
);
new cdk.CfnOutput(this, "RuntimeArn", {
value: runtime.agentRuntimeArn,
description: "ARN of the AgentCore Runtime",
exportName: "AgentRuntimeArn",
});
new cdk.CfnOutput(this, "RuntimeId", {
value: runtime.agentRuntimeId,
description: "ID of the AgentCore Runtime",
exportName: "AgentRuntimeId",
});
}
}
Now that we've added the permissions, let's redeploy.
npm run build
cdk deploy
Alternative Method: Using the grantInvoke() Method
Actually, there's another way to add Bedrock permissions.
Using the @aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-alpha package, you can grant permissions with the grantInvoke() method.
However, at the time of writing, it only supports up to Claude 3.7 Sonnet V1, so it might be difficult when using the latest models. The method introduced earlier is probably more practical for granting permissions.
Installing the Alpha Package
First, you need to install the @aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-alpha package.
npm install @aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-alpha
Method 1: Using BedrockFoundationModel
To grant permissions for specific models, use BedrockFoundationModel.
import * as cdk from "aws-cdk-lib";
import * as path from "path";
import { Construct } from "constructs";
import * as agentcore from "@aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-agentcore-alpha";
import * as bedrock from "@aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-alpha";
export class SampleAgentcoreL2Stack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
const agentRuntimeArtifact = agentcore.AgentRuntimeArtifact.fromAsset(
path.join(__dirname, "../agent"),
);
const runtime = new agentcore.Runtime(this, "StrandsAgentRuntime", {
runtimeName: "simpleStrandsAgent",
agentRuntimeArtifact: agentRuntimeArtifact,
description: "Simple Strands Agent with weather tool",
});
// Grant permissions using BedrockFoundationModel
const model = bedrock.BedrockFoundationModel.ANTHROPIC_CLAUDE_3_5_HAIKU_V1_0;
model.grantInvoke(runtime);
// Outputs omitted
}
}
Method 2: Using CrossRegionInferenceProfile
When using a cross-region inference profile, you can use CrossRegionInferenceProfile.
This is a feature that optimizes model invocation across multiple regions.
import * as cdk from "aws-cdk-lib";
import * as path from "path";
import { Construct } from "constructs";
import * as agentcore from "@aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-agentcore-alpha";
import * as bedrock from "@aws-cdk/aws-bedrock-alpha";
export class SampleAgentcoreL2Stack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
const agentRuntimeArtifact = agentcore.AgentRuntimeArtifact.fromAsset(
path.join(__dirname, "../agent"),
);
const runtime = new agentcore.Runtime(this, "StrandsAgentRuntime", {
runtimeName: "simpleStrandsAgent",
agentRuntimeArtifact: agentRuntimeArtifact,
description: "Simple Strands Agent with weather tool",
});
// Permission granting using CrossRegionInferenceProfile
const inferenceProfile = bedrock.CrossRegionInferenceProfile.fromConfig({
geoRegion: bedrock.CrossRegionInferenceProfileRegion.US,
model: bedrock.BedrockFoundationModel.ANTHROPIC_CLAUDE_3_5_HAIKU_V1_0
});
inferenceProfile.grantInvoke(runtime);
// Output is omitted
}
}
Both methods make it easy to add permissions, which is nice.
Testing
After deployment is complete, let's try calling the agent again from the agent sandbox tab.
{
"prompt": "Tell me the weather in Tokyo"
}
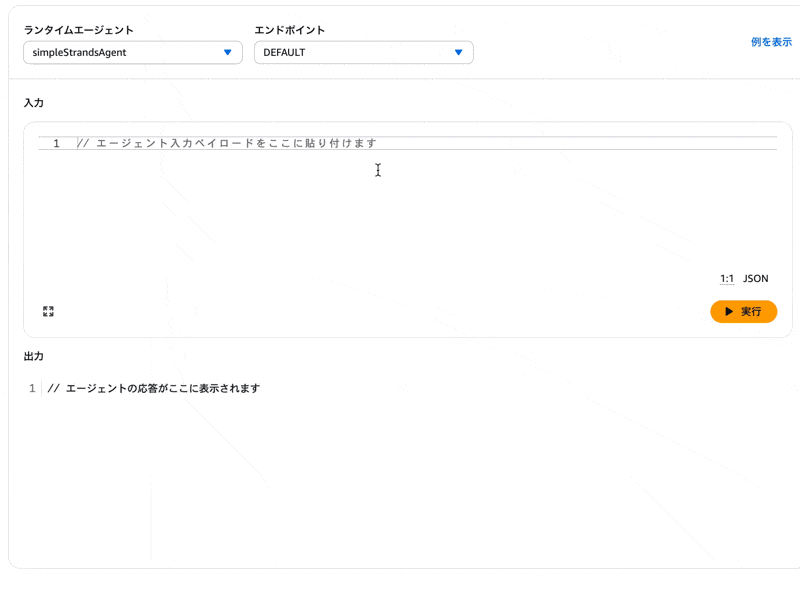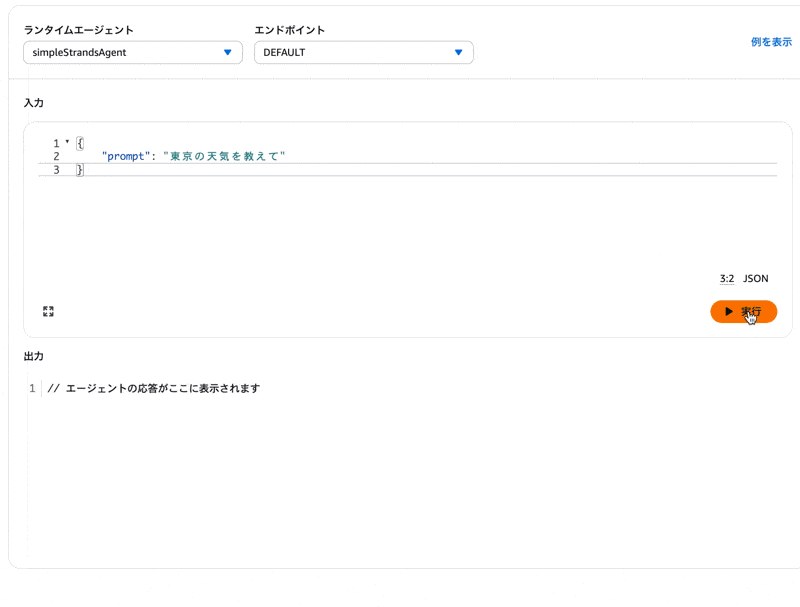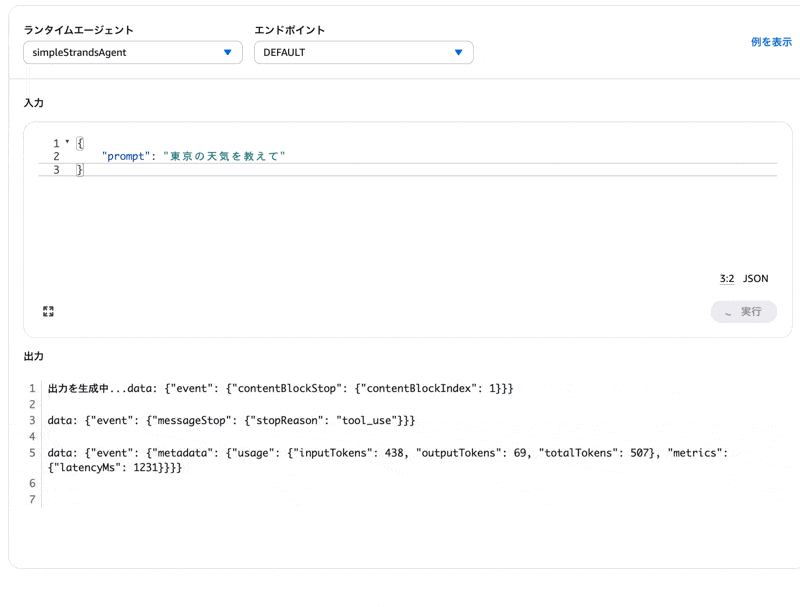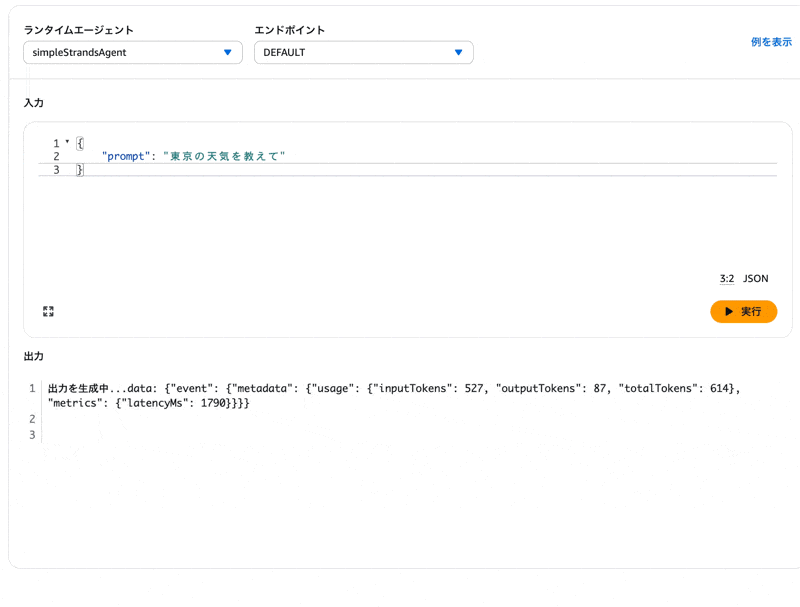
The response came back properly!
Conclusion
In this article, we deployed Strands Agents using the AgentCore L2 Construct added in AWS CDK v2.221.0!
Summarizing what I felt after trying it:
The L2 Construct's abstraction is a benefit as it allows for simple deployment without worrying too much about IAM roles and default settings. On the other hand, when using Bedrock for the LLM, you need to add Bedrock permissions.
While the Starter Toolkit is convenient, using this L2 Construct is also a good option when you want to incorporate it into an existing CDK project or manage it alongside other AWS resources.
I'd like to continue exploring and considering IaC operations for AgentCore in the future!
Thank you for reading to the end!
Additional Notes
While I've given a quick introduction here, the official documentation includes examples of various L2 Construct implementation patterns, so please refer to it.
For example, instead of auto-creating ECR as we did this time, you can create an ECR repository separately and use that repository.
const repository = new ecr.Repository(this, "TestRepository", {
repositoryName: "test-agent-runtime",
});
// The runtime by default create ECR permission only for the repository available in the account the stack is being deployed
const agentRuntimeArtifact = agentcore.AgentRuntimeArtifact.fromEcrRepository(repository, "v1.0.0");
// Create runtime using the built image
const runtime = new agentcore.Runtime(this, "MyAgentRuntime", {
runtimeName: "myAgent",
agentRuntimeArtifact: agentRuntimeArtifact
});



