
I introduced "llms.txt" as a countermeasure against rapidly increasing AI crawlers
This article was published more than one year ago. Please be aware that the information may be outdated.
This page has been translated by machine translation. View original
Due to a surge in excessive access by AI crawlers, we have published a site structure data file "llms.txt" (Large Language Model Specifications) as a countermeasure.
Let me introduce the instruction content that we reflected in this file, intended to guide LLMs on appropriate crawling methods and efficient use of site resources.
I'll introduce the instructions we included in llms.txt to encourage appropriate crawling by LLMs.
Setup
We created a markdown format text file and stored it in the S3 bucket that contains robots.txt and error pages.
It has been published at the following URL:
https://dev.classmethod.jp/llms.txt
llms.txt Content
user-agent
We configured it to apply to all AI crawlers, not limited to specific LLMs.
user-agent: *
License
We reflected content usage conditions in accordance with the site banner.
We specified that AI training use is permitted.
x-content-license: "(c) Classmethod, Inc. All rights reserved."
x-ai-training-policy: "allowed"
Rate Limits
We included instructions to restrict excessive crawling that could cause excessive server load.
crawl-delay: 1
x-rate-limit: 60
x-rate-limit-window: 60
x-rate-limit-policy: "strict"
x-rate-limit-retry: "no-retry"
x-rate-limit-description: "Maximum 60 requests per 60 seconds. If rate limit is exceeded, do not retry and move on to next request."
# Concurrency Limits
x-concurrency-limit: 3
x-concurrency-limit-description: "Please limit concurrent requests to a maximum of 3. This helps us manage server load."
Error Handling and Retry Policy
Regarding retries, we specified backoff processing to avoid load and response codes that prohibit retries.
x-error-retry-policy: "exponential-backoff"
x-error-retry-policy-description: "For transient errors (5xx except 429), implement exponential backoff with initial wait of 2 seconds, doubling on each retry, with maximum 5 retries."
x-rate-limit-exceeded-policy: "wait-and-retry"
x-rate-limit-exceeded-policy-description: "When receiving HTTP 429 (Too Many Requests), do not retry immediately. Wait at least 60 seconds before attempting the request again."
x-max-retries: 5
x-retry-status-codes:
- 500
- 502
- 503
- 504
x-no-immediate-retry-status-codes:
- 429
x-no-retry-status-codes:
- 403
- 404
Canonical URL
We included instructions to clearly specify the official published URL of the site and to avoid direct IP address specification or access with unintended FQDNs.
x-canonical-url-policy: "strict"
x-canonical-url: "https://dev.classmethod.jp/"
x-canonical-url-description: "Access via other FQDNs or IP addresses is invalid. Use only 'https://dev.classmethod.jp/' as the base URL. Within the HTML content, links should also start with 'https://dev.classmethod.jp/'"
Article Pages
We included the path of blog article pages, meta information contained, update frequency, etc.
We reflected information that encourages efficient crawling by clearly communicating the content structure of the site.
x-article-pattern: /articles/{slug}/
x-article-type: "technical-blog"
x-article-description: "Technical blog posts and tutorials by Classmethod Inc., an AWS Premier Tier Services Partner. Articles cover cloud computing (especially AWS), development, and IT, with a focus on practical experiences and reproducible guides."
x-article-example: https://dev.classmethod.jp/articles/browser-use-start/
x-article-metadata:
- author
- title
- description
x-article-update-frequency: "daily"
x-article-new-articles-per-day: "10-50"
x-article-new-articles-per-day-description: "Approximately 10 to 50 new articles are added each day."
Author Pages
We described author pages and information such as RSS.
allow: /author/*
x-author-pattern: /author/{username}/
x-author-description: "Blog author profile pages"
x-author-example: https://dev.classmethod.jp/author/akari7/
x-author-metadata:
- author
- description
- url
x-author-content-update-policy: "dynamic"
x-author-rss-pattern: /author/{username}/feed/
x-author-rss-pattern-example: https://dev.classmethod.jp/author/akari7/feed/
# Author Update Frequency
x-author-update-frequency: "monthly"
x-author-new-authors-per-month: "5-20"
x-author-new-authors-per-month-description: "Approximately 5 to 20 new authors are added each month."
RSS, Sitemap
We included information about the RSS that reflects the 30 newly published articles and the sitemap that reflects all published articles on a monthly basis.
# RSS Feeds
allow: /feed/
x-feed: https://dev.classmethod.jp/feed/
x-feed-format: rss
x-feed-item-count: 30
x-feed-content: "latest"
x-feed-description: "The RSS feed contains the 30 most recent articles published on the site. It is updated whenever new content is published."
x-feed-update-frequency: "real-time"
# Sitemap
allow: /sitemap.xml
allow: /sitemaps/*
x-sitemap: https://dev.classmethod.jp/sitemap.xml
x-sitemap-format: xml
x-sitemap-structure: "monthly"
x-sitemap-pattern: "/sitemaps/sitemap-{year}-{month}.xml"
x-sitemap-pattern-example: "https://dev.classmethod.jp/sitemaps/sitemap-2024-07.xml"
x-sitemap-description: "Articles are organized in monthly sitemaps following the pattern sitemap-YYYY-MM.xml. The main sitemap.xml is an index that references these monthly sitemaps."
x-sitemap-retention: "long-term"
x-sitemap-retention-description: "Monthly sitemaps are retained for multiple years, allowing access to historical content organization."
Access Restriction
We restricted requests for paths that are currently unused and become redirects.
# disallow
disallow: /pages/*
disallow: /tag/*
disallow: /category/*
Publisher Information
As information to demonstrate the reliability of the site operator, we translated About DevelopersIO into English and reflected the structured content.
# Publisher Information
x-publisher-name: "Classmethod, Inc."
x-publisher-description: "Classmethod, Inc. is a technology company with 300+ engineers, specializing in cloud services and digital transformation. It operates a technical blog (dev.classmethod.jp) with over 30,000 articles based on practical engineering experiences, primarily focused on AWS."
x-publisher-credentials:
- "AWS Premier Tier Services Partner (2014-present)"
- "AWS Services Partner of the Year - Japan"
- "LINE Technology Partner (OMO/Engagement certified)"
- "3,000+ client companies, 15,000+ AWS accounts supported"
x-publisher-certifications:
- "AWS Technical Certifications: 2,000+"
- "AWS Competencies: Migration, Mobile, Big Data, DevOps"
- "AWS Service Delivery Programs: 12"
x-publisher-website: "https://classmethod.jp/"
Language
We listed the languages currently used for writing on our blog.
x-supported-languages:
- ja
- en
- ko
- th
- de
- vi
- id
Crawler Hints
We encouraged LLM crawlers to pre-supplement the "/" at the end of URIs when it is missing, expecting to reduce the number of requests that are treated as redirects in the Next app.
x-crawler-hints:
- "Before accessing each URL, check if the URL ends with '/'."
- "If the URL does not end with '/', add '/' to the end of the URL before accessing it."
- "Extract the HTML content of each page."
Effect
In the access logs for the three days after setting up llms.txt, we were able to confirm that requests that referenced llms.txt (with "bot" in the User-Agent) were recorded.
| User-Agent |
|---|
| Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; SBIntuitionsBot/0.1; +https://www.sbintuitions.co.jp/bot/) |
| Mozilla/5.0 AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko); compatible; ChatGPT-User/1.0; +https://openai.com/bot |
| Mozilla/5.0 AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko; compatible; bingbot/2.0; +http://www.bing.com/bingbot.htm) Chrome/116.0.1938.76 Safari/537.36 |
| Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/131.0.0.0 Safari/537.36; compatible; OAI-SearchBot/1.0; +https://openai.com/searchbot |
| Mozilla/5.0 AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko; compatible; GPTBot/1.2; +https://openai.com/gptbot) |
| Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 6.0.1; Nexus 5X Build/MMB29P) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/133.0.6943.53 Mobile Safari/537.36 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html) |
| Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; AhrefsBot/7.0; +http://ahrefs.com/robot/) |
Testing
We gave ChatGPT-4o (latest) the following prompt and attempted to generate a script to download published articles based on the information in the llms.txt we set up.
I want to retrieve the HTML of all published articles on the site that has the following llms.txt published.
Please generate a CLI script that uses curl and xargs for parallel processing, implemented within the allowed limits for efficient retrieval time.
<llms.txt>
(omitted)
</llms.txt>
Response Content
We confirmed that ChatGPT-4o could read the following site policies from llms.txt:
Maximum parallelism: 3 (x-concurrency-limit)
Rate limit: 60 requests/60 seconds (1 request per second)
Retry: Exponential backoff for 5xx series (maximum 5 times)
Wait 60 seconds for 429 (Too Many Requests), skip without retrying
Do not retry 403, 404, 429

Script
The generated script was able to retrieve a list of monthly sitemap URLs from the correct sitemap (XML) URL.
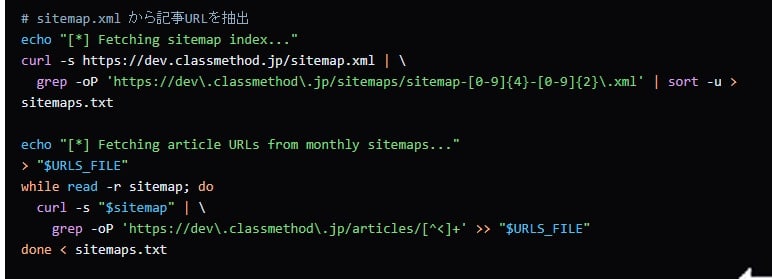
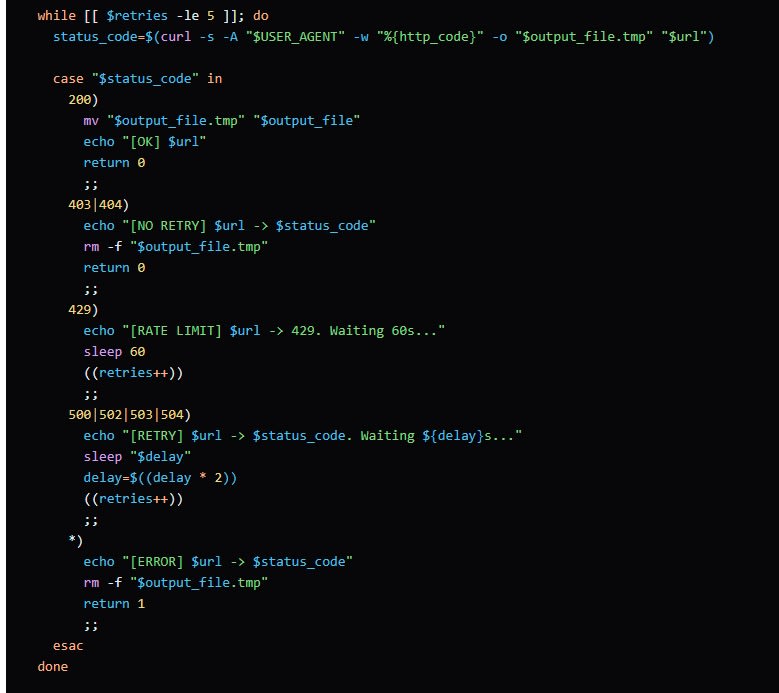
In the article retrieval process using curl, when an error occurs, it judges the HTTP status code and only retries if it's a 5xx server error.
The article retrieval with curl included a mechanism to only retry if the HTTP response is a 5XX server error.
Using xargs for parallel processing, it was controlled not to exceed the maximum parallelism (3) specified in llms.txt.
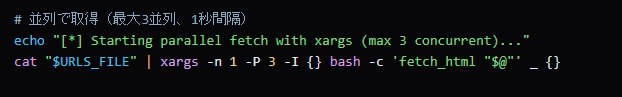
We confirmed that a script that controls the number of simultaneous requests was generated.
Summary
The llms.txt (Large Language Model Specifications) introduced here is not standardized as of 2025, but it is considered an effective approach for coexistence with AI crawlers in the future.
We plan to continue optimizing while measuring the effectiveness of this configuration and monitoring future standardization trends.
If you operate a public website that accepts AI access, we recommend providing information about your site's structure, crawling policy, and content usage as llms.txt to crawlers to suppress inefficient crawling.
Also, when using web services outside your organization as information sources for local LLMs or RAG initiatives, or when directly using content, we strongly recommend checking for the presence of "llms.txt" along with site policies, and if specific instructions regarding crawling or content usage are stated in llms.txt, following those instructions.



