
Automatically Deploy Twilio Functions from GitHub Actions
This page has been translated by machine translation. View original
Introduction
I will introduce how to automatically deploy Twilio Functions JavaScript code managed with Git from GitHub Actions. We'll use twilio-run from the Twilio Serverless Toolkit for deployment. By using GitHub Actions Secrets, we can operate without storing sensitive information in the repository.
What is Twilio
Twilio is a cloud service that provides communication functions such as SMS and voice calls as APIs. By calling Twilio's API from your application, you can integrate communication features. With Twilio Functions, you can run Node.js code in Twilio's serverless environment. It can be published as an HTTP endpoint, allowing you to run code without worrying about server operations.
Target Audience
- Those who want to stop manual deployment of Twilio Functions
- Those who want to deploy from the main branch to the dev environment with GitHub Actions
- Those who want to operate without putting secret information in Git
References
- Continuous Deployment using the Serverless Toolkit
- Deploying with the Serverless Toolkit
- Configuration and Meta Files
Configuration
We'll deploy Twilio Functions code managed in a GitHub repository to Twilio from GitHub Actions.
The workflow is triggered by a push to the main branch, and authentication information and environment variables stored in GitHub Actions Secrets are injected into the execution environment. twilio-run uses the injected authentication information to deploy Functions and Assets to the dev environment of the Service test-function-ci on Twilio.
Implementation
Create a Service in Twilio Console
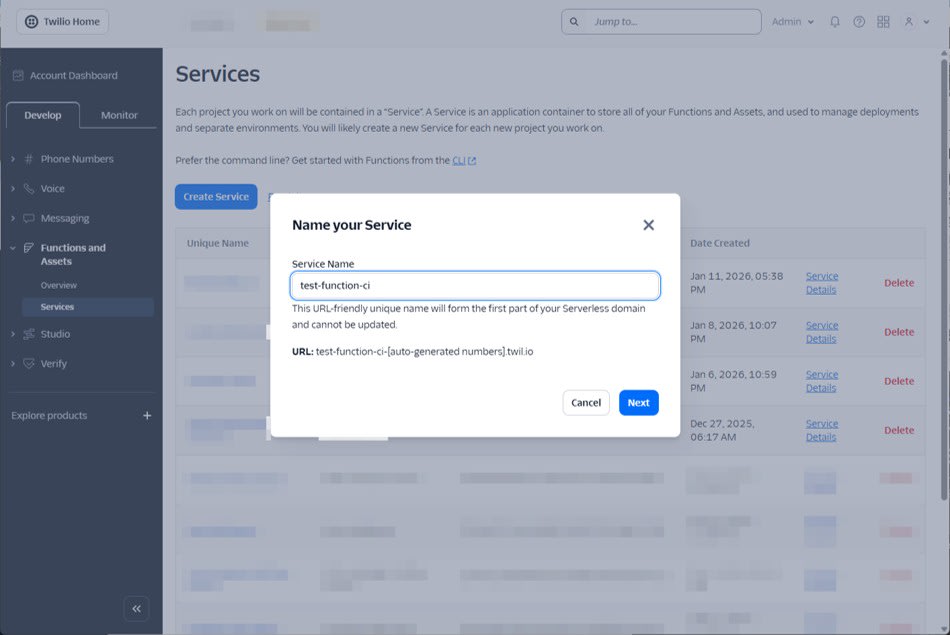
CI/CD deployment identifies and overwrites the target Service. In this article, we assume that the Service is created in advance on the Twilio Console, and CI/CD deploys to an existing Service.
In this case, we will verify with the Service name test-function-ci. This Service name will be referenced in subsequent settings. The Service name can be specified as serviceName in .twilioserverlessrc.
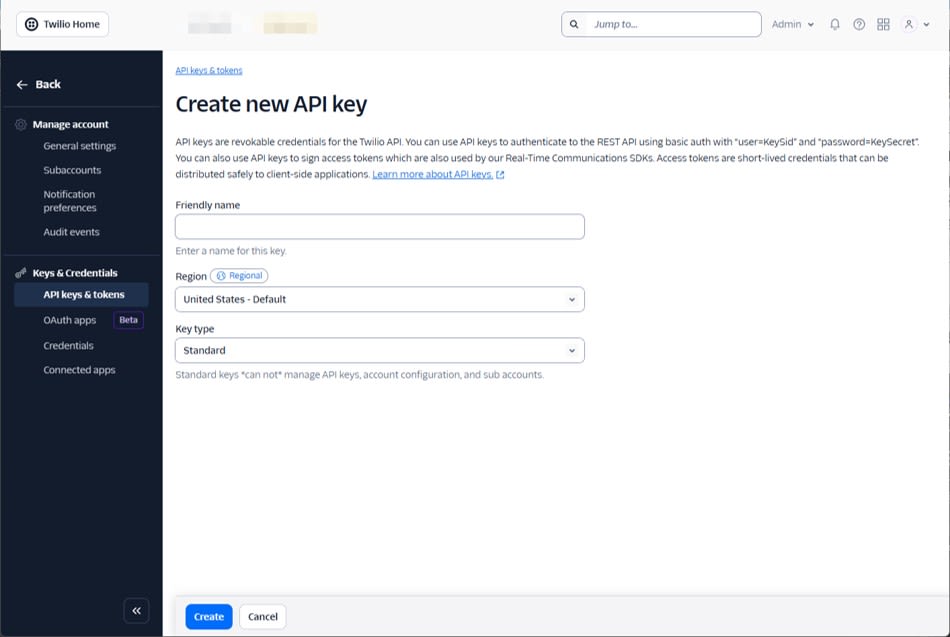
Prepare API Key and API Secret
Create an API Key from the Keys & Credentials > API keys & tokens menu.
Prepare the Repository Structure
The Serverless Toolkit handles Functions and Assets in a specific directory structure. A minimal example is shown below.
.
├─ functions
│ └─ hello.js
├─ assets
│ └─ index.html
├─ .env.example
├─ .twilioserverlessrc
└─ package.json
For testing purposes, let's prepare functions/hello.js as follows:
exports.handler = async function (context, event, callback) {
callback(null, { ok: true });
};
Add twilio-run
Twilio recommends adding twilio-run as a devDependency for CI/CD purposes. (Reference)
Add it with the following command. Make sure twilio-run is version 3.0.0 or higher. (In the author's environment, it was 5.0.0.)
npm install --save-dev twilio-run
Add deploy to the scripts in package.json. In CI/CD, we'll execute npm run deploy rather than calling twilio-run directly.
{
"scripts": {
"deploy": "twilio-run deploy --username $TWILIO_API_KEY --password $TWILIO_API_SECRET"
},
"devDependencies": {
"twilio-run": "^5.0.0"
}
}
Create .env.example
In CI/CD, it's common to inject environment variables from Secrets. Meanwhile, the Serverless Toolkit uses the .env file to determine "which keys to upload to the deployment environment." Therefore, we create .env.example as a template without values. This file only lists the key names that you want to reflect in the deployment environment.
For example, to reflect APP_NAME in the deployment environment:
APP_NAME=
Create .twilioserverlessrc
Next, we summarize the necessary settings for CI/CD in .twilioserverlessrc.
- Fix the deployment destination to
test-function-ci - Fix the deployment environment to dev
- Load keys listed in
.env.examplefrom GitHub Actions environment variables
Using loadSystemEnv and env, you can pick up only the keys written in .env.example from system environment variables and reflect them in the deployment environment.
{
"commands": {
"deploy": {
"serviceName": "test-function-ci",
"environment": "dev",
"overrideExistingProject": true,
"loadSystemEnv": true,
"env": ".env.example"
}
}
}
Set up GitHub Actions Secrets
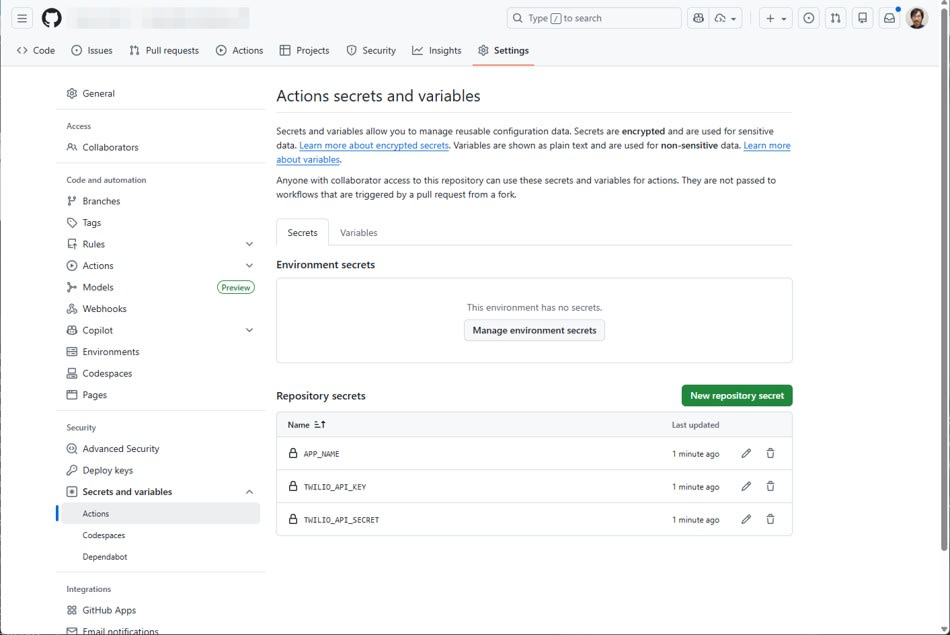
Add Secrets in the GitHub repository settings.
TWILIO_API_KEYTWILIO_API_SECRETAPP_NAME(in this example, we set it totest-function-ci-app)
Add GitHub Actions workflow
The goal is to execute npm run deploy triggered by a push to the main branch. Add the following file as .github/workflows/deploy.yml.
name: deploy-twilio-functions
on:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 22
cache: npm
- run: npm ci
- run: npm run deploy
env:
TWILIO_API_KEY: ${{ secrets.TWILIO_API_KEY }}
TWILIO_API_SECRET: ${{ secrets.TWILIO_API_SECRET }}
APP_NAME: ${{ secrets.APP_NAME }}
Verification
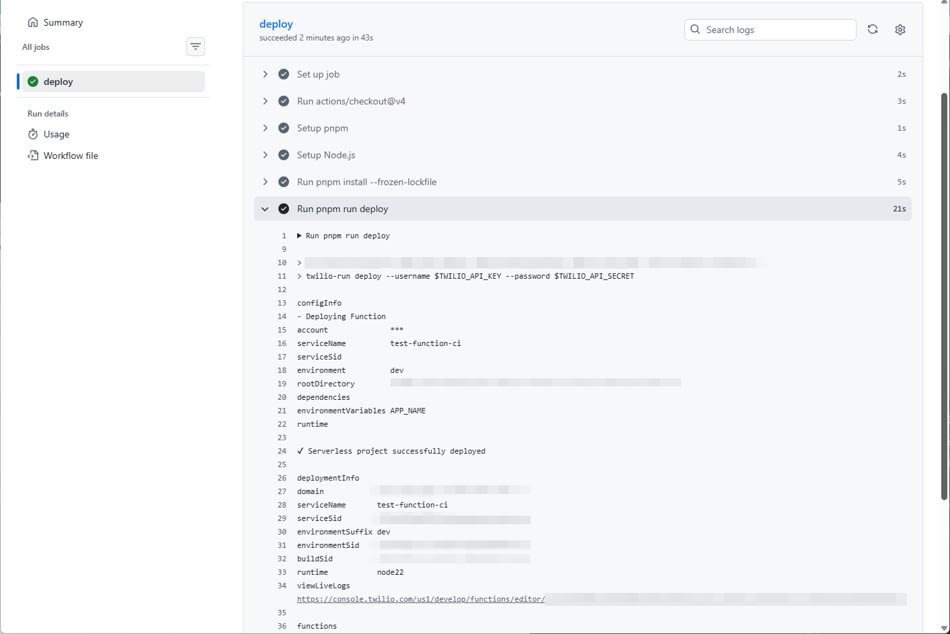
Confirm Successful Deployment
Push to the main branch and confirm that the GitHub Actions job succeeds. Also confirm in the log that the destination Service is test-function-ci.
Call the Function to Check Connectivity
After deployment, check the Function URL in the GitHub Actions log.
(omitted)
functions
public /hello https://test-function-ci-****.twil.io/hello
(omitted)
Check connectivity by accessing with curl.
curl -sS https://test-function-ci-****.twil.io/hello
{"ok":true}
Confirm that Environment Variables are Applied
Change hello.js to reference context.APP_NAME and deploy again. If the keys listed in .env.example are reflected from GitHub Actions environment variables, it's successful.
hello.js
exports.handler = async function (context, event, callback) {
const appName = context.APP_NAME || 'unknown';
callback(null, { ok: true, appName });
};
Connectivity check
curl -sS https://test-function-ci-****.twil.io/hello
{"ok":true,"appName":"test-function-ci-app"}
Summary
I've shown how you can automatically deploy Twilio Functions from GitHub Actions using twilio-run. By using GitHub Actions Secrets, you can operate without putting sensitive information in your repository.