
I'll incorporate validators into GitHub Actions to detect inconsistencies in VST3 plugins during pull requests
This page has been translated by machine translation. View original
Introduction
VST3 plugins can be reassuring when they load and produce sound in a DAW. However, manual verification often gets pushed to later stages, and if broken code gets merged at the pull request (PR) stage, the cost of investigating the cause increases.
By setting up a CI environment that runs the validator included in the VST3 SDK, we can catch plugin inconsistencies. In this article, I'll introduce an example of setting up an environment to automatically run the validator in GitHub Actions, using the Steinberg VST3 SDK's sample AGain as the subject.
What are VST plugins?
VST (Virtual Studio Technology) is a common interface for connecting host applications like DAWs with audio plugins such as effects and synthesizers.
In October 2025, Steinberg released VST 3.8 SDK and simultaneously changed the license to the MIT license (reference). Previously, Steinberg's proprietary license (and sometimes individual contracts) was required, but now it can be freely used even in commercial products by following the MIT license. The main conditions are to retain the copyright notice and license text. Please check the license text for details.
Why include validator in CI?
The validator is a tool for loading VST3 plugins and performing basic checks against the VST3 specifications. By running the validator in CI, issues like the following can be found at the PR stage:
- The plugin cannot be loaded
- Exceptions or crashes occur during initialization
- Behavior that violates basic VST3 specifications (call order expected by the host, return values, reference counts, process prerequisites, etc.)
While manual verification in a DAW is important, automatically discovering basic inconsistencies before that stage helps stabilize the development flow.
Target audience
- Those who can build VST3 SDK samples with Visual Studio 2022
- Those who want to create CI for C++ projects using GitHub Actions
- Those who want to detect inconsistencies in their VST plugins at the PR stage without relying solely on manual verification in a DAW
- Those who want to try running Steinberg's official validator first
References
- Validator command line - VST 3 Developer Portal
- VST 3 Plug-In SDK (GitHub repository)
- VST 3 Now Available Under MIT License (Steinberg Press)
- Host compatibility testing (Steinberg Forums)
Local Setup
Getting and Building the SDK
First, let's get the VST3 SDK and set it up so we can build the official samples.
-
Clone the VST3 SDK from GitHub.
git clone --recursive https://github.com/steinbergmedia/vst3sdk.git cd vst3sdk -
Create a build directory and generate Visual Studio project files using CMake.
mkdir build cd build cmake -G "Visual Studio 17 2022" -A x64 .. -DSMTG_CREATE_PLUGIN_LINK=OFF -
Open the generated
vstsdk.slnin Visual Studio.
-
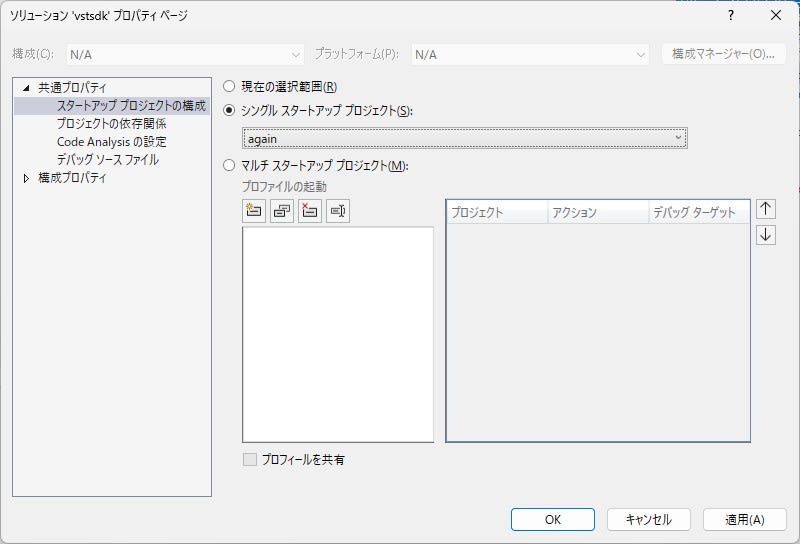
Open the solution properties, and set
Common Properties > Startup Project ConfigurationtoSingle startup project > again.
-
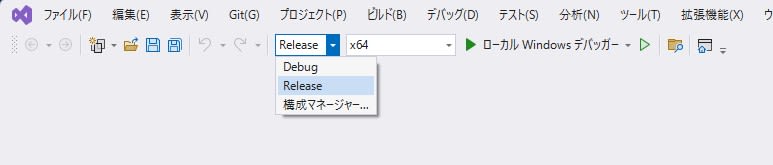
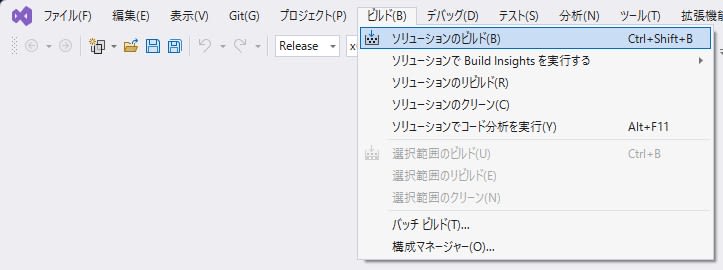
Close the properties window with OK. Set the configuration to
Releaseand platform tox64, then selectBuild > Build Solution(orRebuild) to create the build files.
When the build is successful, again.vst3 will be generated in build/VST3/Release.
Preparing VST3PluginTestHost
VST3PluginTestHost is provided as part of the full VST3 SDK. Download the full SDK zip from the official site. After extracting, extract the VST3PluginTestHost_x64_Installer_x.xx.xx.zip found in the following path:
VST_SDK/
vst3sdk/
bin/
Windows_x64/
VST3PluginTestHost_x64_Installer_x.xx.xx.zip
Run the extracted VST3PluginTestHost_x64.msi to install VST3PluginTestHost.

Launch the Host from Visual Studio
To observe AGain's behavior, let's launch VST3PluginTestHost from Visual Studio.
-
In the Solution Explorer in Visual Studio, right-click the
Plugin-Examples > againproject and open "Properties".
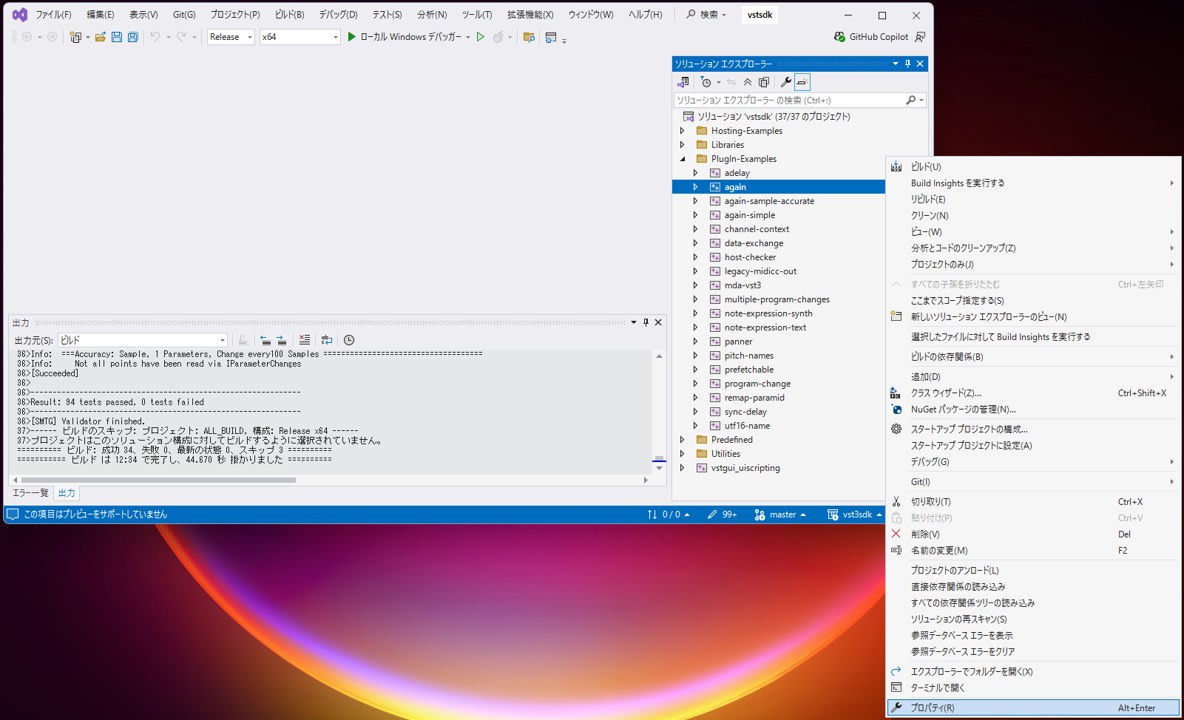
-
Set the configuration to
Releaseand platform tox64, then configure "Configuration Properties > Debugging" as follows:- Command:
C:\path\to\VST3PluginTestHost.exe(path to the VST3PluginTestHost.exe installed in the previous step) - Command Arguments:
--pluginfolder "C:\path\to\build\VST3\Release"(folder containing the built again.vst3)
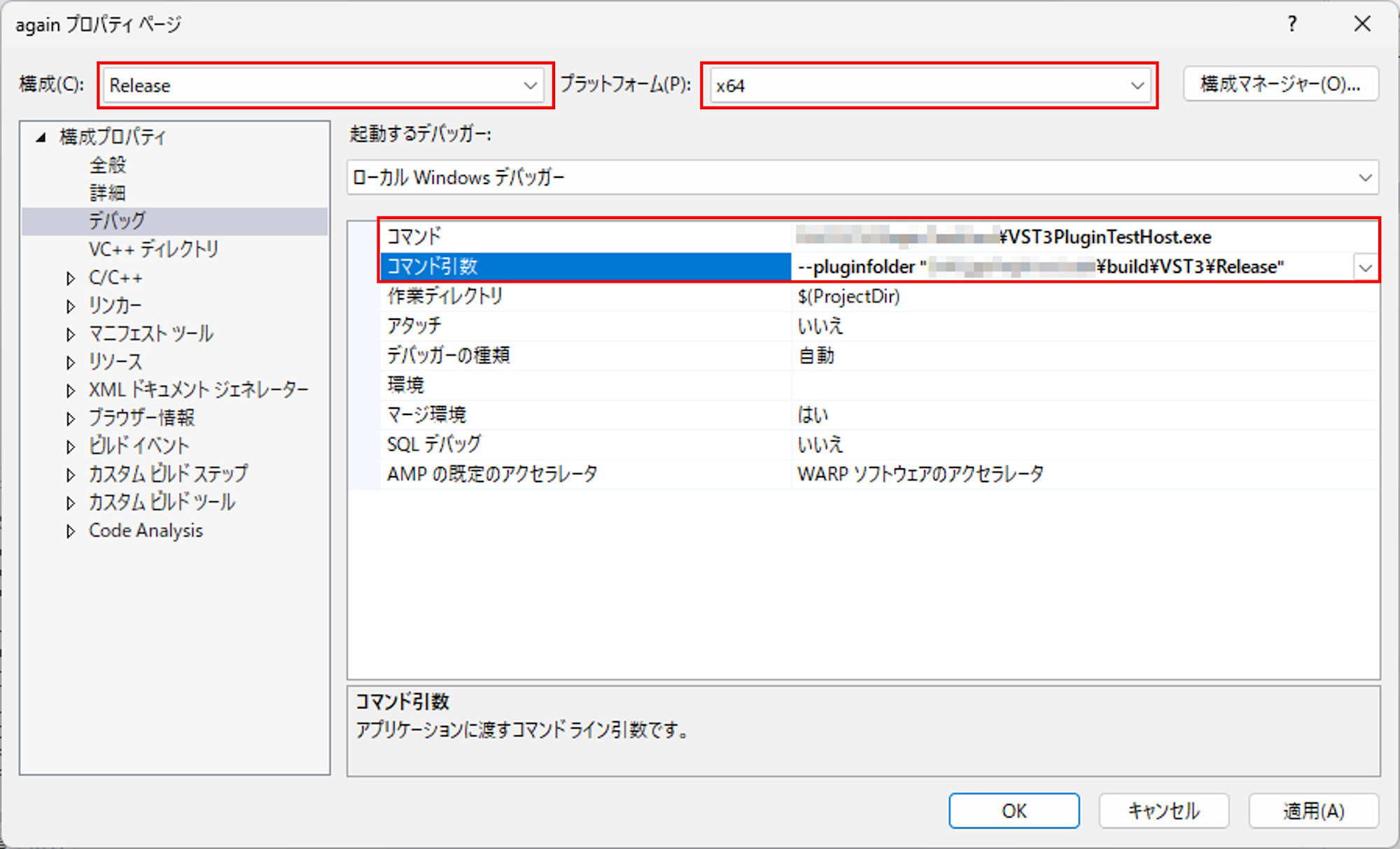
- Command:
-
Close the properties screen with OK, set the configuration to
Releasex64, and pressLocal Windows Debuggerto launch VST3PluginTestHost.
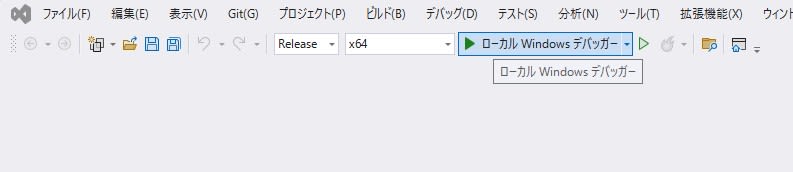
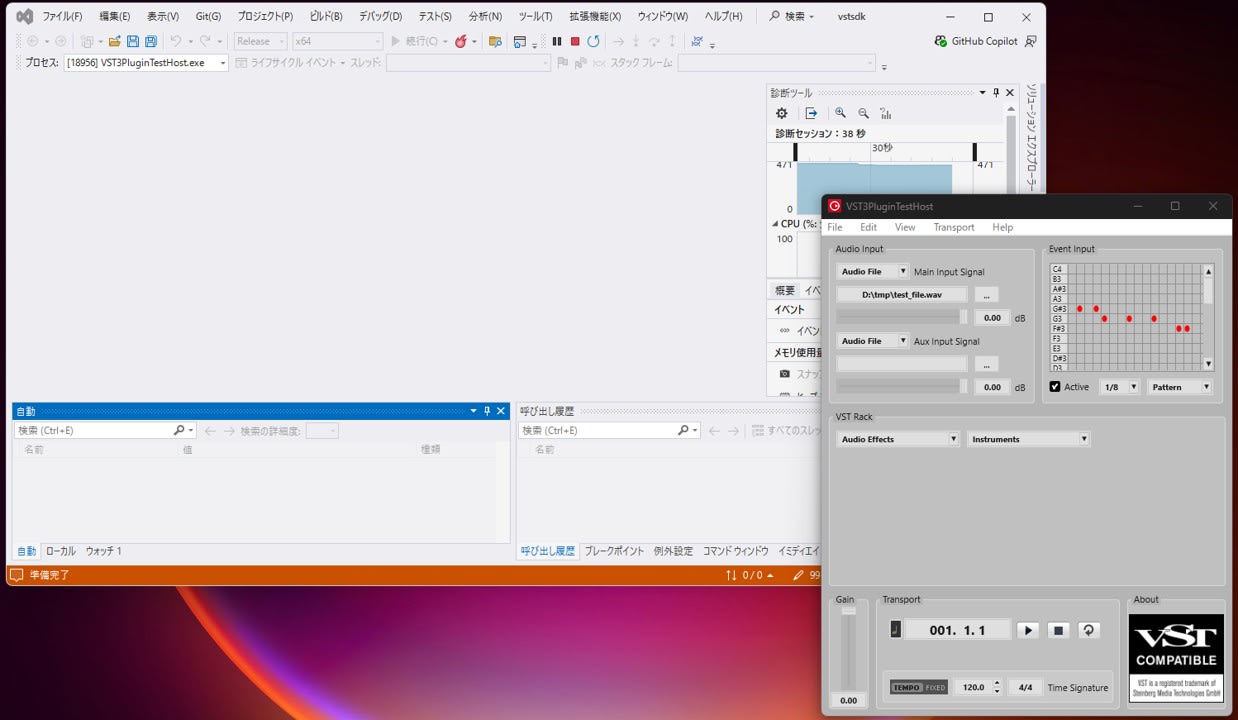
-
When loading AGain in VST3PluginTestHost, AGain's UI will be displayed.
Find and Run validator with AGain
Let's try running the validator manually. In this environment, the validator is output to build\bin\Release\validator.exe.
In Git Bash or PowerShell, run the following to check the help:
cd D:\CppProj\vst3sdk\build
./bin/Release/validator.exe -h
The result of -h is as follows. It shows available options and that it takes a vst3module as an argument:
VST 3.8.0 Plug-in Validator:
-help | Print help
-version | Print version
-l | Use local instance per test
-suite | [name] Only run a special test suite
-e | Run extensive tests [may take a long time]
-q | Only print errors
-cid | Only test processor with specified class ID
-test-component | [path] Path to an additional component which includes custom tests
-list | Show all installed Plug-Ins
-selftest | Run a selftest
-snapshots | List snapshots from all installed Plug-Ins
Usage: vstvalidator [options] vst3module
Now, let's run it with AGain specified. The validator takes the path to the .vst3 folder:
./bin/Release/validator.exe ./VST3/Release/again.vst3
At the beginning of the execution results, it loads the module, checks the bundle structure, and enumerates class information:
* Loading module...
./VST3/Release/again.vst3
* Check valid bundle structure...
* Scanning classes...
Factory Info:
vendor = Steinberg Media Technologies
url = http://www.steinberg.net
email = mailto:info@steinberg.de
Class Info 0:
name = AGain VST3
category = Audio Module Class
subCategories = Fx
version = 3.8.0.0
sdkVersion = VST 3.8.0
cid = 84E8DE5F92554F5396FAE4133C935A18
In the middle, it also checks for the presence of snapshots (images that hosts use when displaying the plugin list):
* Checking snapshots...
Found snapshots for 'AGain VST3'
- ./VST3/Release/again.vst3/Contents/Resources/Snapshots/84E8DE5F92554F5396FAE4133C935A18_snapshot.png [1x]
- ./VST3/Release/again.vst3/Contents/Resources/Snapshots/84E8DE5F92554F5396FAE4133C935A18_snapshot_2.0x.png [2x]
Finally, the tests are executed, and in this environment, it completed with 94 tests passed, 0 tests failed:
-------------------------------------------------------------
Result: 94 tests passed, 0 tests failed
-------------------------------------------------------------
As you can see, the validator can load plugins and perform basic inspections with a single command. By incorporating it into CI, you can detect minimal inconsistencies at the PR stage.
Run on Windows and macOS with GitHub Actions
The CI strategy will be:
- Use
actions/checkoutto get the repository including submodules - Configure and build with CMake
- Run validator after the build
- Save validator logs as artifacts
.github/workflows/vst3sdk-again-validator.yml
Example of ./.github/workflows/vst3sdk-again-validator.yml:
name: vst3sdk-again-validator
on:
pull_request:
push:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
build-and-validate:
strategy:
fail-fast: false
matrix:
os: [ windows-2022, macos-14 ]
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
steps:
- name: Checkout (with submodules)
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
submodules: recursive
- name: Configure (Windows)
if: runner.os == 'Windows'
shell: pwsh
run: |
$ErrorActionPreference = "Stop"
cmake -S . -B build -G "Visual Studio 17 2022" -A x64 -DSMTG_CREATE_PLUGIN_LINK=OFF
- name: Build (Windows, Release)
if: runner.os == 'Windows'
shell: pwsh
run: |
$ErrorActionPreference = "Stop"
cmake --build build --config Release
- name: Configure (macOS, Xcode)
if: runner.os == 'macOS'
shell: bash
run: |
set -euo pipefail
cmake -S . -B build -G Xcode -DSMTG_CREATE_PLUGIN_LINK=OFF \
-DCMAKE_XCODE_ATTRIBUTE_CODE_SIGNING_ALLOWED=NO \
-DCMAKE_XCODE_ATTRIBUTE_CODE_SIGNING_REQUIRED=NO
- name: Build (macOS, Release)
if: runner.os == 'macOS'
shell: bash
run: |
set -euo pipefail
cmake --build build --config Release --target validator again
- name: Run validator (Windows)
if: runner.os == 'Windows'
shell: pwsh
run: |
./scripts/ci/run-validator-windows.ps1 -BuildDir build
- name: Make scripts executable (macOS)
if: runner.os == 'macOS'
shell: bash
run: |
set -euo pipefail
chmod +x ./scripts/ci/run-validator-macos.sh
- name: Run validator (macOS)
if: runner.os == 'macOS'
shell: bash
run: |
./scripts/ci/run-validator-macos.sh build
- name: Upload validator logs
if: always()
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: validator-log-${{ matrix.os }}
path: |
validator-windows.log
validator-macos.log
- On macOS, use
Xcodeas the generator and disable Code Signing - For macOS build, specify necessary targets with
--target validator again - Move validator execution to scripts
- Upload logs as artifacts
scripts/ci/run-validator-windows.ps1
scripts/ci/run-validator-windows.ps1
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true)]
[string]$BuildDir
)
$ErrorActionPreference = "Stop"
$validatorPath = Join-Path $BuildDir "bin\Release\validator.exe"
if (-not (Test-Path $validatorPath)) {
$validator = Get-ChildItem -Path $BuildDir -Recurse -Filter "validator.exe" | Select-Object -First 1
if (-not $validator) { throw "validator.exe not found under $BuildDir" }
$validatorPath = $validator.FullName
}
$pluginPath = Join-Path $BuildDir "VST3\Release\again.vst3"
if (-not (Test-Path $pluginPath)) {
$plugin = Get-ChildItem -Path $BuildDir -Recurse -Filter "again.vst3" | Select-Object -First 1
if (-not $plugin) {
$plugin = Get-ChildItem -Path $BuildDir -Recurse -Filter "AGain.vst3" | Select-Object -First 1
}
if (-not $plugin) { throw "again.vst3 / AGain.vst3 not found under $BuildDir" }
$pluginPath = $plugin.FullName
}
& $validatorPath -h | Out-Null
& $validatorPath $pluginPath 2>&1 | Tee-Object -FilePath "validator-windows.log"
if ($LASTEXITCODE -ne 0) { exit $LASTEXITCODE }
scripts/ci/run-validator-macos.sh
scripts/ci/run-validator-macos.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -euo pipefail
BUILD_DIR="${1:?build dir is required}"
VALIDATOR="$(find "${BUILD_DIR}" -type f -name validator -perm -111 | grep '/Release/' | head -n 1 || true)"
if [ -z "${VALIDATOR}" ]; then
VALIDATOR="$(find "${BUILD_DIR}" -type f -name validator -perm -111 | head -n 1 || true)"
fi
PLUGIN="$(find "${BUILD_DIR}" -type d \( -name 'AGain.vst3' -o -name 'again.vst3' \) | grep '/Release/' | head -n 1 || true)"
if [ -z "${PLUGIN}" ]; then
PLUGIN="$(find "${BUILD_DIR}" -type d \( -name 'AGain.vst3' -o -name 'again.vst3' \) | head -n 1 || true)"
fi
echo "VALIDATOR=${VALIDATOR}"
echo "PLUGIN=${PLUGIN}"
test -n "${VALIDATOR}"
test -n "${PLUGIN}"
"${VALIDATOR}" -h >/dev/null || true
"${VALIDATOR}" "${PLUGIN}" 2>&1 | tee validator-macos.log
- Pass
.vst3to the validator argument (.vst3on macOS is a bundle)
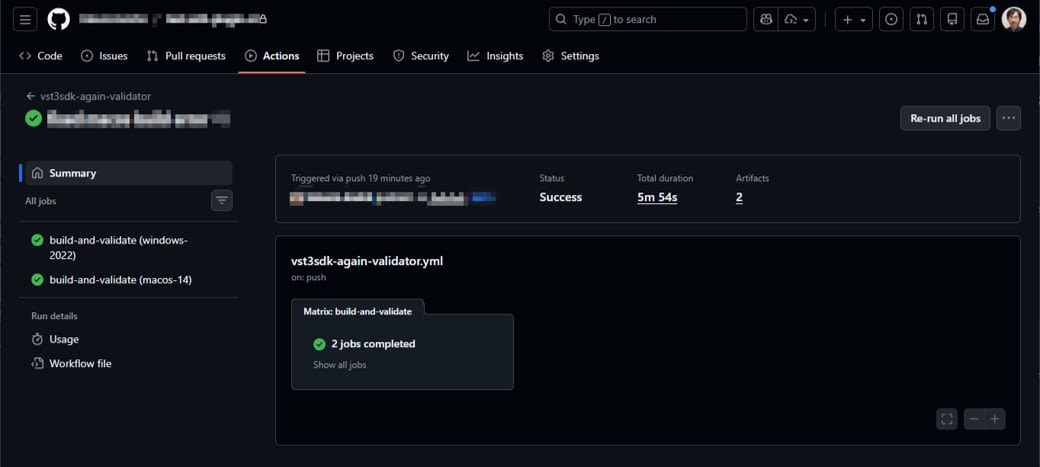
Check job execution
Push to git and confirm that the jobs are executed.
Consideration: How much can be automated?
The validator is a good fit as a first step for CI. However, it's difficult to discuss host compatibility with the validator alone. The Steinberg forum explains that VST3PluginTestHost has more speaker arrangement and parameter change tests than the validator. If you need more in-depth compatibility checks, third-party tools like pluginval can also be considered.
Summary
In this article, I introduced how to incorporate Steinberg's official validator into GitHub Actions to automate basic checks of VST3 plugins at the PR stage. Even if Windows distribution is assumed, running macOS builds and validator in CI can help detect environment-dependent issues earlier.