
Amazon ElastiCache for Valkey Practical Guide: From Building to Operating Real-Time Rankings for Games
This page has been translated by machine translation. View original
Introduction
In recent years, there has been an increasing demand for real-time responsiveness and scalability that traditional relational databases alone cannot handle in various services such as web applications and online games. In this context, Redis, an in-memory data store, has been widely used as a solution offering extremely high performance and flexible data structures. In 2024, following Redis OSS's license change, Valkey was born under open source community leadership, and AWS officially supports it. This article explains the latest implementation techniques using ElastiCache for Valkey and its effective use cases.
Target Audience
- Engineers interested in AWS and in-memory data stores
- Those interested in migrating from Redis to Valkey or the latest cloud configurations
- System administrators looking to enhance real-time functionality in games and web services
Expected Use Cases
- Displaying scores and rankings without delay even during high concurrent access
- Managing and referencing login sessions and temporary data at high speed
- Resolving database performance bottlenecks and improving overall response times
What is ElastiCache for Valkey
Since 2024, Amazon ElastiCache has officially supported "Valkey" in addition to the traditional "Redis OSS." Valkey is an open source in-memory data store compatible with Redis OSS 7.0, with the same APIs, command systems, and client libraries as Redis OSS. Valkey features continuous development by the open source community and a cost structure optimized for cloud operations, with AWS officially recommending Valkey as the future cornerstone of cloud in-memory data stores.
References:
- https://aws.amazon.com/jp/blogs/news/get-started-with-amazon-elasticache-for-valkey/
- https://valkey.io/
What is Redis
Redis is an in-memory NoSQL data store. By keeping all data in memory, it enables extremely fast data reading and writing. Unlike relational databases (e.g., MySQL or PostgreSQL) that primarily store data on disk, Redis uses volatile memory, allowing for systems with very low latency. Redis supports various data structures such as lists, sets, and sorted sets (ZSET) in addition to being a key-value data store, and this flexibility allows it to meet the requirements of various applications.
Reference:
Redis is widely used in the following use cases due to its speed and temporary data management capabilities:
-
Session Management
Used to store user login status and temporary application data, enabling support for large-scale concurrent connections. -
Caching
Temporarily stores frequently accessed database data in Redis to improve the overall system response. -
Ranking Aggregation
In scenarios requiring real-time functionality, such as games, player score rankings can be efficiently managed using sorted sets (ZSET). -
Rate Limiting (Access Control)
Used to count the number of accesses within a certain time period to prevent unauthorized access and excessive requests. -
Pub/Sub (Message Delivery)
Can also be used in systems that notify messages between servers in real-time.
In game development, Redis is adopted in the following scenarios:
-
Real-time Ranking Aggregation and Display
- For purposes such as score registration by numerous players and immediate ranking display, Redis is more effective than relational databases due to its speed.
-
Player Session Retention
- Used to manage each player's login status and temporary in-game information. It maintains high performance even with massive concurrent connections.
-
Cheat Prevention and Access Restrictions
- Used to measure the number of actions within a certain time period to detect and control fraudulent behavior and excessive requests.
Redis thus demonstrates its strengths in scenarios demanding "fast processing" and "temporary data" management. Meanwhile, for data requiring permanence, such as user accounts and payment history, it's common to use a configuration that combines Redis with relational databases.
Setting Up AWS ElastiCache for Valkey
Below are the standard steps to set up an ElastiCache for Valkey environment using the AWS Management Console.
Prerequisites
- Possession of an AWS account
Cluster Creation Procedure
- Open the Amazon ElastiCache console
- Create a Valkey cache
- Mode: Valkey
- Deployment option: Serverless
- Creation method: New cache
- Name: As desired
- Description: As desired
- Engine version: Default or select according to requirements
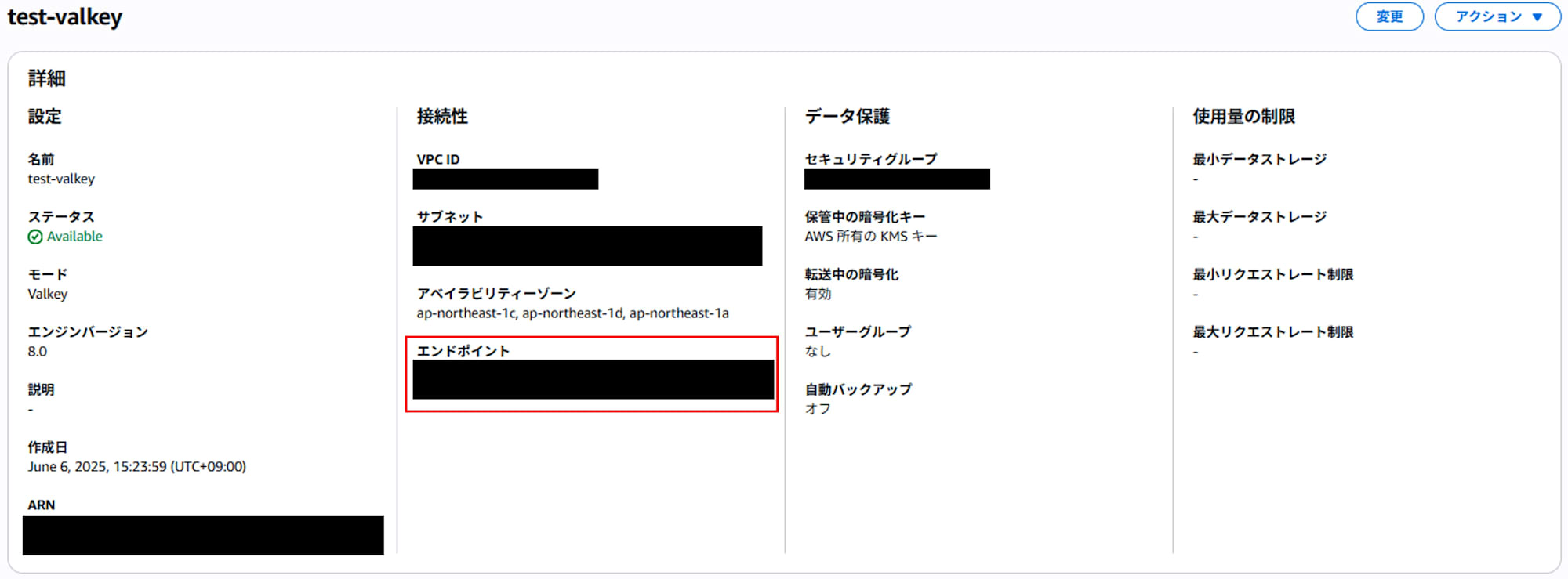
- When the cluster is created, an "Endpoint" will be displayed. You can connect to this endpoint (e.g.,
xxxxx.abcdefg.ng.0001.apne1.cache.amazonaws.com:6379) from your application or the Valkey CLI.
Verification: Connection Example from Valkey CLI
Here's an example of connecting from the Valkey CLI on a server (such as AWS EC2) that's in the same VPC as your Valkey cache.
EC2 Instance Connection
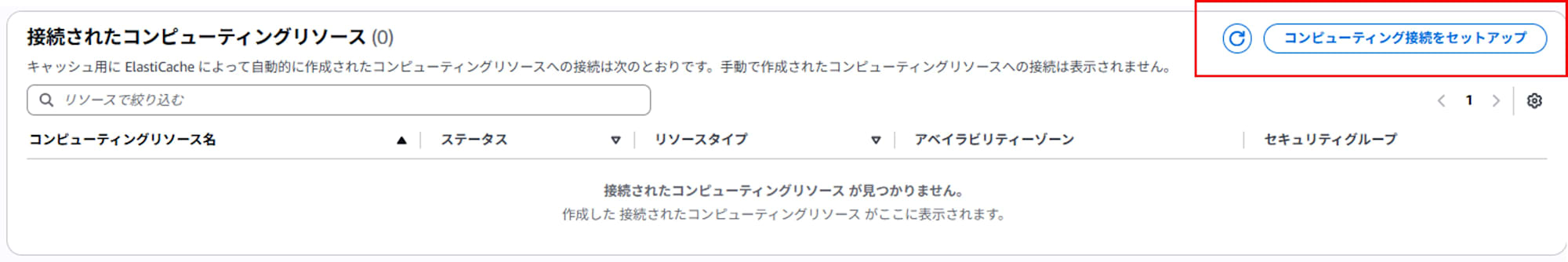
Click on "Connected compute resources > Set up compute connection" on the details page of the Valkey cache you created.
If you haven't created an EC2 instance yet, create one.
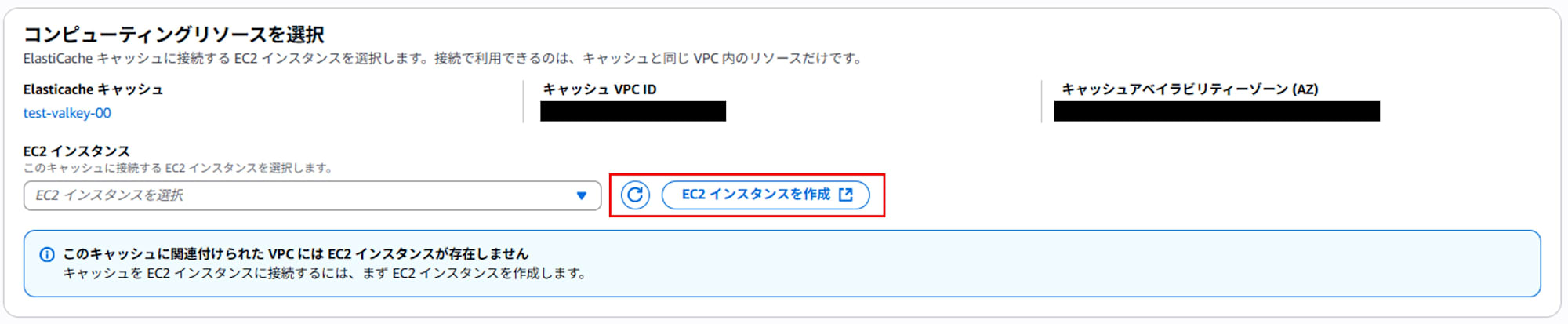
Configure the instance to connect to and click "Setup."
Installing the Valkey CLI
Connect to the instance.
ssh -i PATH_TO_PEM_KEY ec2-user@PUBLIC_IP
Install valkey.
sudo yum install valkey
Reference:
Connecting to the Valkey Cache
Connect using the following command. Replace YOUR_END_POINT with your Valkey cache endpoint. (Remove the :6379 from the end of the endpoint and specify it with the -p option.)
valkey-cli --tls -h YOUR_END_POINT -p 6379
Type the ping command to confirm that pong is returned.
> ping
PONG
Reference:
Basic Valkey Operations
Here, we explain basic command operations using the Valkey CLI. Since Valkey is compatible with Redis OSS 7.0, it can be used with the same interface as traditional Redis commands.
Saving and Retrieving String Data
The most basic data operations are SET and GET.
For example, here's how to save the value hello to the key sample_key and retrieve it:
> SET sample_key hello
OK
> GET sample_key
"hello"
Saving Data with Expiration
For cache or temporary data management purposes, you can set an expiration time (TTL) for data.
Specify the number of seconds with the EX option.
> SET session_token_123 abcdefg EX 300
OK
> TTL session_token_123
(integer) 295
Managing Score Rankings (Using ZSET)
In game development, Valkey's "sorted set (ZSET)" type is useful when you want to efficiently implement real-time rankings.
Registering Scores
As an example, we'll record each player's score in a ranking called game_leaderboard.
> ZADD game_leaderboard 1200 playerA
(integer) 1
> ZADD game_leaderboard 990 playerB
(integer) 1
> ZADD game_leaderboard 1500 playerC
(integer) 1
Retrieving Top N Entries
To get the top 3 players in descending order of score, use ZREVRANGE.
> ZREVRANGE game_leaderboard 0 2 WITHSCORES
1) "playerC"
2) "1500"
3) "playerA"
4) "1200"
5) "playerB"
6) "990"
Getting a Specific Player's Rank
To find the rank of a specific player, use ZREVRANK.
> ZREVRANK game_leaderboard playerB
(integer) 2
Incrementing Scores
To add to a specific player's score, use ZINCRBY.
> ZINCRBY game_leaderboard 200 playerB
"1190"
Supplement 1: Other Frequently Used Valkey Commands
-
Getting a List of Keys (SCAN)
> SCAN 0 -
Deleting All Data (For Development Use Only: FLUSHALL)
> FLUSHALL
Supplement 2: Differences Between Redis and Valkey and Points to Consider When Migrating
When considering migration to ElastiCache for Valkey, many people first wonder "Will existing Redis systems work as-is with Valkey?" and "What should we be aware of regarding cost, licensing, and version management?"
Existing operational systems using Redis OSS up to 7.x can be migrated to Valkey "almost as-is" safely and cost-efficiently. Valkey is recommended if you prioritize avoiding legal risks in commercial and cloud services or long-term support continuity. However, if you use "new features in Redis v8 or later" or "license conditions (such as AGPLv3)," additional legal and technical considerations are necessary. Please also note that on ElastiCache, building a new cluster + explicit data migration is required.
API and Command Compatibility
Valkey maintains high compatibility with the API and commands of Redis OSS up to 7.2.4 (final BSD licensed version). If your application operates with the standard command set up to Redis 7.2.x, it will basically work the same when migrated to Valkey. Major client libraries (redis-py, Jedis, node-redis, etc.) can also be used as is.
Performance and Operational Costs
-
Cost Aspect
ElastiCache for Valkey can reduce costs by up to approximately 33% compared to equivalent Redis OSS specifications (as of June 2024/AWS published value). Especially by choosing a serverless configuration, cost optimization according to usage becomes easier. -
Performance Aspect
Valkey achieves performance and availability equivalent to Redis 7.2 series. Support from major cloud vendors is also extensive, so there are few concerns in terms of actual operation.
License and Commercial Use Perspective
-
Redis OSS (v8 and later)
From May 2025, Redis OSS uses a "tri-license" approach with AGPLv3 (OSI approved), SSPLv1, and RSALv2. AGPLv3 is a powerful copyleft license that requires source disclosure even when providing services over a network, requiring legal consideration for commercial SaaS and cloud providers. The latest features of Redis v8 and later (e.g., Vector Sets) are not available in Valkey. -
Valkey
Maintains the BSD 3-Clause (permissive license), making it available for commercial and cloud services without license restrictions. Major cloud providers including AWS, Google Cloud, and Oracle Cloud officially support Valkey.
Reference:
Summary
Valkey (and Redis OSS) demonstrates high effectiveness as an ultra-fast in-memory data store not only for session management and caching purposes but also in scenarios demanding real-time responsiveness and scalability, such as game rankings. By using AWS ElastiCache for Valkey with a serverless configuration, you can significantly reduce operational management burdens while addressing diverse use cases by leveraging API and command compatibility.
References
- https://aws.amazon.com/jp/elasticache/
- https://aws.amazon.com/jp/blogs/news/get-started-with-amazon-elasticache-for-valkey/
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonElastiCache/latest/dg/VersionManagement.HowTo.html#VersionManagement.HowTo.cross-engine-upgrade
- https://valkey.io/
- https://valkey.io/topics/installation/
- https://valkey.io/topics/cli/
- https://redis.io/
- https://redis.io/blog/agplv3/
- https://dev.classmethod.jp/articles/amazon-elasticache-for-redis-amazon-elasticache-for-valkey/


