The story of how structuring game specifications in Contentful made it easy to reuse for things like quiz bots
This page has been translated by machine translation. View original
Introduction
This article is the 9th blog in the Game Development Accelerated by SaaS - Advent Calendar 2025.
In this article, I'll introduce a demo of a small web application that automatically generates quizzes from game "stage" specifications by combining Contentful REST API and Next.js. By structuring game specifications on Contentful, you can quickly launch applications like quiz bots without adding much additional implementation.
What is Contentful
Contentful is a headless CMS service that manages content in JSON format and allows retrieval via REST API or GraphQL API. In this article, we'll use the Content Delivery API to query game stage information and convert it into quiz data on the Next.js side.
Why Use Contentful
By maintaining game specifications as structured data on Contentful rather than just documents, it becomes easier to reuse for various peripheral tools, including quiz demo apps like this one. Also, by specifying query parameters such as content_type, fields.stageType, select, etc., the application side can efficiently retrieve only the necessary information without having to implement filtering logic.
Target Audience
- Those considering managing game specifications with CMS
- Those wanting to try Contentful for gaming industry use cases
- Those wanting to learn Contentful integration while building a light demo app with Next.js and TypeScript
Reference Information
Overall Structure
First, let's check the structure of the demo app we created.
-
Next.js App
- Calls
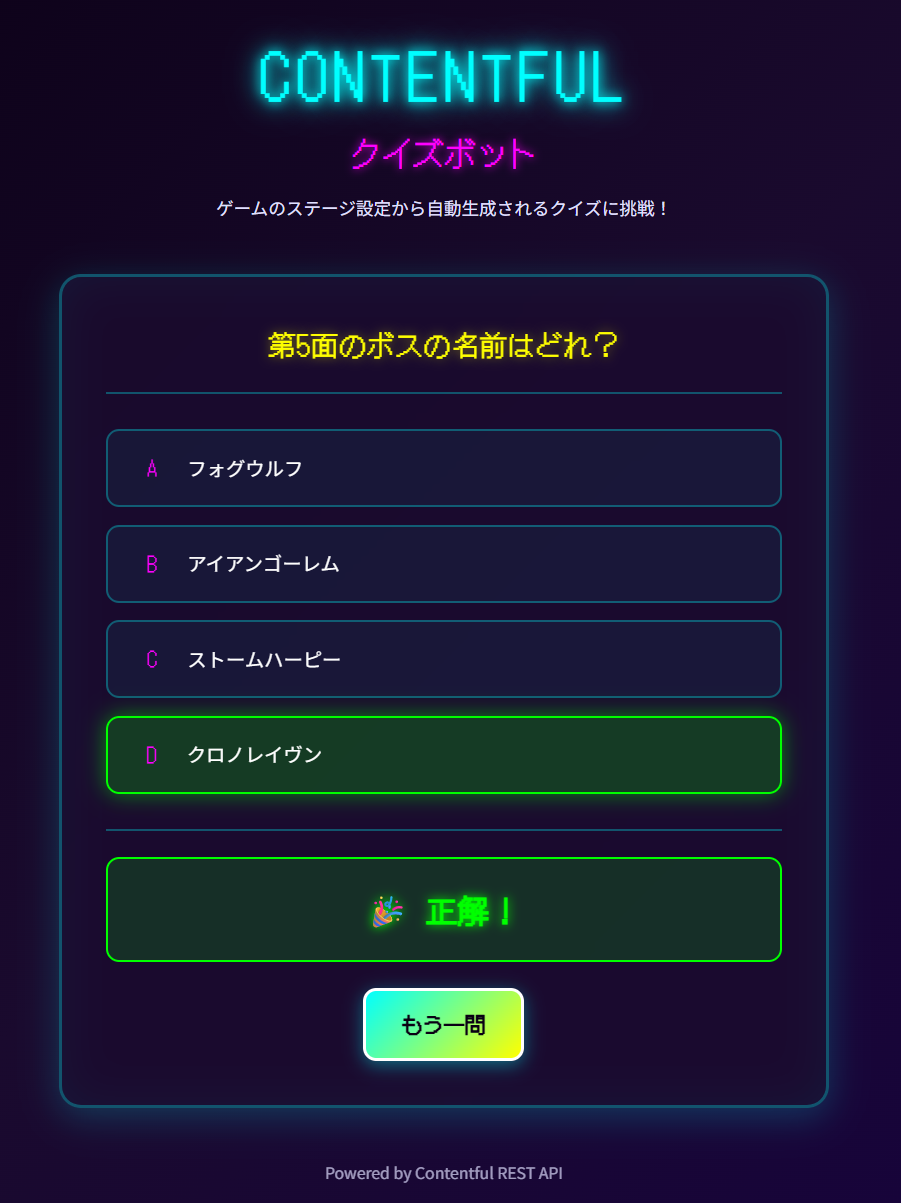
/api/quizto retrieve quizzes and displays the question text, four choices, and judgment results in the browser.
- Calls
-
Next.js API Route
- Fetches
Stageentries from Contentful REST API, assembles random quiz data for one question, and returns it as JSON.
- Fetches
-
Contentful
- Manages configuration information such as stage number, stage name, boss name, and stage type as a
StageContent Model. - Distinguishes between battle stages, town stages, etc. with
stageType, allowing only stages with bosses to be targeted for quizzes.
- Manages configuration information such as stage number, stage name, boss name, and stage type as a
Content Model Design
First, we'll structure the game's "stage" specifications as structured data on Contentful. We create a Content Model called Stage and register each game stage as an entry.
Stage Content Model
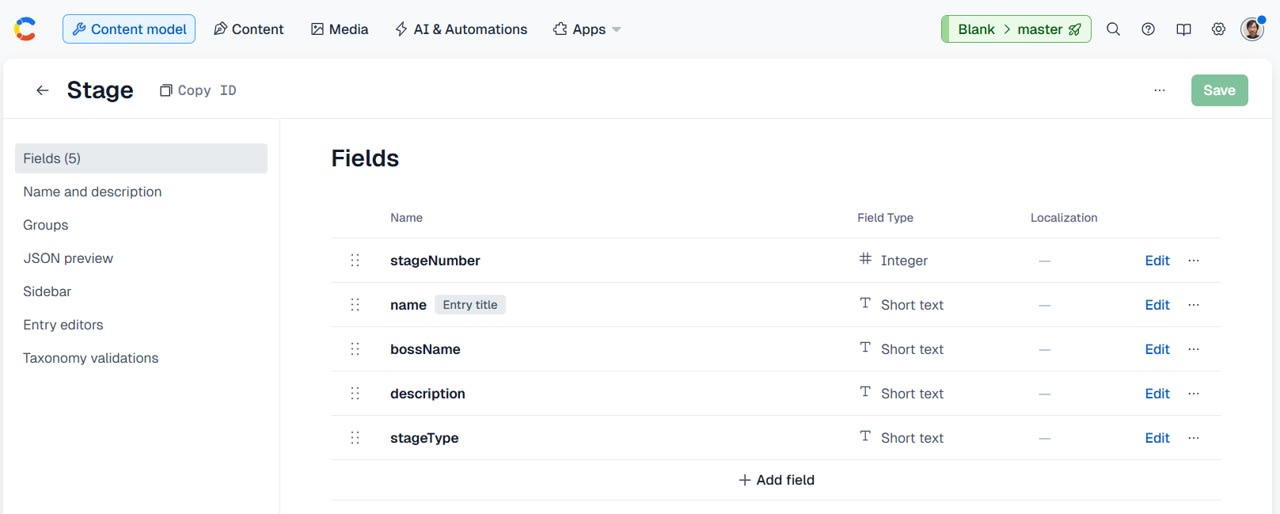
We defined the following fields for the Stage Content Model:
-
stageNumber(required)- Type: Integer
- Description: Stage number (1, 2, 3 ...)
-
name(required)- Type: Short text
- Description: Stage name
-
bossName- Type: Short text
- Description: Boss name
- Not required as some stages like tutorial stages or town areas don't have bosses.
-
description- Type: Long text
- Description: Stage description or world setting text
-
stageType(required)- Type: Short text
- Description: Code indicating stage type
For stageType, we're using Contentful's Predefined values to allow only the following three types:
battletownevent
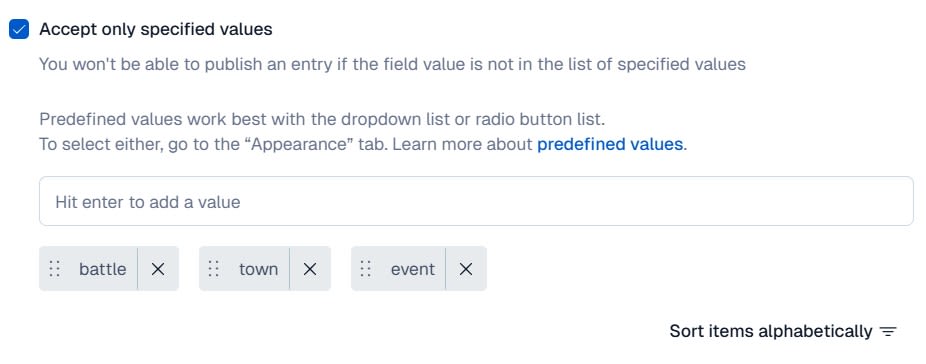
This prevents input variations while allowing the API to strictly filter only battle stages with conditions like fields.stageType=battle.
Setting the Appearance to Dropdown makes field input easier when creating models.
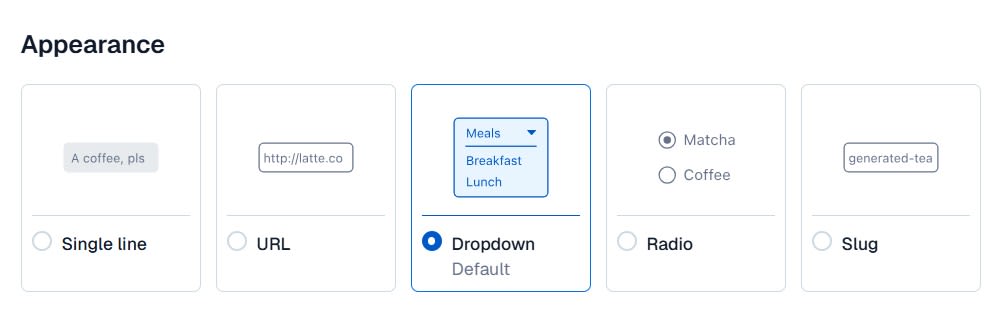
This is how it looks on the field input screen.

Quiz Target Definition
For this demo, we defined stages we want to use for quizzes as follows:
-
Must be a battle stage
stageTypeisbattle
-
Must have a boss
bossNameis set
By clearly expressing this rule in Contentful's data, the quiz generation logic on the app side can be kept simple as "retrieve only battle stages that have boss names."
Data Retrieval with REST API
We combine query parameters to efficiently retrieve only the information needed for quiz generation.
Query to Retrieve Only Battle Stages
For quizzes, we only need battle stage entries that have bosses. Therefore, we include the following conditions in our REST API calls:
content_type=stage- Targets only the
StageContent Model.
- Targets only the
fields.stageType=battle- Retrieves only battle stages.
fields.bossName[exists]=true- Targets only entries where
bossNameis set.
- Targets only entries where
select=...- Selects only fields needed for quizzes, such as
stageNumber,name,bossName,stageType.
- Selects only fields needed for quizzes, such as
Sample Code
Excerpt from src/lib/contentful.ts
import type { ContentfulResponse, StageEntry } from "@/types/contentful";
function getContentfulConfig() {
const spaceId = process.env.CONTENTFUL_SPACE_ID || "vw67dgbqxobj";
const environmentId = process.env.CONTENTFUL_ENVIRONMENT_ID || "master";
const accessToken = process.env.CONTENTFUL_CDA_TOKEN;
if (!accessToken) {
throw new Error("CONTENTFUL_CDA_TOKEN is not set");
}
return { spaceId, environmentId, accessToken };
}
export async function getBattleStages(): Promise<StageEntry[]> {
const { spaceId, environmentId, accessToken } = getContentfulConfig();
const params = new URLSearchParams({
content_type: "stage",
"fields.stageType": "battle",
"fields.bossName[exists]": "true",
select:
"sys.id,fields.stageNumber,fields.name,fields.bossName,fields.stageType",
});
const url = `https://cdn.contentful.com/spaces/${spaceId}/environments/${environmentId}/entries?${params}`;
const response = await fetch(url, {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(
`Failed to fetch stages from Contentful: ${response.status} ${response.statusText}`,
);
}
const data: ContentfulResponse<StageEntry["fields"]> = await response.json();
return data.items;
}
Specifying REST API filtering like this keeps the data handled by the application small. A major advantage of Contentful in this demo is that Contentful's content model and query parameters allow you to straightforwardly express requirements like "I only want stages that meet this condition."
Quiz API and Frontend Implementation
Quiz Generation API Route
The API for quiz generation is implemented at /api/quiz. The process flow is as follows:
- Retrieve a list of
Stageentries with the conditions mentioned earlier. - Randomly select one from the array and make that stage the current question.
- Extract
bossNamefrom other stages and randomly select a few as incorrect answer candidates. - Shuffle correct and incorrect answers together to calculate the choices array and the correct answer index.
- Generate a Japanese question like "Which is the boss name of Stage X" using
stageNumberand return as JSON.
Sample Code
Excerpt from src/app/api/quiz/route.ts
import { NextResponse } from "next/server";
import { getBattleStages } from "@/lib/contentful";
import type { Quiz } from "@/types/quiz";
function getRandomElement<T>(array: T[]): T {
return array[Math.floor(Math.random() * array.length)];
}
function shuffle<T>(array: T[]): T[] {
const shuffled = [...array];
for (let i = shuffled.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
const j = Math.floor(Math.random() * (i + 1));
[shuffled[i], shuffled[j]] = [shuffled[j], shuffled[i]];
}
return shuffled;
}
export async function GET() {
const stages = await getBattleStages();
if (stages.length < 3) {
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: "クイズを生成するには最低3つのバトルステージが必要です" },
{ status: 400 },
);
}
// Randomly select one stage for the correct answer
const correctStage = getRandomElement(stages);
const correctBossName = correctStage.fields.bossName!;
const stageNumber = correctStage.fields.stageNumber;
// Collect boss names for incorrect answers
const otherStages = stages.filter(
(stage) => stage.sys.id !== correctStage.sys.id,
);
const wrongChoices = shuffle(otherStages)
.slice(0, 3)
.map((stage) => stage.fields.bossName!);
const choices = shuffle([correctBossName, ...wrongChoices]);
const answerIndex = choices.indexOf(correctBossName);
const quiz: Quiz = {
stageNumber,
questionText: `第${stageNumber}面のボスの名前はどれ`,
choices,
answerIndex,
};
return NextResponse.json(quiz);
}
With this setup, the frontend only needs to call /api/quiz to retrieve quiz data for one question.
Quiz Screen Composition
The frontend is implemented on the top page of the Next.js App Router. The screen contains the following elements:
- State before quiz generation
- "Generate quiz" button

-
State during quiz
- Question text
- Four choices
- Answer button
-
State after answering
- Message indicating whether the answer is correct
- "One more question" button
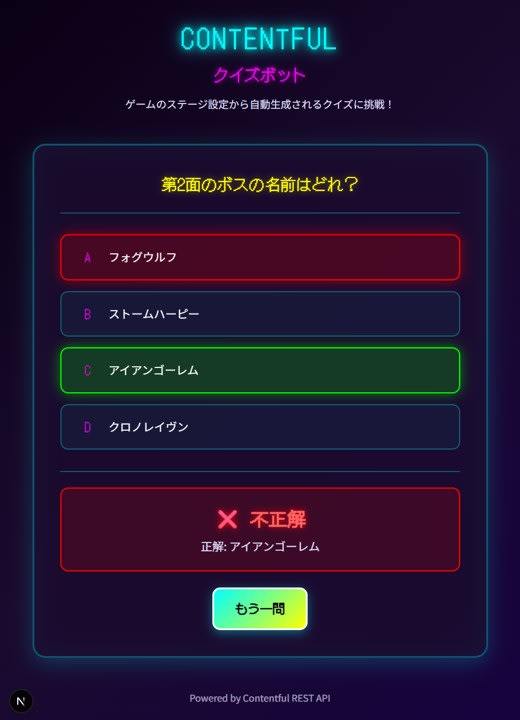
For state management, we use React hooks to switch between three states: quiz not generated, quiz displayed, and answered.
Sample Code
Excerpt from src/app/page.tsx
"use client";
import { useState } from "react";
import type { Quiz } from "@/types/quiz";
type GameState = "idle" | "playing" | "answered";
export default function Home() {
const [quiz, setQuiz] = useState<Quiz | null>(null);
const [selectedChoice, setSelectedChoice] = useState<number | null>(null);
const [gameState, setGameState] = useState<GameState>("idle");
const fetchQuiz = async () => {
const response = await fetch("/api/quiz");
if (!response.ok) {
// See implementation example for error handling
return;
}
const data: Quiz = await response.json();
setQuiz(data);
setSelectedChoice(null);
setGameState("playing");
};
const handleSubmit = () => {
if (selectedChoice === null) return;
setGameState("answered");
};
const isCorrect =
gameState === "answered" &&
quiz &&
selectedChoice !== null &&
selectedChoice === quiz.answerIndex;
return (
<main>
<button onClick={fetchQuiz} disabled={gameState === "playing"}>
クイズを出題
</button>
{quiz && (
<>
<p>{quiz.questionText}</p>
<ul>
{quiz.choices.map((choice, index) => (
<li key={choice}>
<label>
<input
type="radio"
name="choice"
value={index}
checked={selectedChoice === index}
onChange={() => setSelectedChoice(index)}
/>
{choice}
</label>
</li>
))}
</ul>
<button onClick={handleSubmit}>回答する</button>
{gameState === "answered" && (
<p>{isCorrect ? "正解です" : "残念、はずれです"}</p>
)}
</>
)}
</main>
);
}
The style uses CSS Modules for a simple panel-like appearance, but since the main focus of the demo app is the flow of converting Contentful data into quizzes, the style explanation is kept to a minimum.
Verification and Consideration
Verification Process
- Create multiple
Stageentries from the Contentful management screen.- Enter
stageNumber,name, andstageType. - Set
bossNamefor battle stages you want to include in quizzes.

- Enter
- Run
npm devin the root of the Next.js project and access the top page from a browser. - Press the "Generate quiz" button and confirm that quizzes corresponding to the data on Contentful are displayed.

If you want to add stages, just create new Stage entries in Contentful to increase quiz variations. Changes to boss names or stage configurations work the same way, allowing you to update quiz content without rewriting code.
Benefits of Using Contentful
Let me summarize the points I felt were beneficial about using Contentful through this demo:
- By consolidating game setting materials in Contentful, they could be immediately reused in a different form as a quiz app.
- Designing fields like
stageTypeandbossNameallowed us to push the quiz target definition to the data side, keeping the app-side logic thin. - The REST API allows condition specification and field selection via query parameters, enabling efficient retrieval of only the information needed for quiz generation.
In game development environments, stage setting lists are often needed for specification reviews and balance adjustments. By centrally managing such information on Contentful, it can be easily extended not only to quiz demos like this one but also to internal confirmation tools and debug views.
Summary
In this article, I introduced a demo app that automatically generates multiple-choice quizzes from game "stage" specifications stored in Contentful using Next.js. By defining stage numbers, boss names, and stage types in Stage and extracting only battle stages with REST API query parameters, we were able to keep the quiz generation logic simple.
Putting game specifications on a headless CMS like Contentful makes it easier to add peripheral tools later, including quiz apps like this one.