I tried dbt-jobs-as-code which allows defining dbt Cloud jobs in yaml
I am Sagara.
dbt Cloud includes a standard feature called "jobs," which allows scheduled execution of dbt commands.
However, with the standard functionality, these jobs can only be defined through the GUI interface.
In this article, I'll share my experience trying out dbt-jobs-as-code, an open-source tool provided by dbt Labs that allows you to define dbt Cloud jobs using YAML.
dbt-jobs-as-code
To reiterate, dbt-jobs-as-code is an open-source tool provided by dbt Labs' official GitHub account that allows you to define dbt Cloud jobs using YAML.
Beyond simply defining jobs in YAML, you can also use Jinja templates to dynamically input project_id and environment_id, making it possible to apply a single job definition to both Staging and Production environments.
Difference from Terraform
Terraform is another method for defining dbt Cloud jobs as code.
Regarding how to distinguish between using Terraform and dbt-jobs-as-code, based on the official documentation and my own opinion, I believe the distinction is as follows:
- Terraform
- Purpose: Managing other dbt Cloud objects besides jobs, such as Environments and groups, as code
- Users: Those who manage infrastructure and the entire data platform layer
- Since Terraform development and execution requires an environment outside of dbt Cloud, it's used by people at a different layer than those who only use dbt Cloud
- dbt-jobs-as-code
- Purpose: Managing jobs as code by writing YAML within dbt Cloud
- Users: Those who develop within dbt Cloud and also configure jobs
- Once GitHub Actions is defined, jobs can be defined simply by writing YAML in the dbt Cloud IDE and merging to the main branch
Trying it out
I'll actually define a GitHub Action using dbt-jobs-as-code, write YAML from dbt Cloud, send a pull request, and define jobs through GitHub Actions.### Obtaining a dbt Cloud service token and registering it as a Secret in the repository
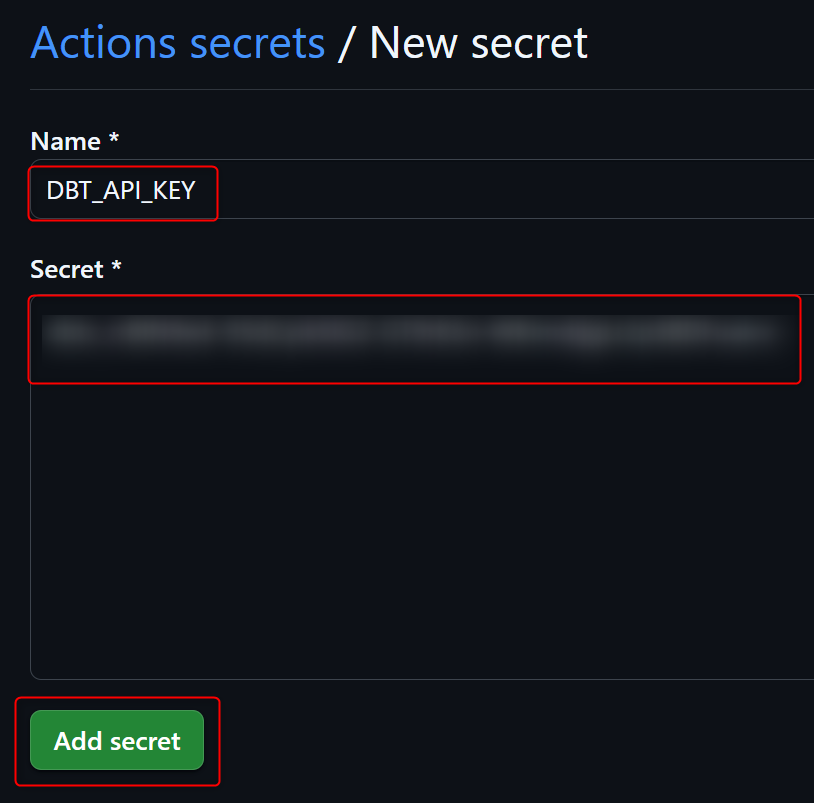
First, obtain a service token from dbt Cloud and register it as a Secret in the repository with the name DBT_API_KEY. (Although it's a service token, according to the tool's specifications, it needs to be registered as a Secret with the name DBT_API_KEY. For more details, please refer to this content.)
For the Permission set, having Job Admin for the target dbt project is sufficient.
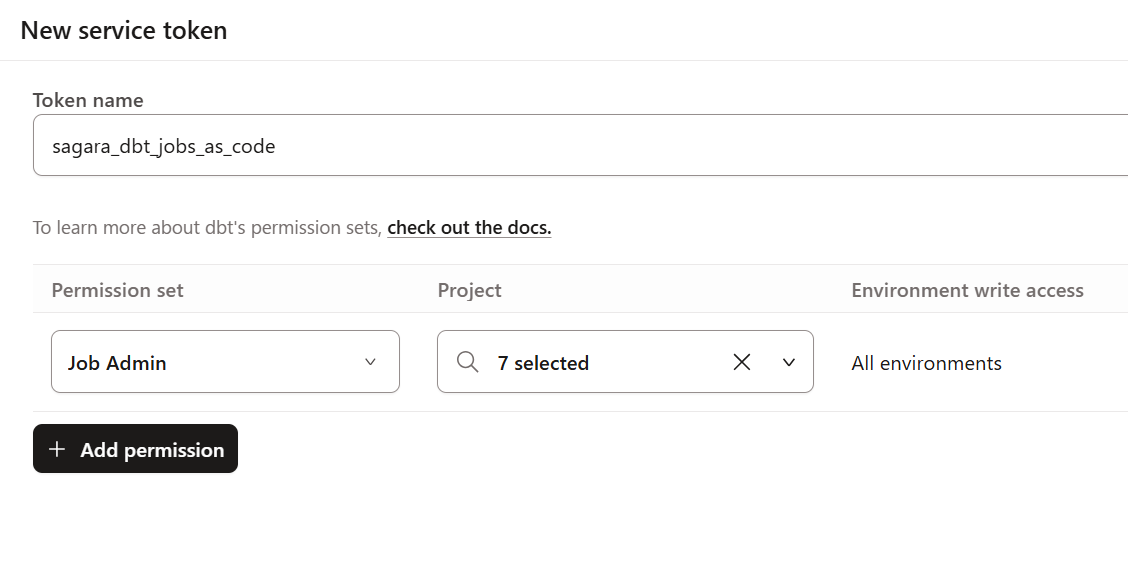
Once the token is displayed, make sure to save it.
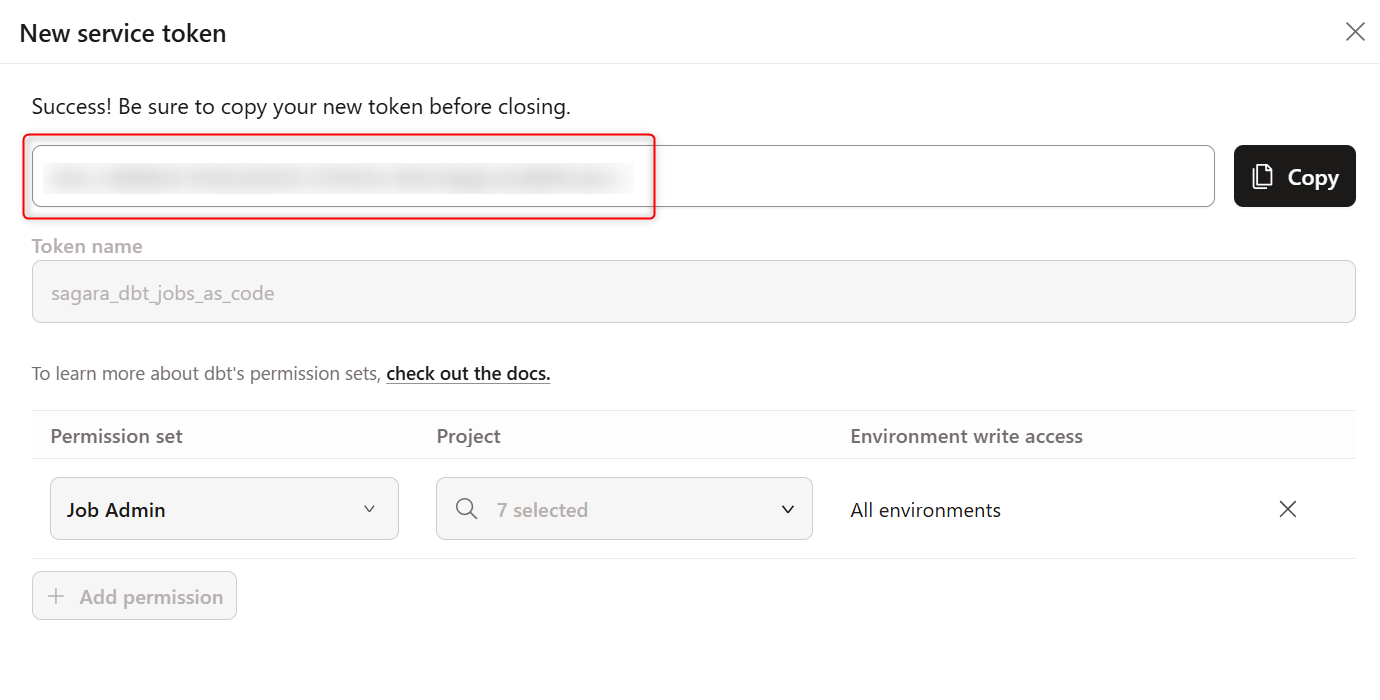
Next, register it as a Secret in the target GitHub repository.
 ### Defining GitHub Actions
### Defining GitHub Actions
Next, we'll define the GitHub Actions jobs. The following link also mentions various patterns for defining GitHub Actions jobs, which may be useful as a reference.
Open dbt Cloud and create two folders from the root hierarchy: .github/workflows.
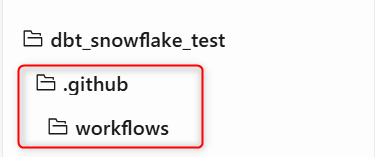
Create a file to define the GitHub Actions job. The file name can be anything, but we'll create it with the name dbt_jobs_cicd.yml.
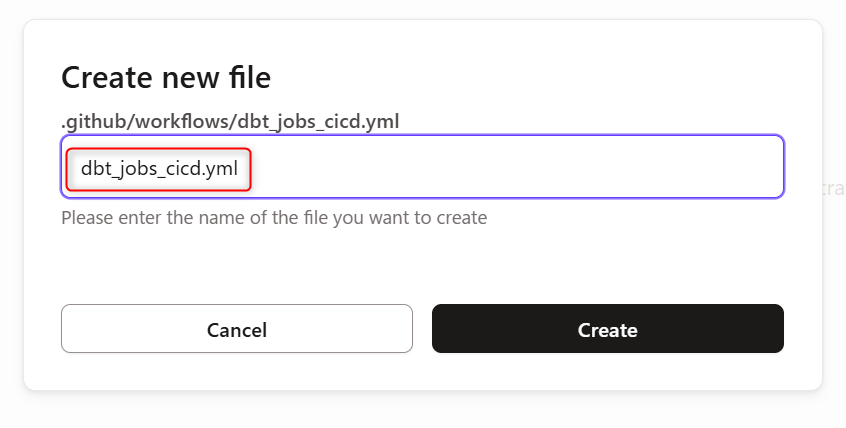
Define the file contents as follows:
name: CI/CD for dbt Cloud Jobs
on:
pull_request:
branches:
- main
paths:
- 'jobs/**' # Only execute when changes are made to the jobs directory
push:
branches:
- main
paths:
- 'jobs/**'
jobs:
dbt-jobs-as-code:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Check out repository code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: "3.12"
- name: Install dbt-jobs-as-code
run: pip install dbt-jobs-as-code
- name: Run 'plan' on Pull Request
if: github.event_name == 'pull_request'
run: dbt-jobs-as-code plan jobs/jobs.yml
env:
DBT_API_KEY: "${{ secrets.DBT_API_KEY }}"
- name: Run 'sync' on Merge to main
if: github.event_name == 'push' && github.ref == 'refs/heads/main'
run: dbt-jobs-as-code sync jobs/jobs.yml
env:
DBT_API_KEY: "${{ secrets.DBT_API_KEY }}"
After this definition, issue a pull request and merge it into the main branch once.## Define jobs in YAML and reflect in dbt Cloud
Next, we'll define jobs in YAML according to the dbt-jobs-as-code specifications.
First, create a jobs folder from the root directory.
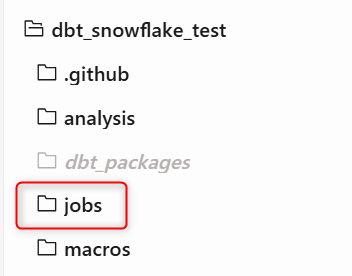
Then, create a file named jobs.yml inside the jobs folder. (The folder name and file name can be anything, but we're matching the reference in the GitHub Actions we defined earlier.)
The content will be as follows. Note that you should modify account_id, project_id, and environment_id to match your environment. (These IDs can be found in the URL when you open the target Environment.)
jobs:
# Unique job ID (arbitrary)
weekly_build_job:
# Replace with your dbt Cloud account information
account_id: 12345
project_id: 67890
environment_id: 11223
# Job name displayed in the dbt Cloud interface
name: "毎週月曜5時build"
# Commands to execute
execute_steps:
- "dbt build"
# Schedule settings
schedule:
# Specified in UTC. "Every Sunday at 20:00" = "Every Monday at 05:00 Japan time"
cron: "0 20 * * 0"
# Trigger settings
triggers:
github_webhook: false
git_provider_webhook: false
schedule: true # Enable scheduled execution
# Other settings
settings:
threads: 4
target_name: production
state: 1 # 1: active, 2: deleted
generate_docs: true
run_generate_sources: true
After this, commit and create a pull request.
This will execute dbt-jobs-as-code plan jobs/jobs.yml, which shows that running sync will create a new weekly_build_job.
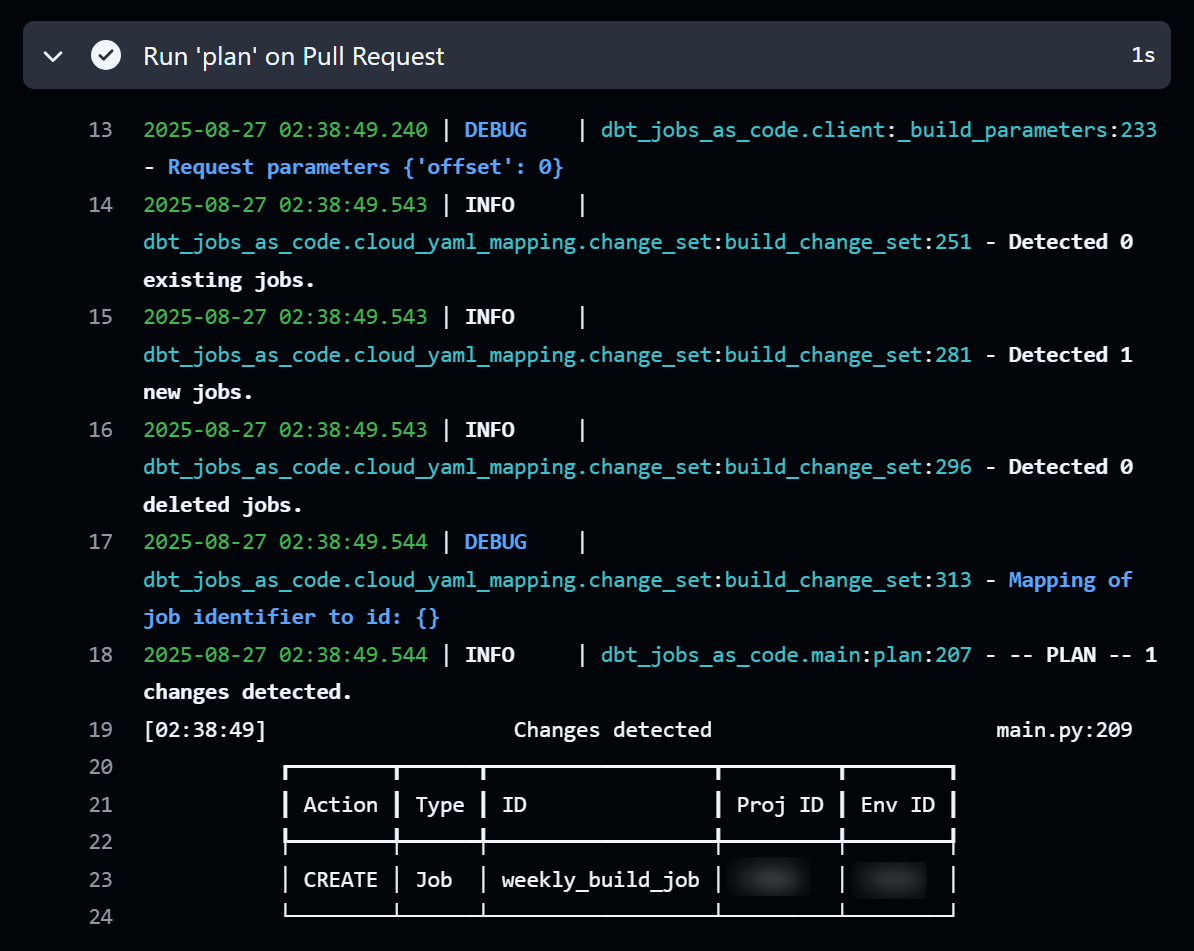
After merging, dbt-jobs-as-code sync jobs/jobs.yml will be executed.
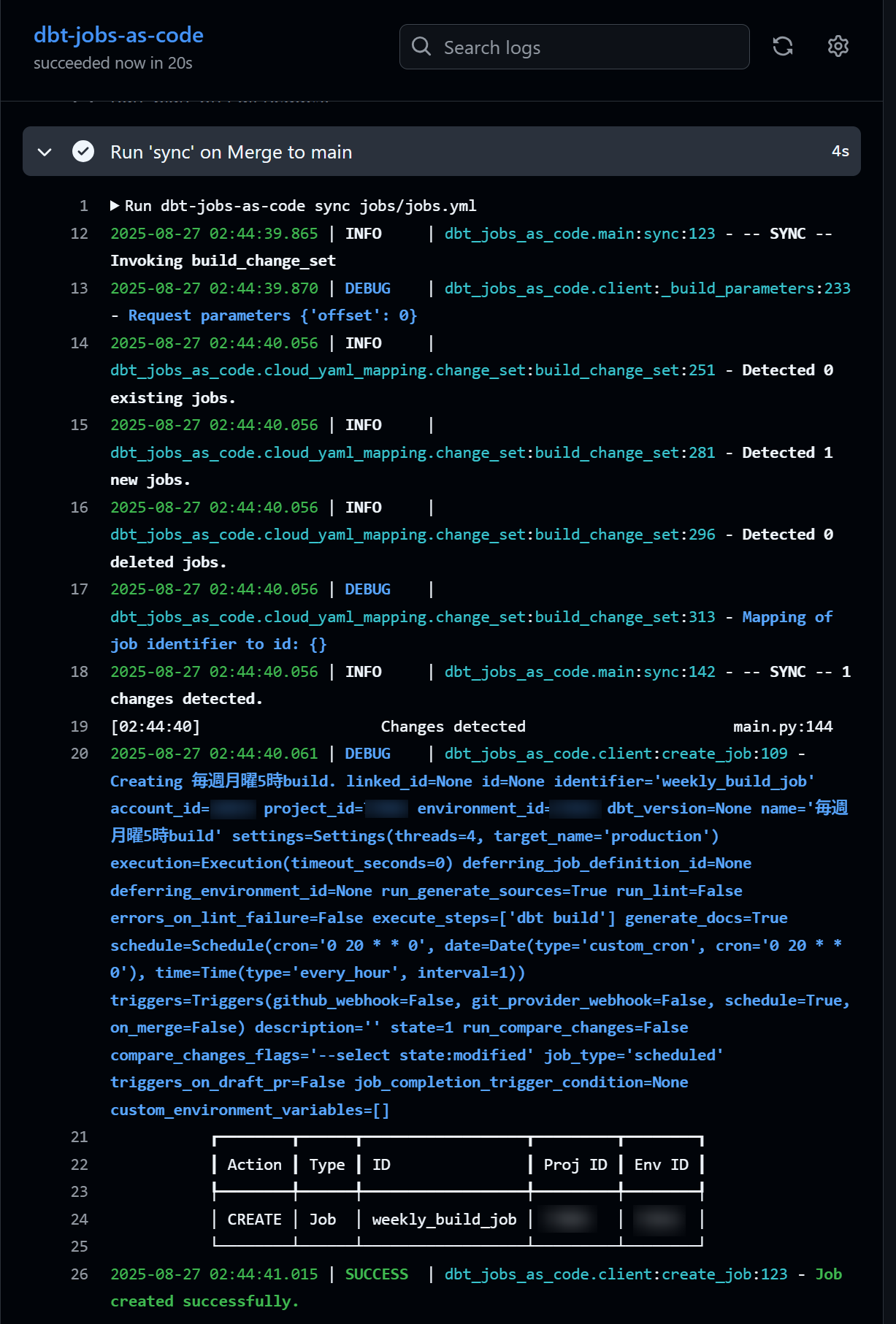
Checking the dbt Cloud job management screen, we can see that the job has been created with the specified settings! Note that the job name has the YAML job ID appended in [[ ]] at the end, as per the specification.
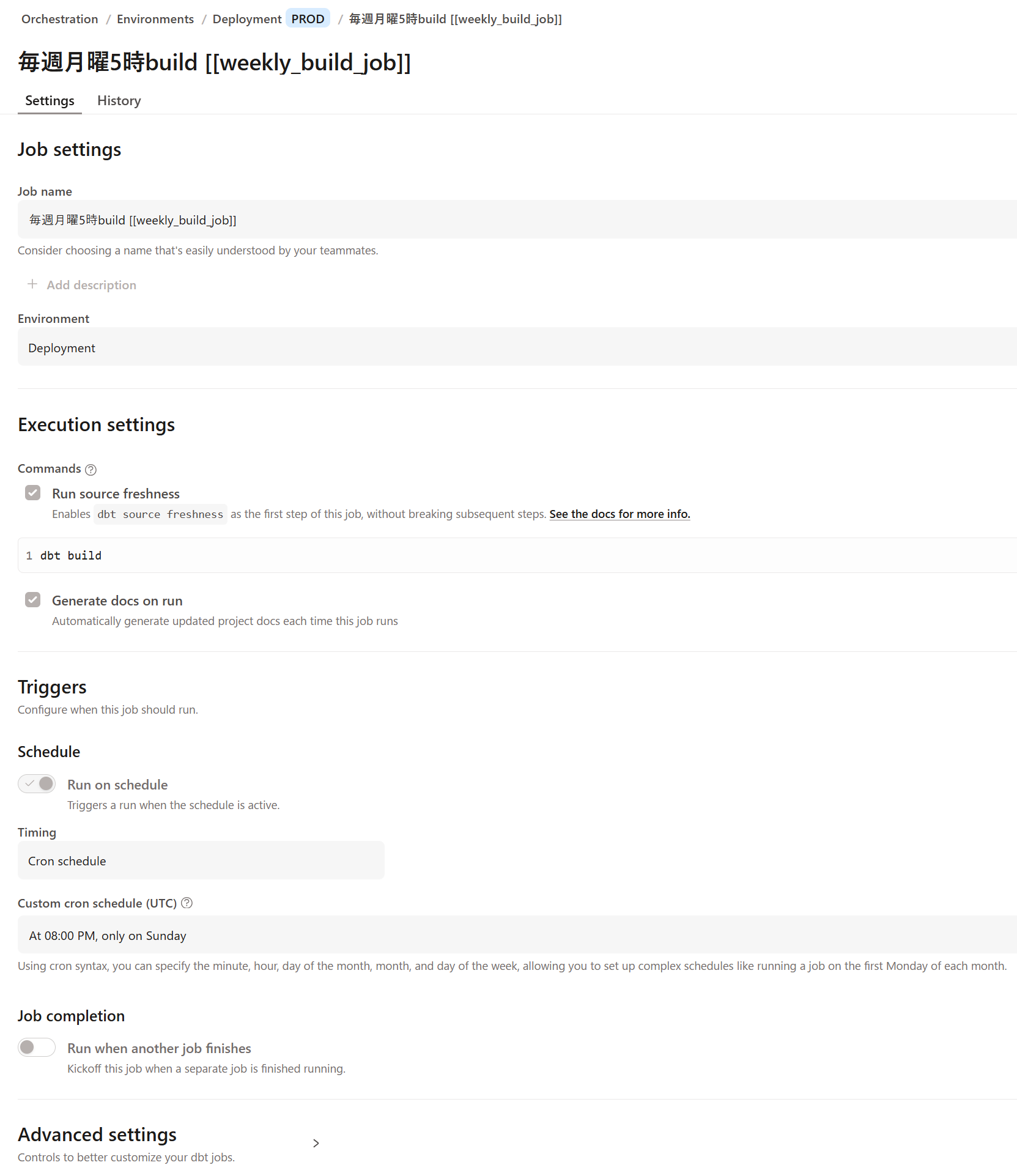
If you want to delete a job definition
Finally, let's look at how to remove a job definition.### Delete Job Definition
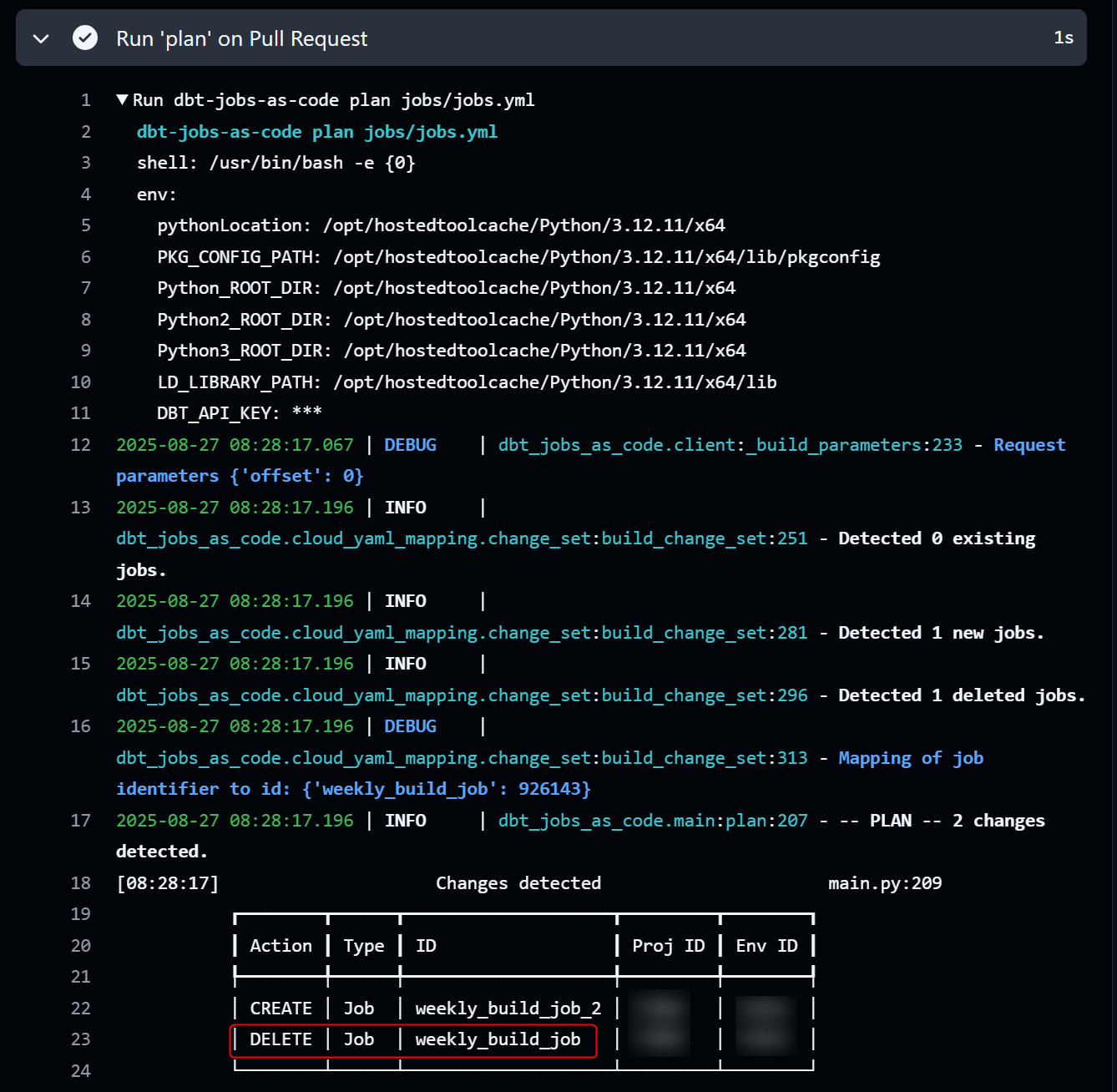
As shown in the figure below, it is possible to delete a job even if you have removed the definition of a job that has already been implemented in dbt Cloud. (However, as mentioned in "Notes" below, please be aware that you will get an error if there is not at least one job defined.)
- weekly_build_job: Already implemented in dbt Cloud, but definition is deleted (commented out)
- weekly_build_job_2: Newly created

When a pull request is issued in this state and dbt-jobs-as-code plan jobs/jobs.yml is executed, it will be displayed as shown in the figure below. You can see that weekly_build_job, which was removed from the yaml, is marked as DELETE.
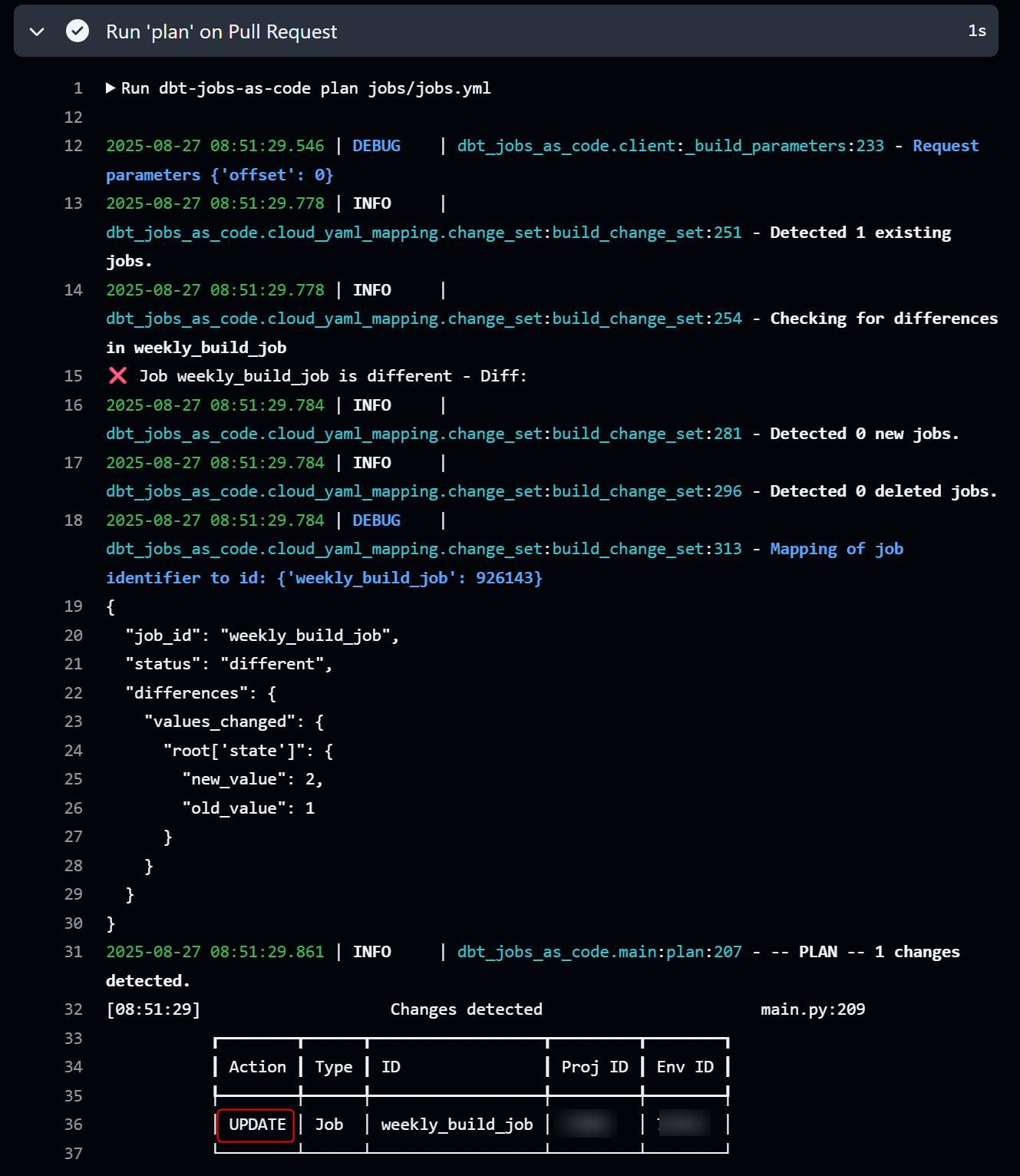
Set state: 2
In the job definition, there is a parameter called state, and by setting it to state: 2, the target job will be deleted according to the specification.

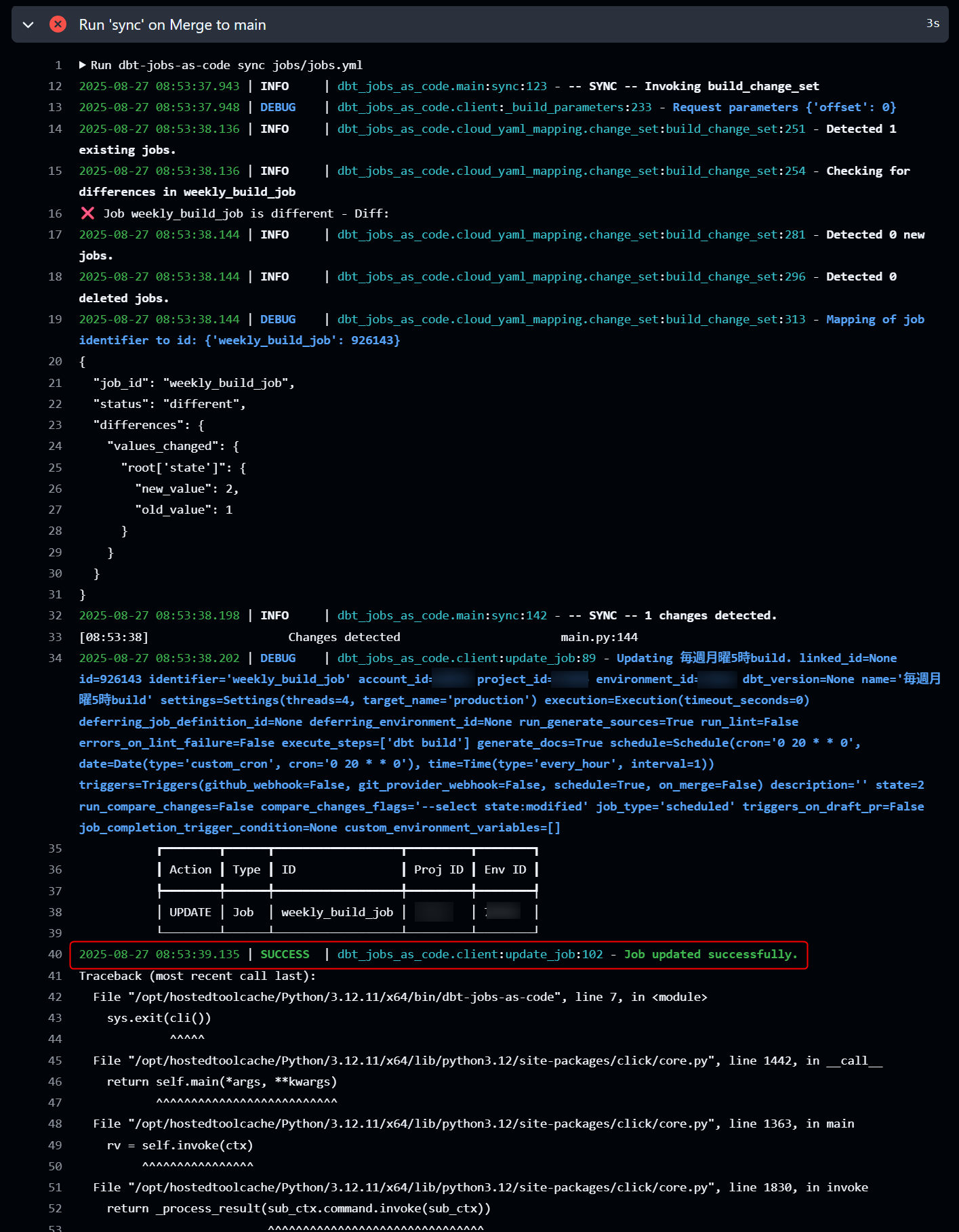
When a pull request is issued in this state and dbt-jobs-as-code plan jobs/jobs.yml is executed, it will be displayed as shown in the figure below. You can see that weekly_build_job is marked as UPDATE.
When the pull request is merged in this state and dbt-jobs-as-code sync jobs/jobs.yml is executed, it will be displayed as shown in the figure below. (In my case, it resulted in an error for some reason... I'm guessing it's because there are no job definitions left.)
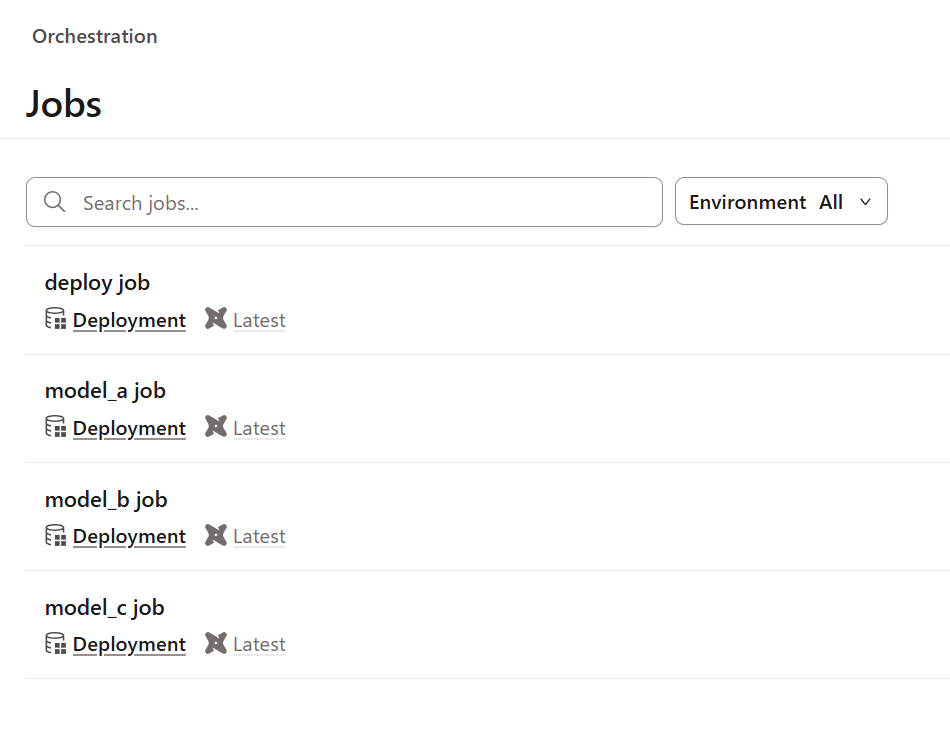
After this, when I looked at the target dbt project in dbt Cloud, the job had been deleted!
 ### Notes
### Notes
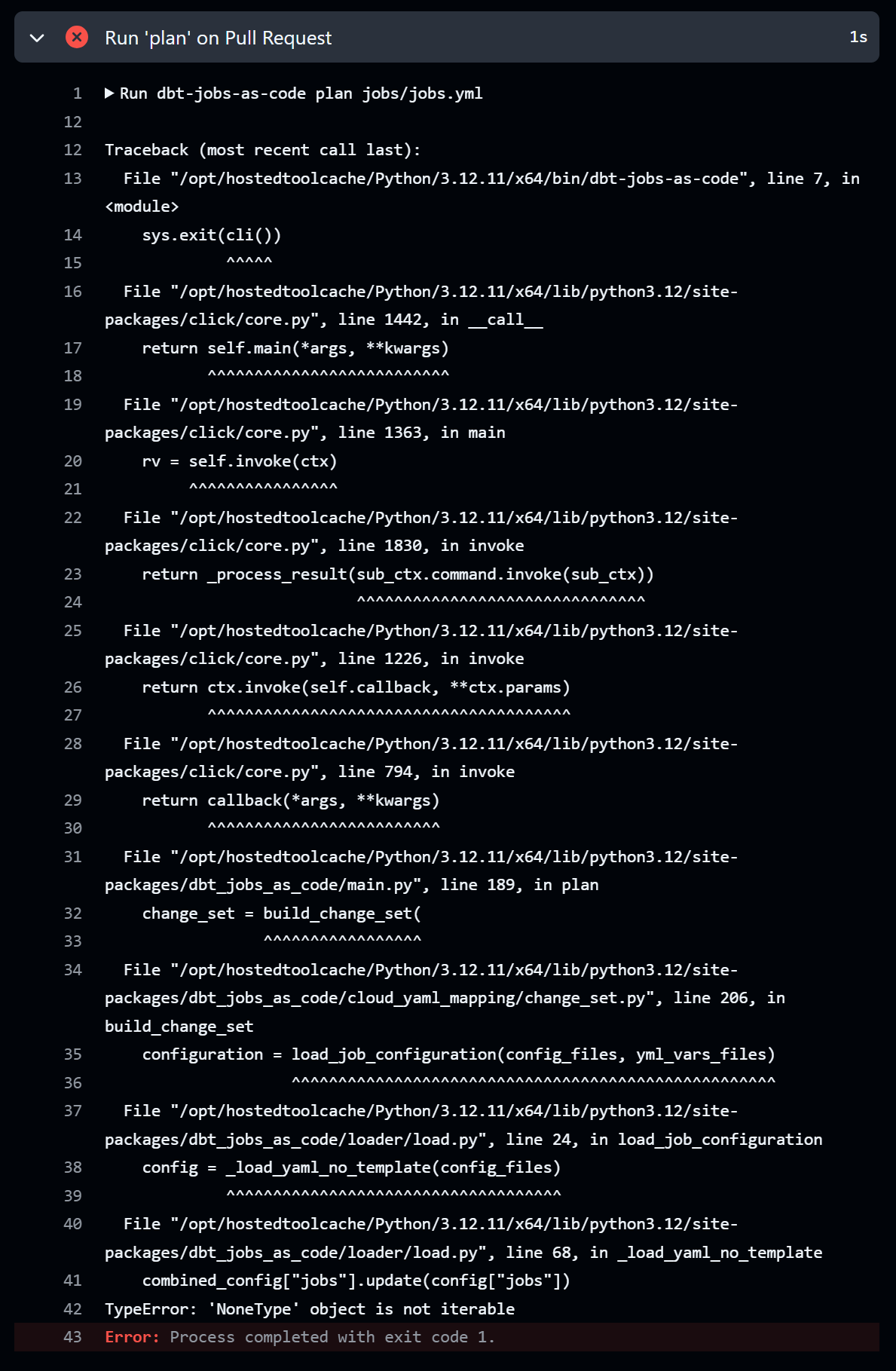
When making the following changes to jobs.yml, please note that it will result in errors or incorrect detection!!
- A pattern where all descriptions of defined jobs are removed (commented out) from the content of
jobs.yml, leaving onlyjobs:

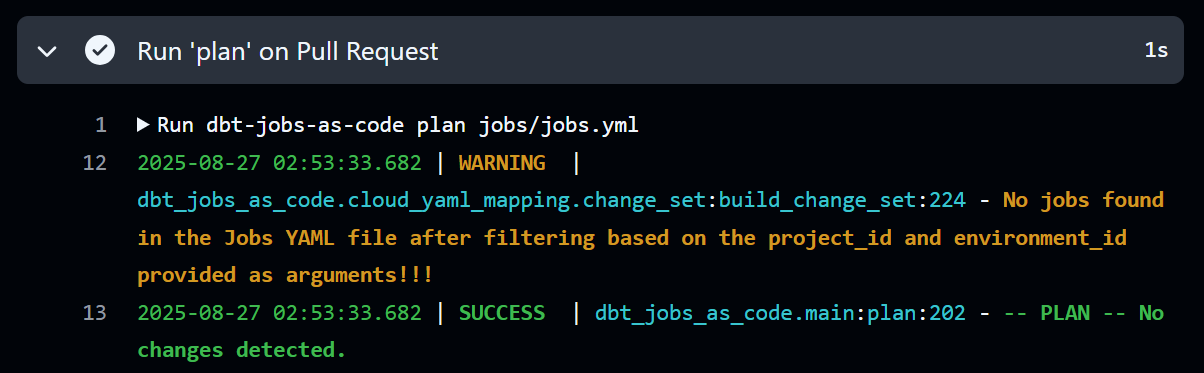
- A pattern where all content of the
jobs.ymlfile is deleted (commented out)

Reference: CI Job Configuration
I tried to set up dbt Cloud-specific CI Jobs, but it didn't work well...
I felt that the documentation doesn't explain each parameter, so I hope for improvements in the documentation and functionality!
In Conclusion
I tried dbt-jobs-as-code, an OSS tool provided by dbt Labs that allows you to define dbt Cloud jobs in YAML.
As the number of dbt jobs increases, GUI-based management can become difficult, so dbt-jobs-as-code can be helpful when you want to define jobs in YAML! Currently, I believe it can be used for regular Deploy Jobs, except for CI Jobs and Merge Jobs.
Please consider using it.



