
I tried data migration using DMS
I plan to try using DMS with the following configuration to learn how it works.
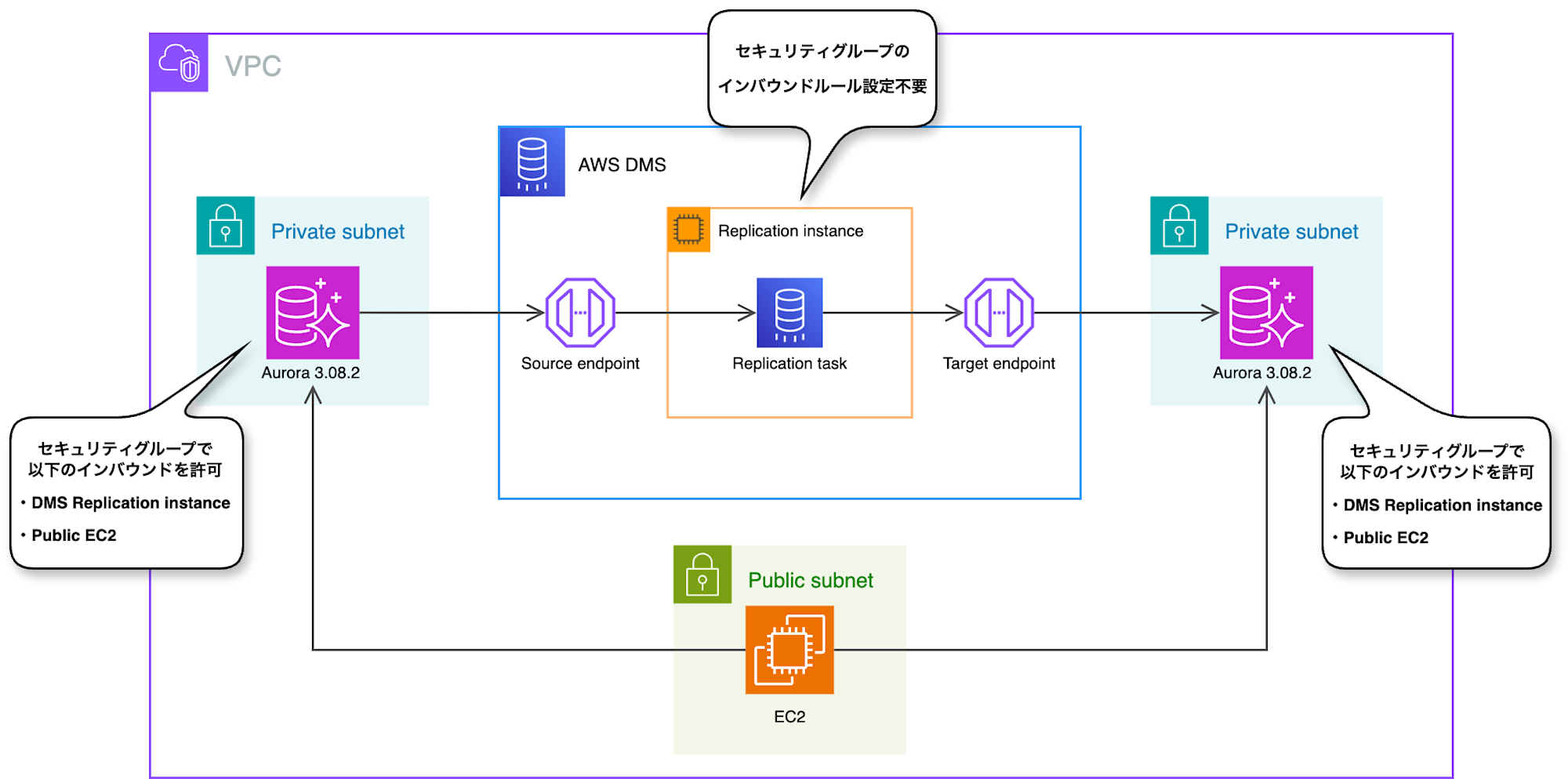
- Source database: 8.0.mysql_aurora.3.08.2
- Target database: 8.0.mysql_aurora.3.08.2
- What to migrate with DMS: test_db database created in the source database and the user table within test_db
The EC2 instance in the architecture diagram is for connecting to the source DB to create test databases and to connect to the target DB to verify that the migration has been completed properly.
Since the purpose this time is to understand what DMS is, I will try the simplest migration between the same engine versions.
Also, for the user table to be migrated, I will only insert data and not create any indexes.
Let's proceed with the verification.
Creating Security Groups
First, I'll create security groups.
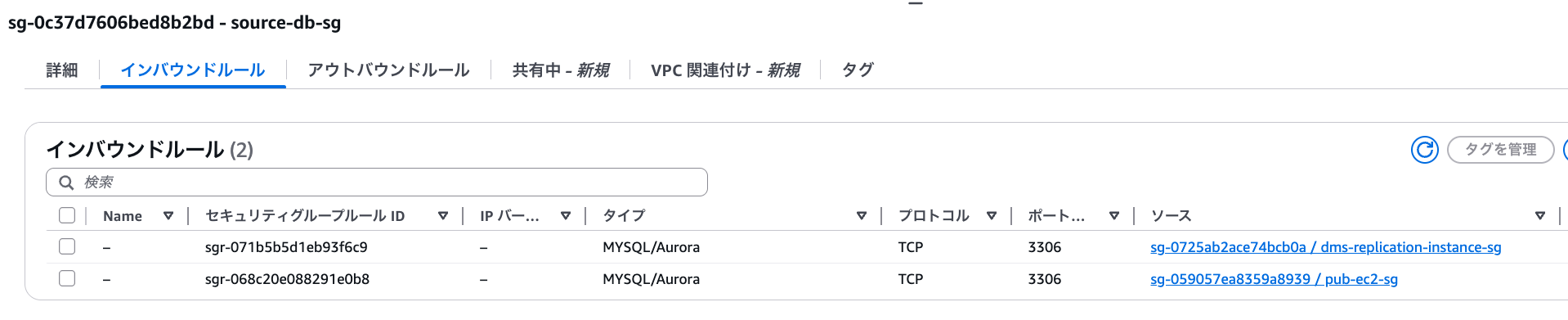
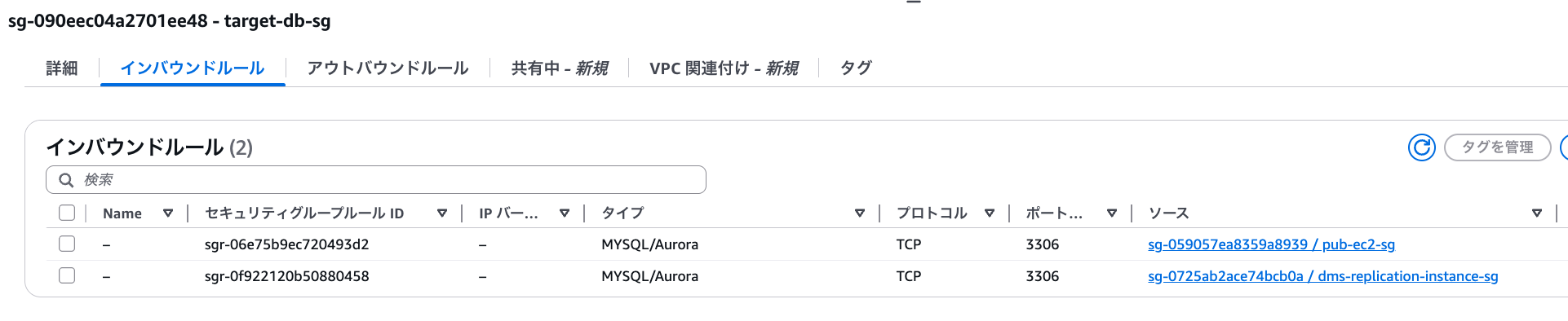
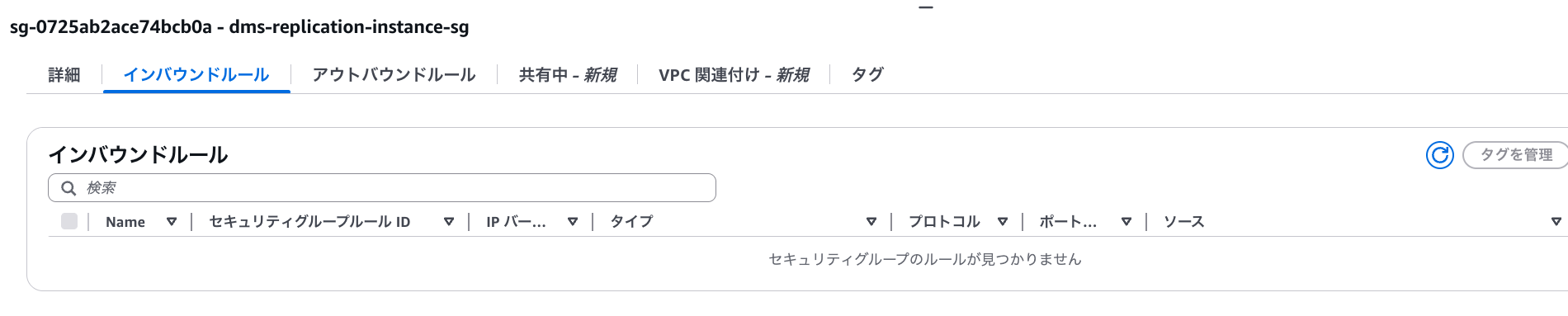
Security groups need to be set up for a total of three: the source database, target database, and replication instance.
For source and target, I'll allow inbound rules from the DMS replication instance. I'll also allow inbound from EC2 as it's needed for verification.
For the replication instance, no configuration is needed.
-
source-db-sg
-
target-db-sg
-
dms-replication-instance-sg
Creating the Source Database
I'll create the source DB with the following parameters. I'll use the security group from the previous section.
| Configuration item | Value |
|---|---|
| Engine version | Aurora MySQL3.08.2 |
| DB cluster identifier | source-db |
| Master username | admin |
| Master password | <any password> |
| Security group | source-db-sg |
| DB cluster parameter group | default.aurora-mysql8.0 |
| DB parameter group | default.aurora-mysql8.0 |
| Subnet | Placed in private subnet |
Successfully created.
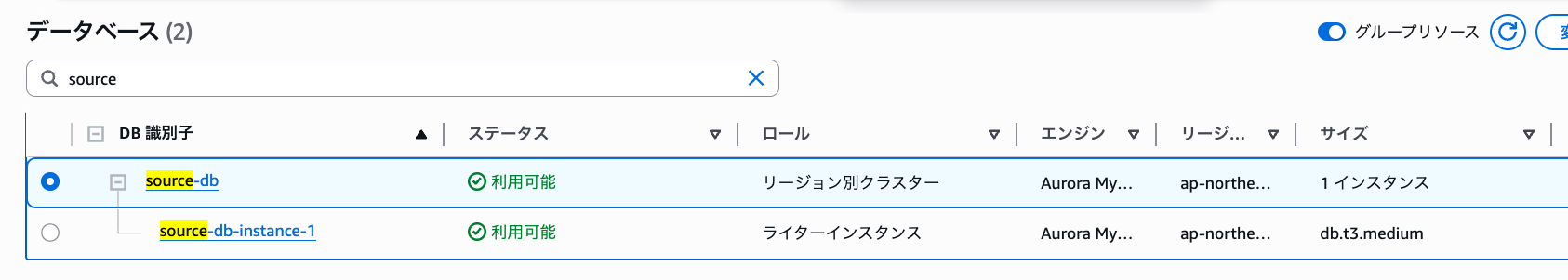
Creating the Target Database
I'll create it with the identifier target-db. I'll use the security group mentioned earlier. Other settings are the same as the source DB.
| Configuration item | Value |
|---|---|
| DB cluster identifier | target-db |
| Security group | target-db-sg |
Successfully created.
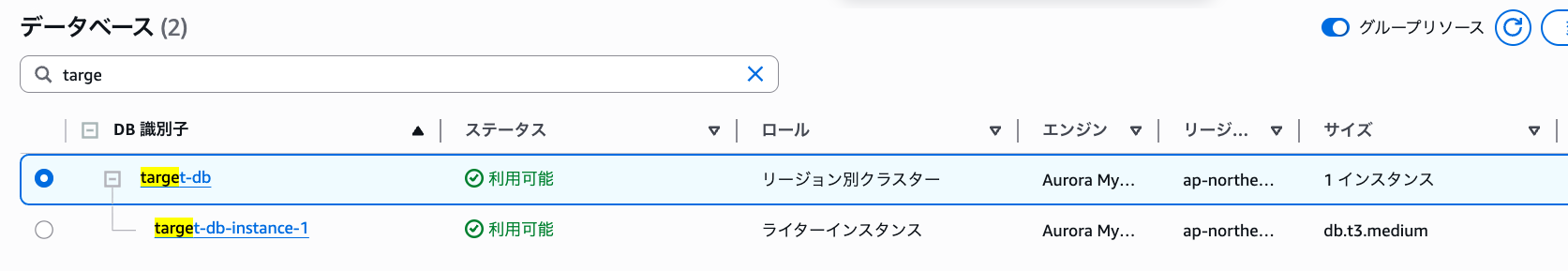 ## Creating EC2 and Logging into the Source DB
## Creating EC2 and Logging into the Source DB
Create an EC2 with the following configuration:
- Amazon Linux 2023
- Same VPC as the Aurora cluster
- Public subnet
Login to the EC2 and install the mysql client by following this blog:
Connect to the source DB.
mysql -u admin -p -h <source DB instance endpoint>
Create a test database test_db and table user. We will migrate this using DMS later.
mysql> create database test_db;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
| test_db |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> create table test_db.user (id int, name varchar(10), address varchar(10));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)
mysql> insert into test_db.user values (1, 'Yamada', 'Tokyo');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into test_db.user values (2, 'Satou', 'Chiba');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into test_db.user values (3, 'Kinjo', 'Okinawa');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from test_db.user;
+------+--------+---------+
| id | name | address |
+------+--------+---------+
| 1 | Yamada | Tokyo |
| 2 | Satou | Chiba |
| 3 | Kinjo | Okinawa |
+------+--------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
DMS Configuration
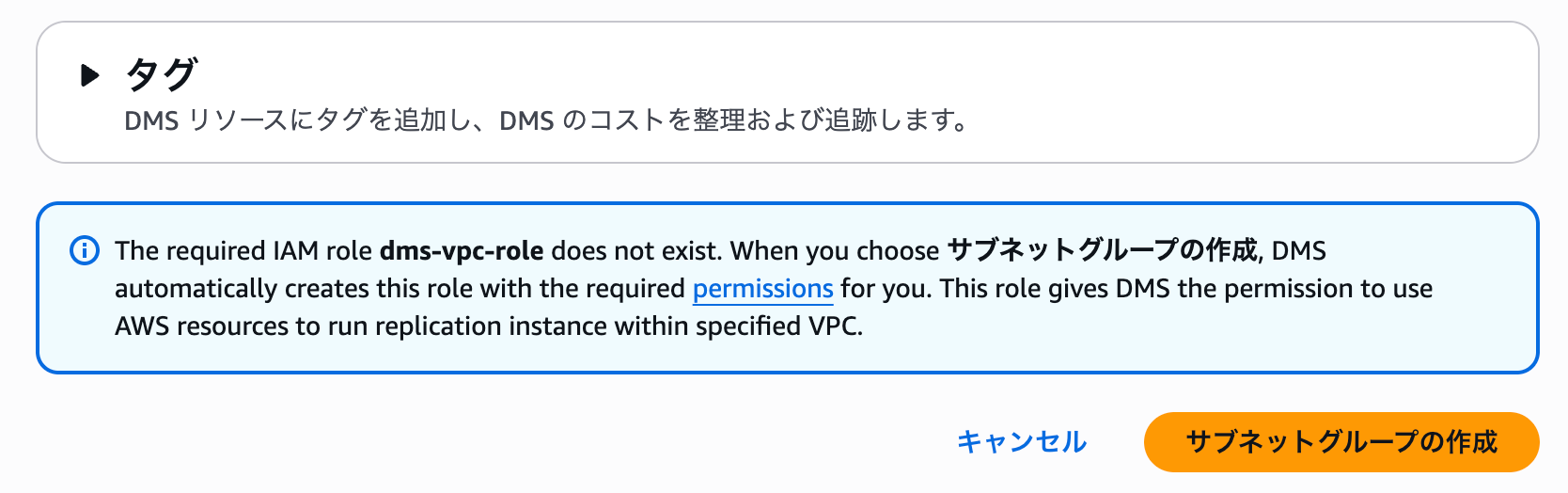
Creating a Subnet Group
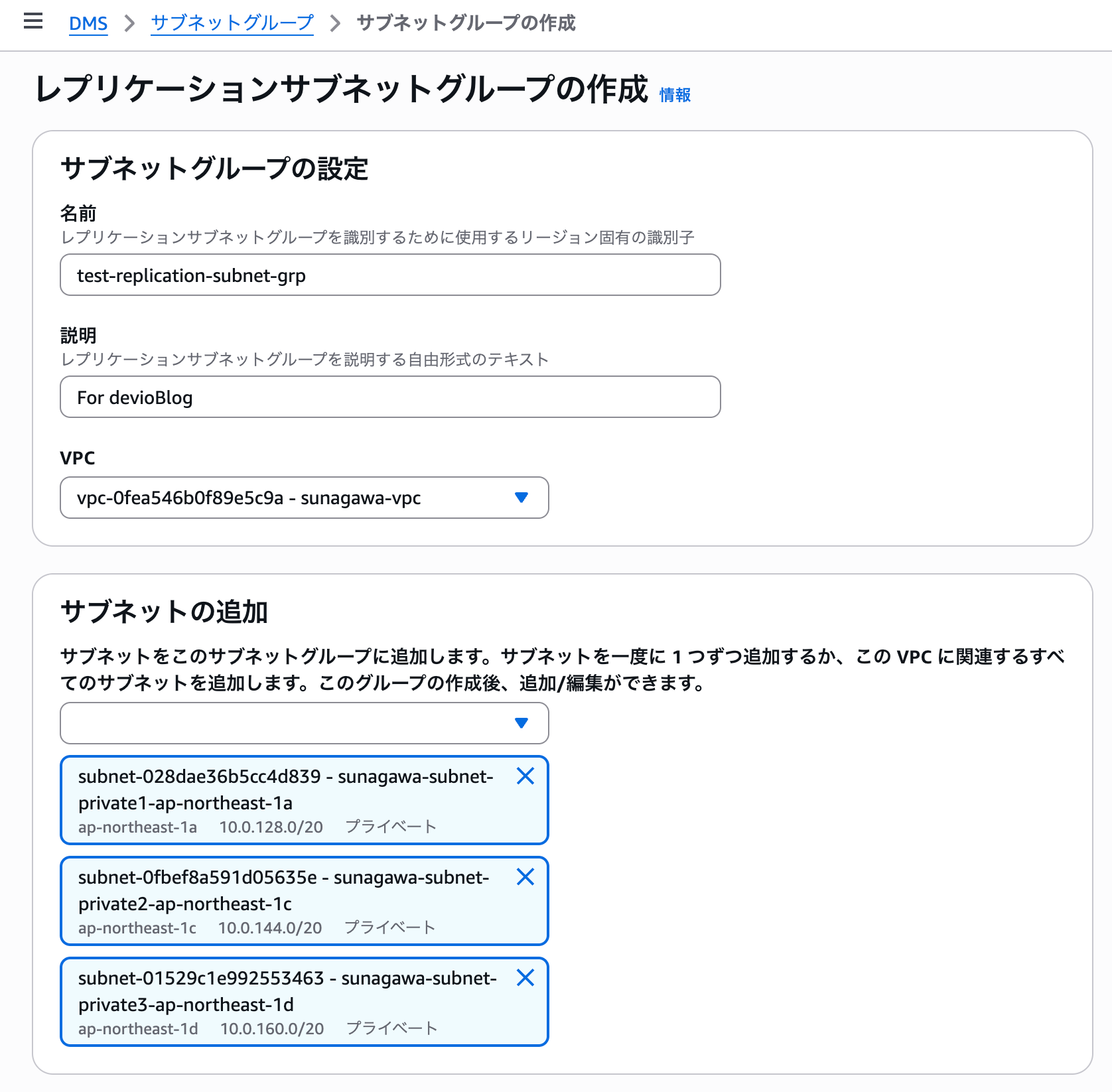
Create a subnet group for the replication instance.
Select the same VPC as the Aurora source database and target database.
 ### Creating Endpoints
### Creating Endpoints
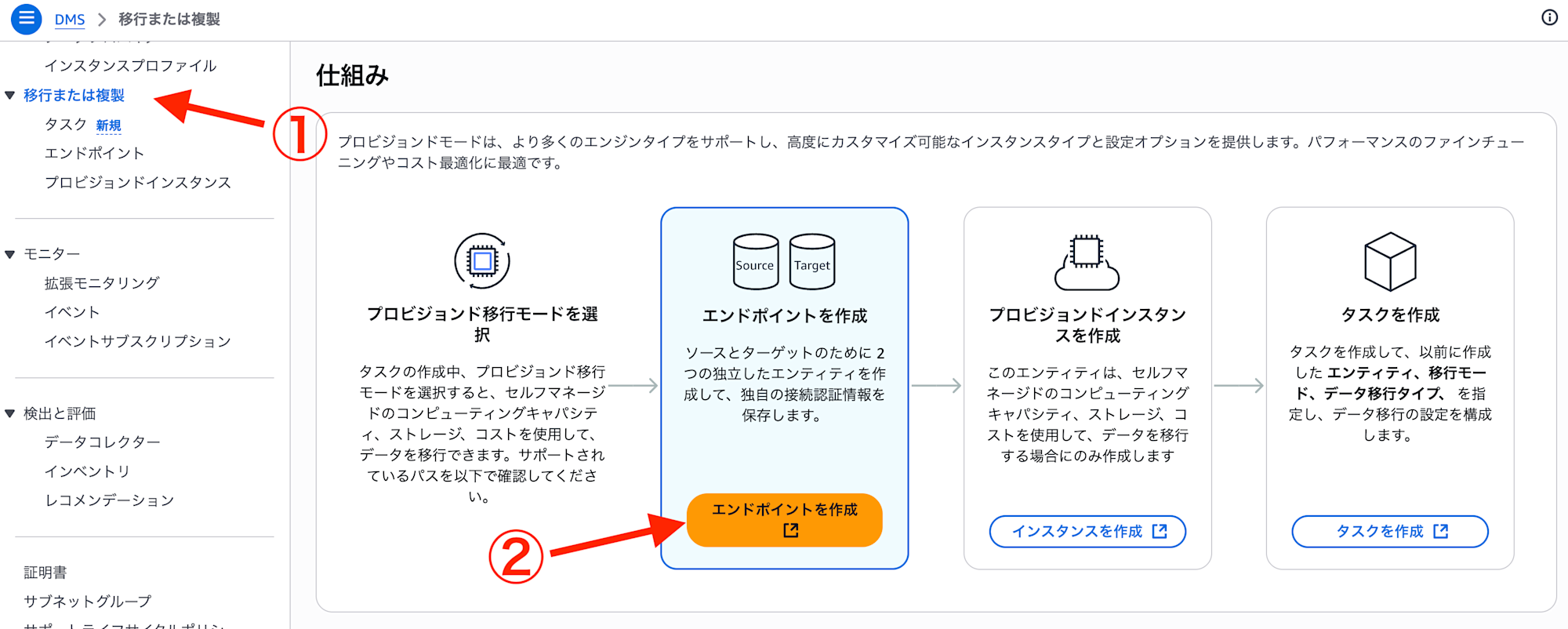
Select "Migrate or replicate" from the navigation pane on the left. This will display the DMS setup procedure.
Following the screen instructions, start with creating endpoints.
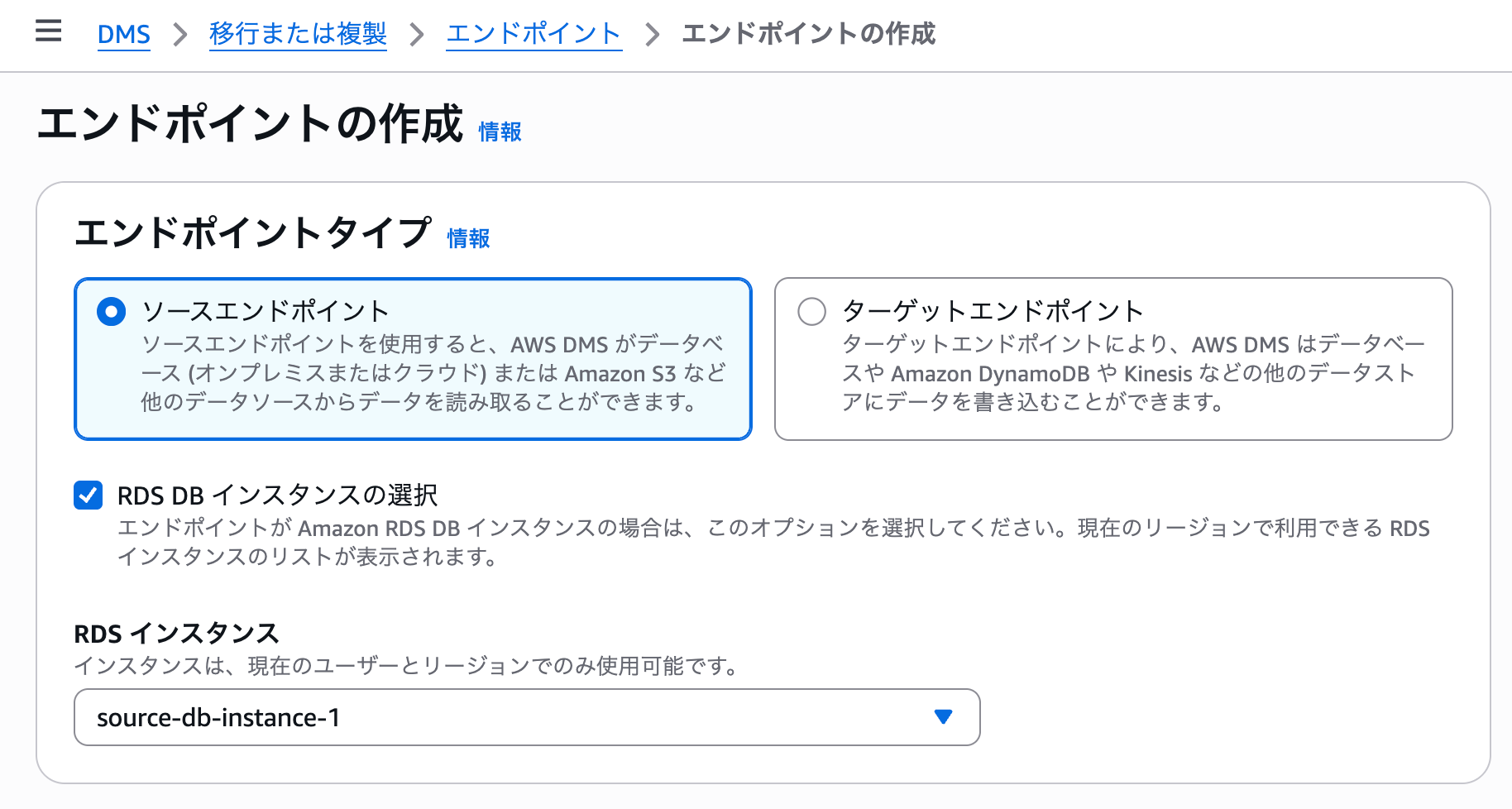
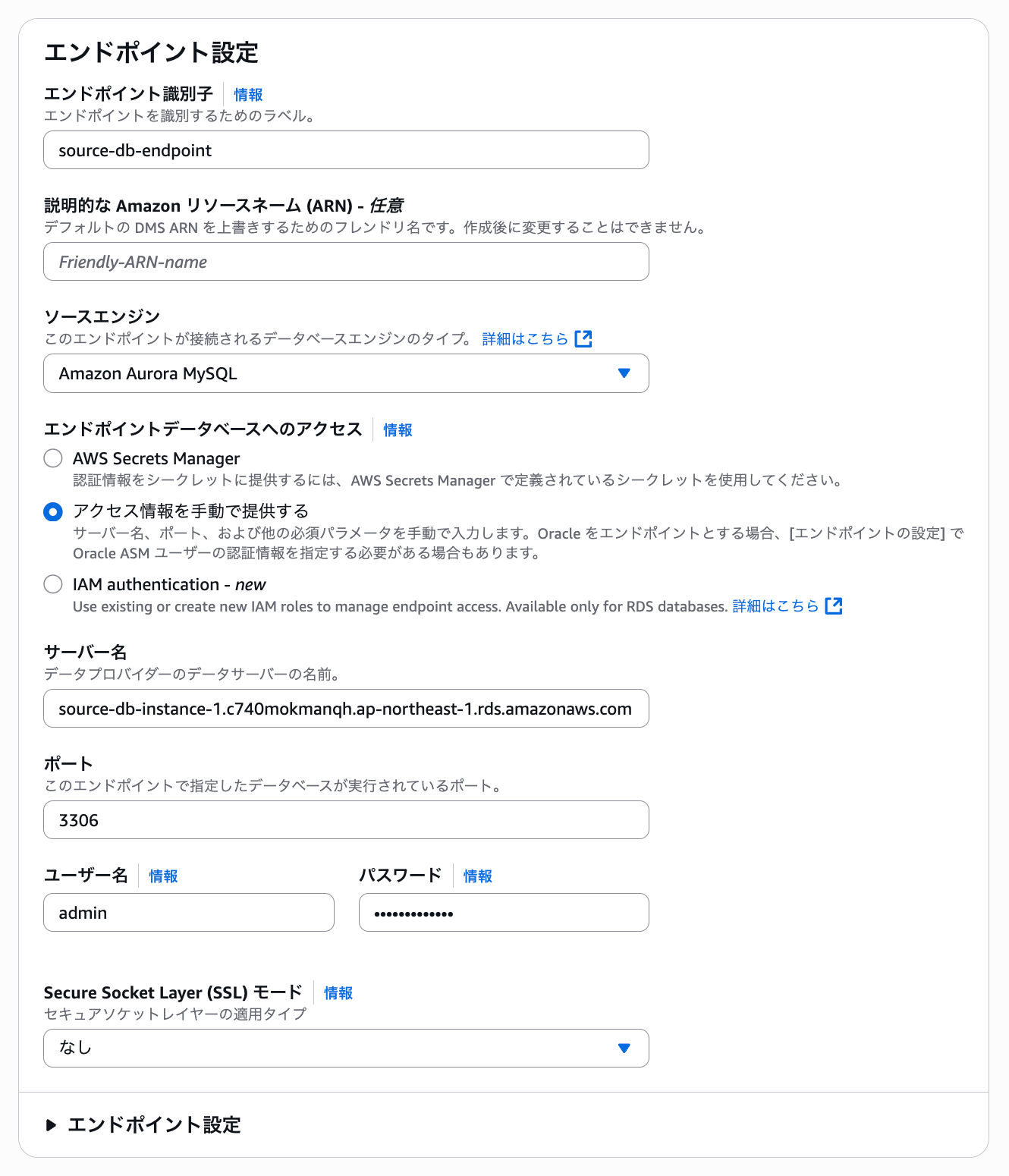
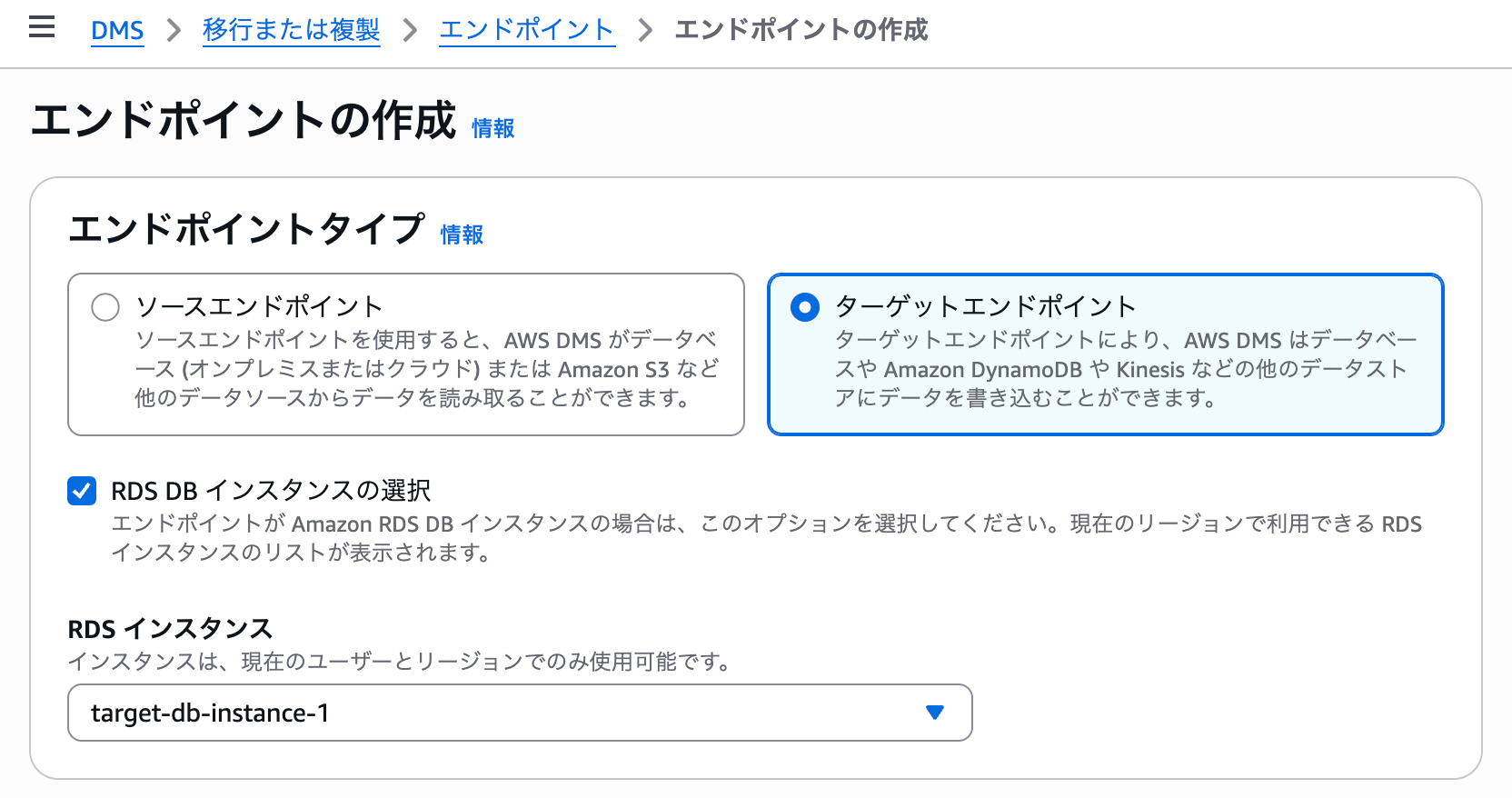
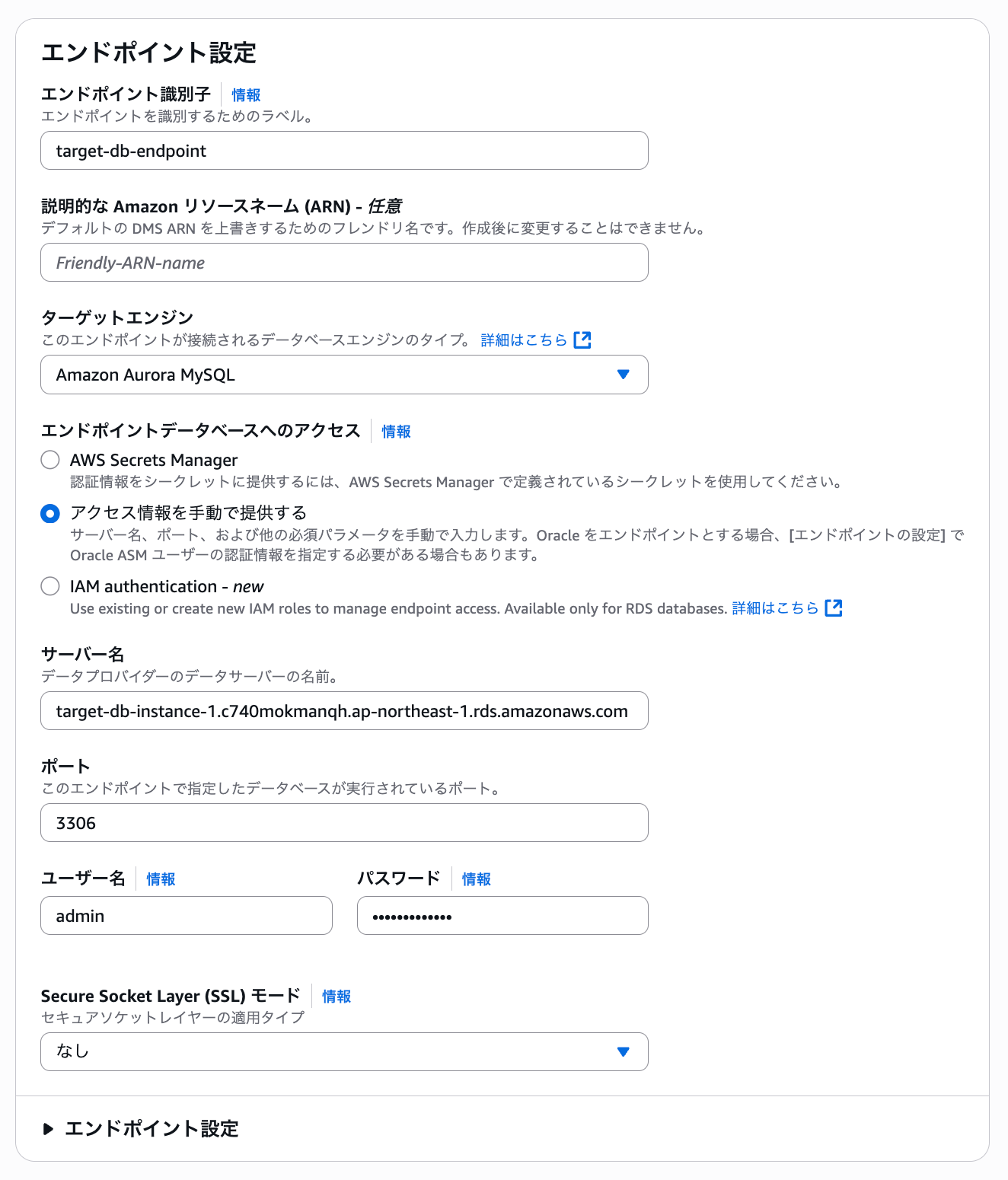
Create the source endpoint as follows. Select the RDS instance of the source database.
For access information, set up the master username and master password used to connect to the source.
Create the target endpoint using the same procedure.
We have successfully created the source endpoint and target endpoint.
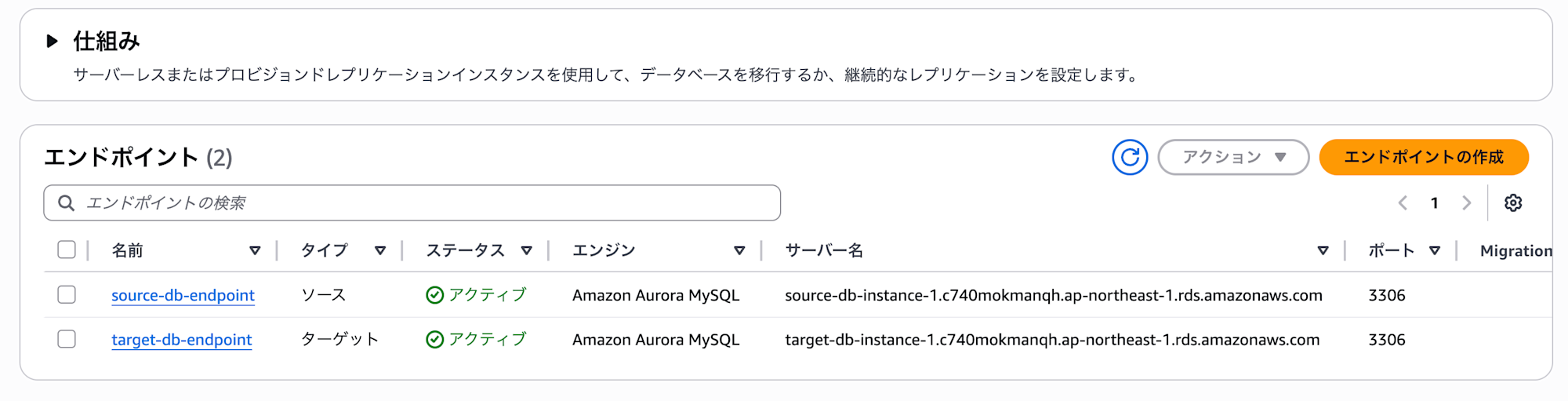 ### Creating a Replication Instance
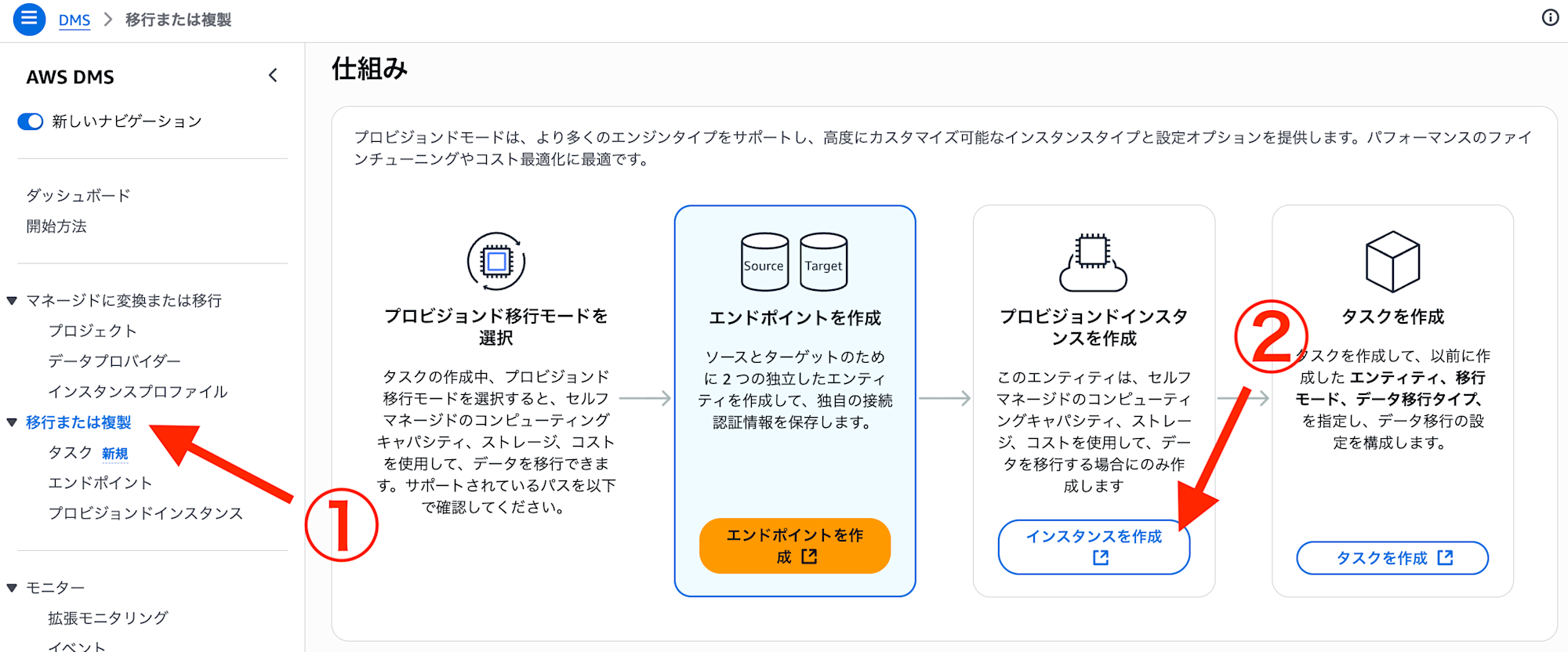
### Creating a Replication Instance
Now that we have created the endpoints, let's proceed to create a replication instance. From the "Migrate or replicate" screen, select "Create instance".
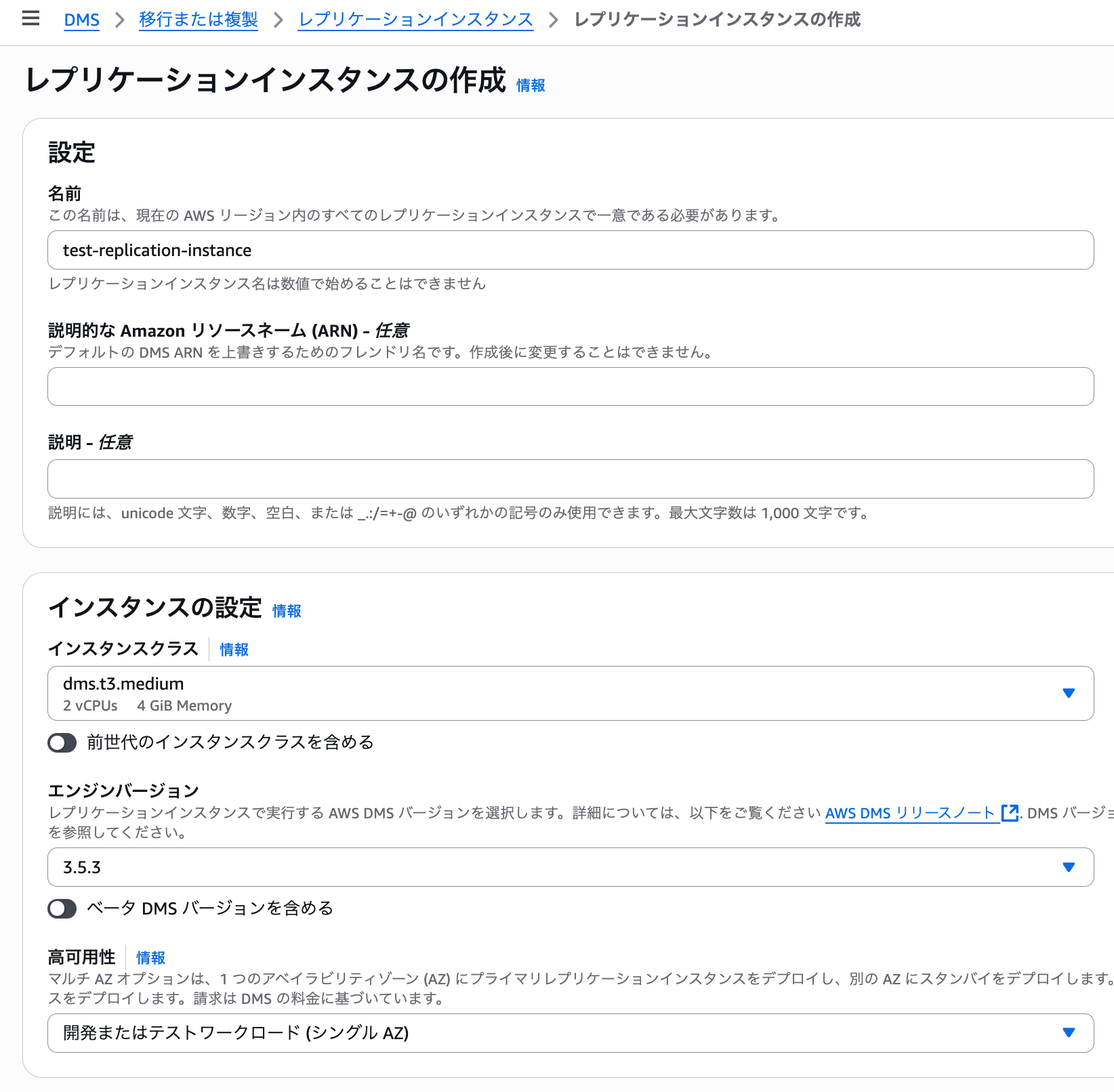
Let's configure the replication instance.
Since this is for testing purposes, we'll set the high availability part to single AZ.
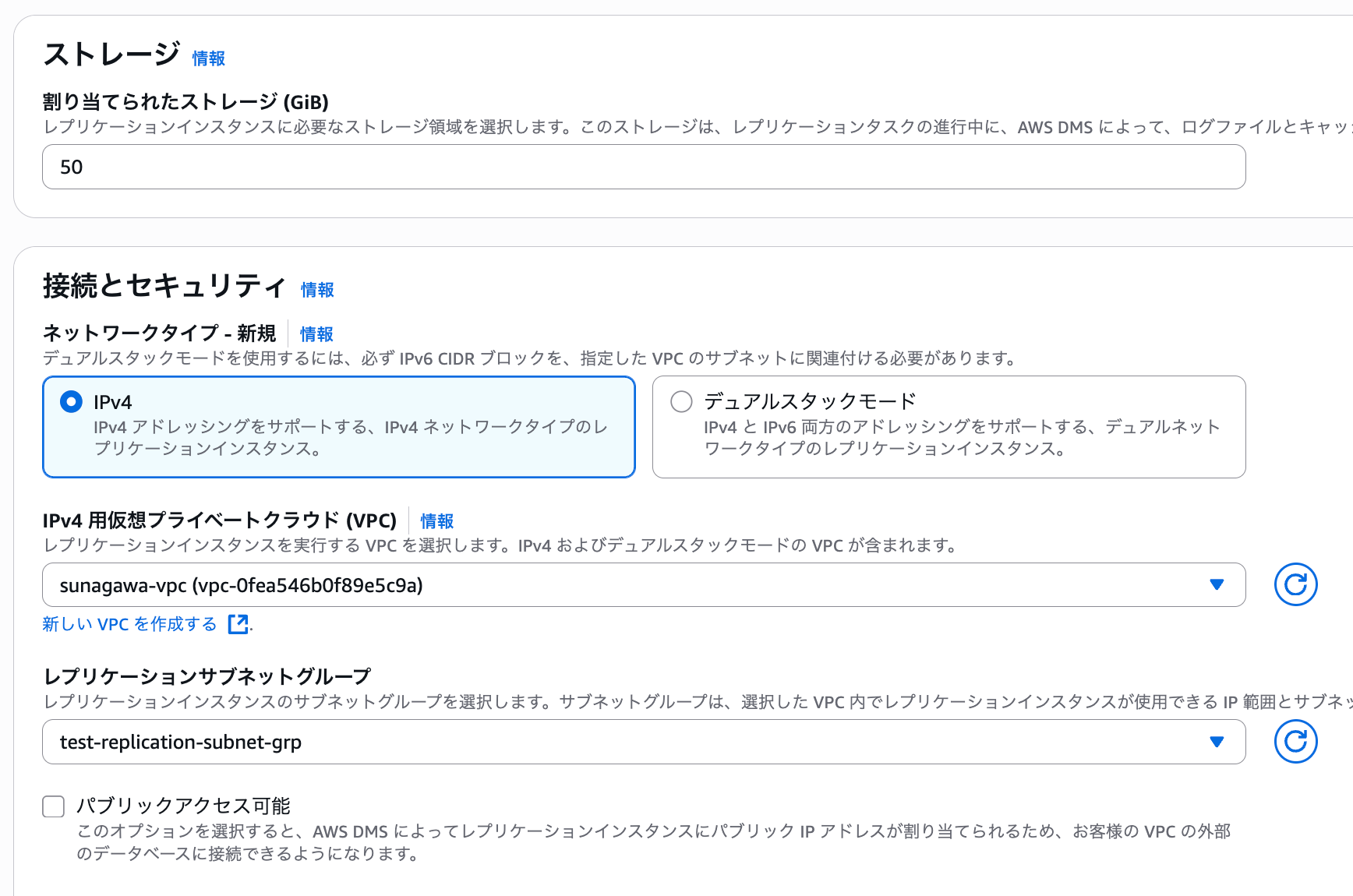
For the replication subnet group, select the group we created earlier.
Uncheck "Publicly accessible" as it's not needed.
For the security group, specify the previously created dms-replication-instance-sg.
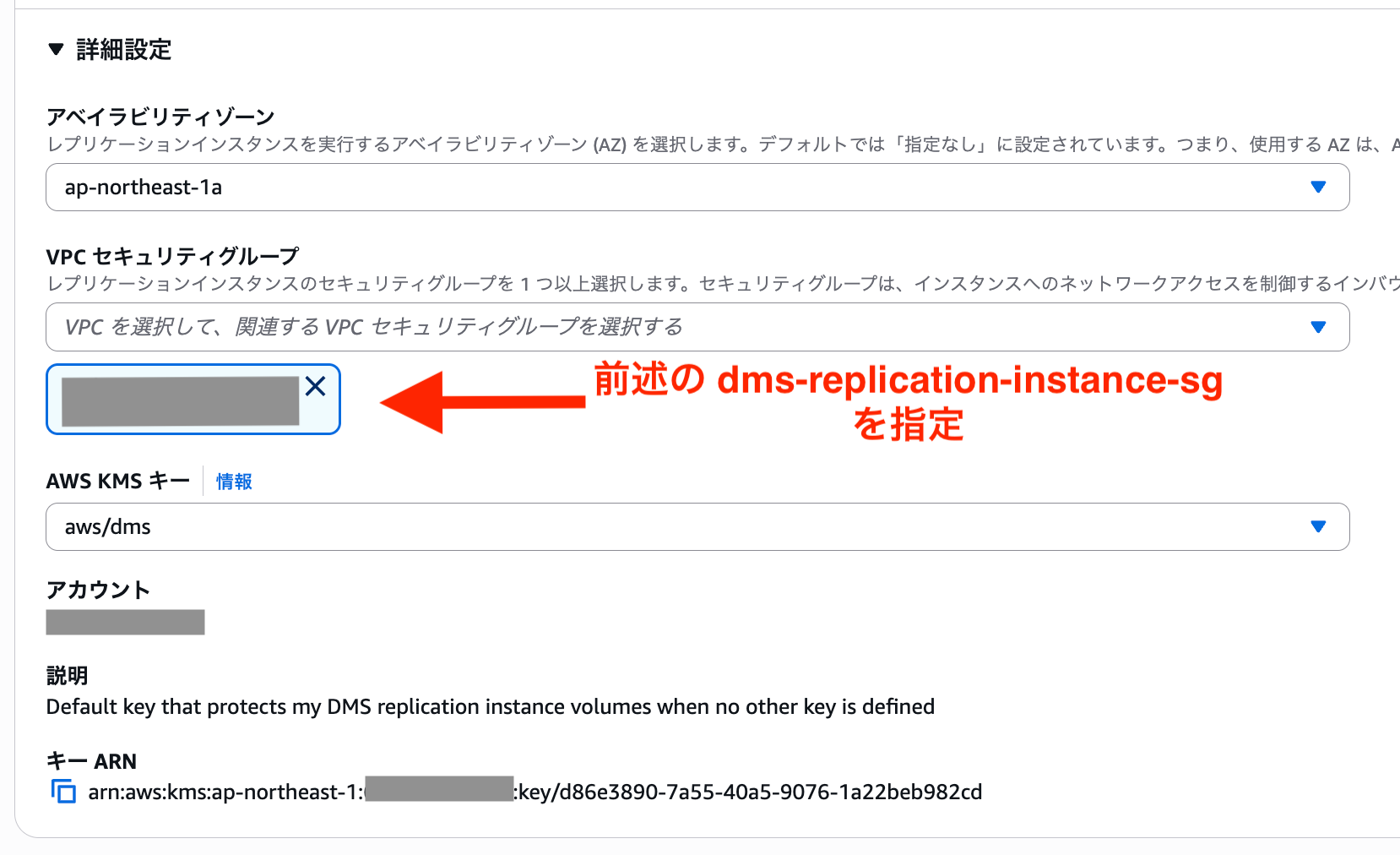
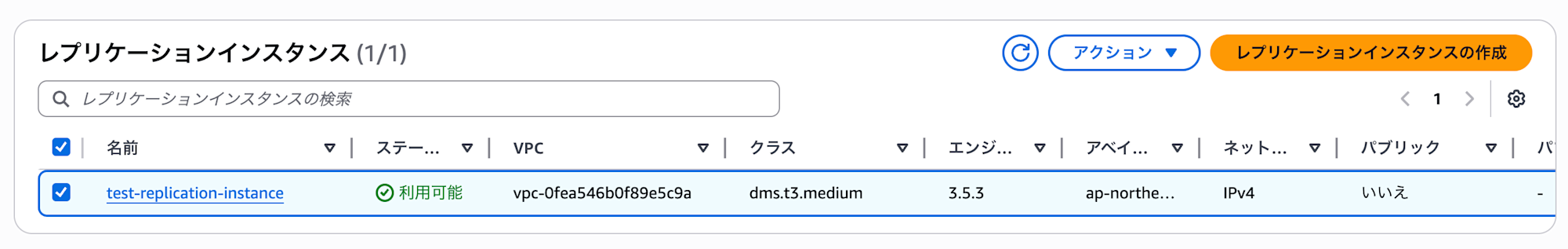
We have successfully created the replication instance.
 ### Creating Tasks
### Creating Tasks
Now that we have prepared the environment for data migration with DMS, we'll proceed to configure the specific task settings to determine which databases and tables to migrate.
Tasks define what will be executed on the DMS replication instance (such as which tables to migrate).
Select "Create task" from the following screen.
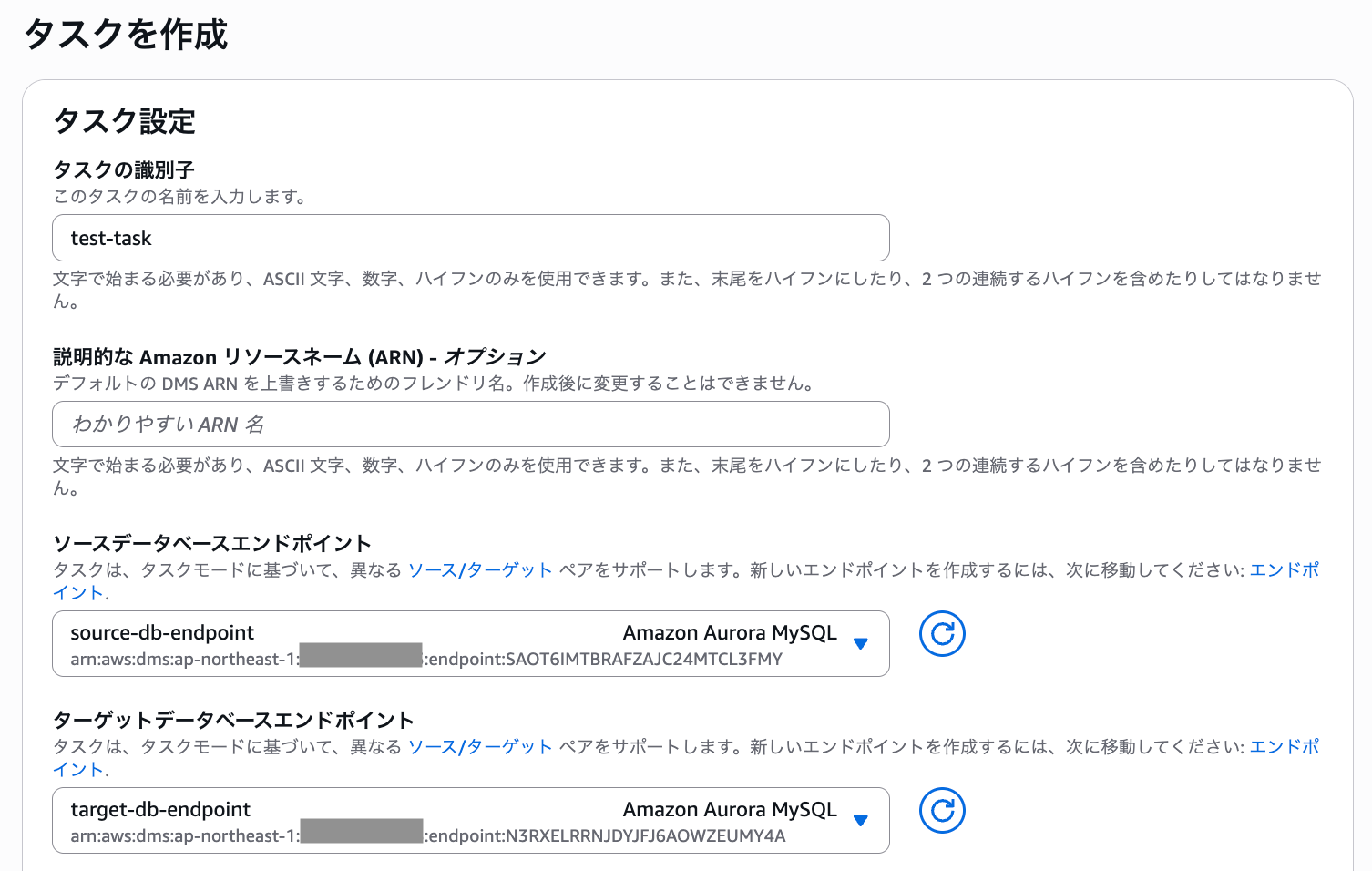
In the task settings, specify the previously created source database endpoint and target database endpoint.
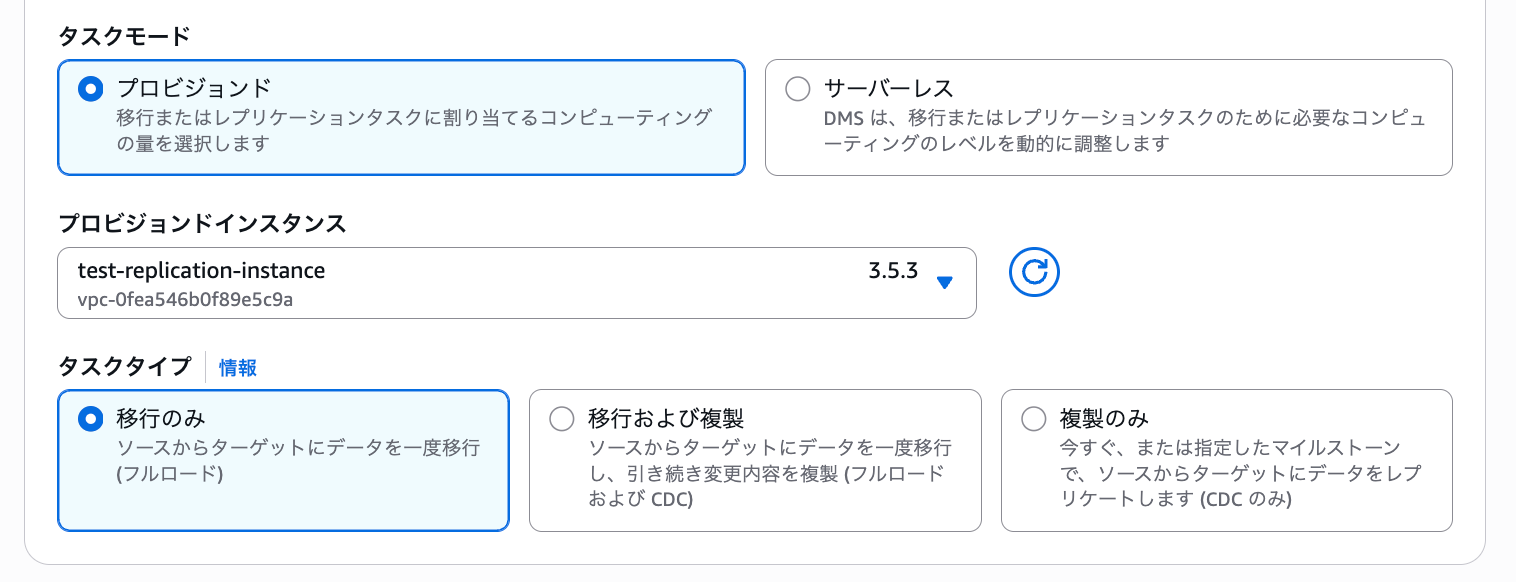
Since we're only migrating the test_db and the user table within test_db from the source database, we'll specify "Full load" as the task type.
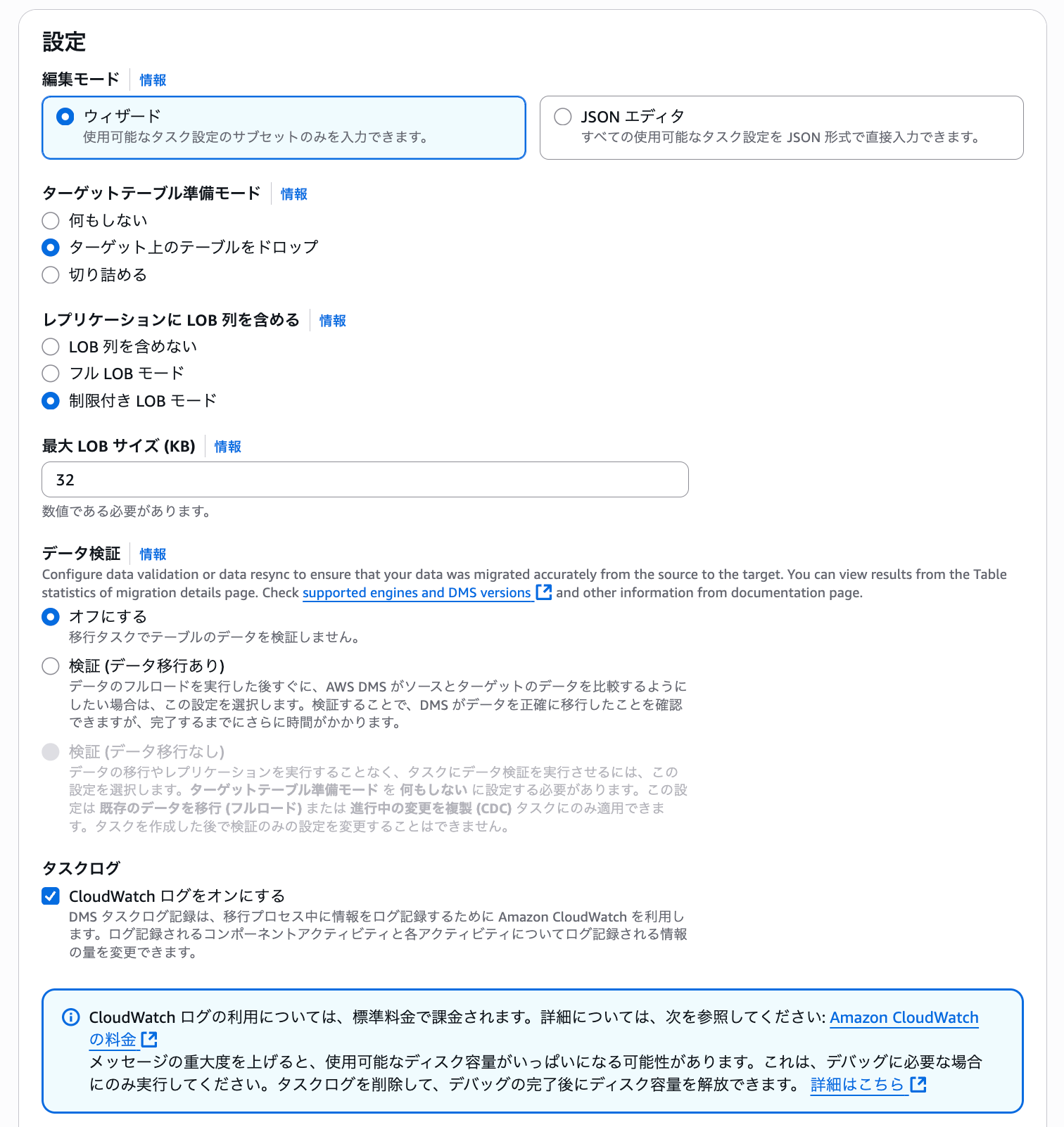
Since the target database is empty, set the Target table preparation mode to "Drop tables on target".
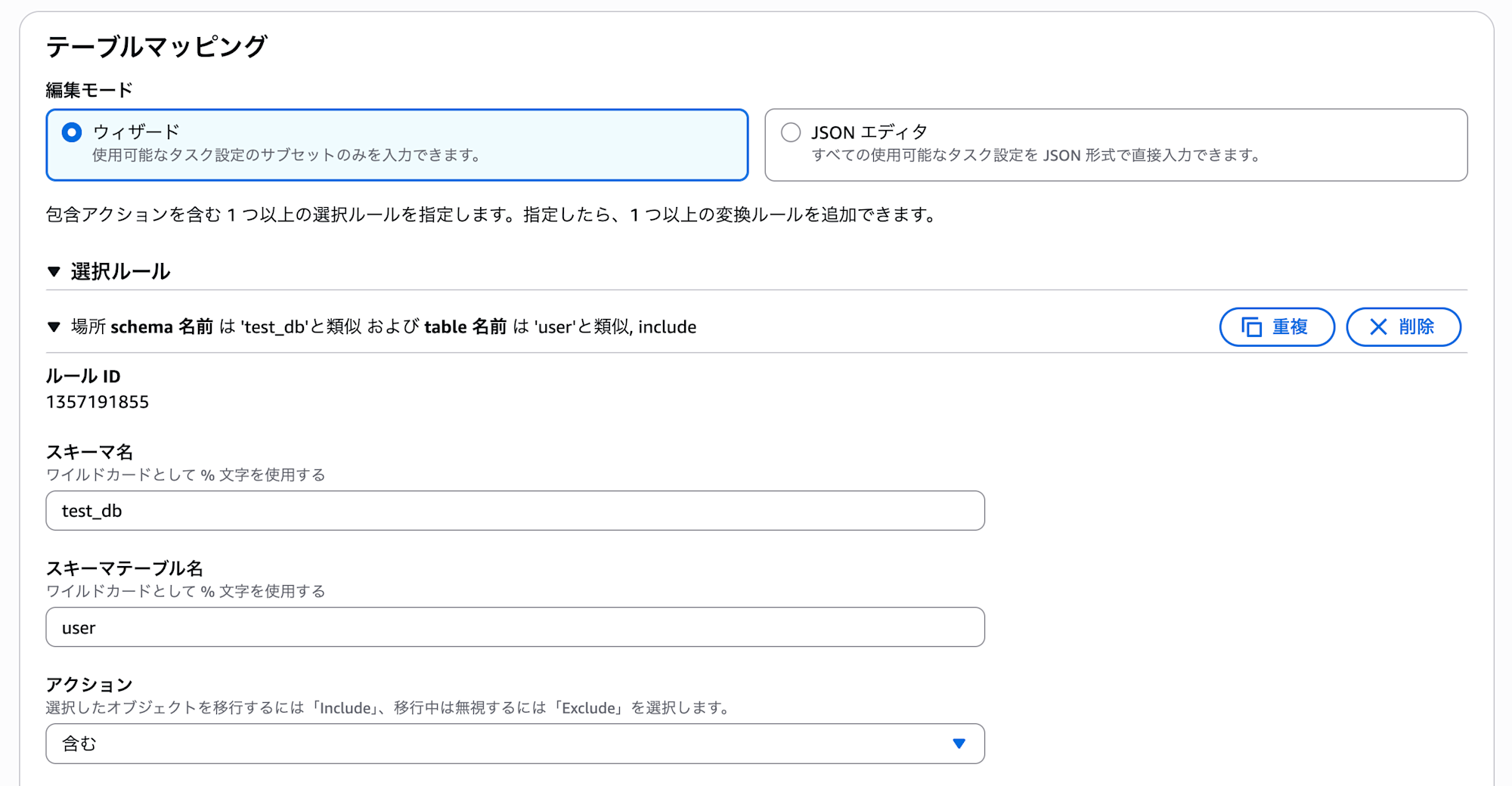
In Table mappings, you can select the database schemas and tables to migrate.
Specify the test_db and user table that we previously created in the source database.
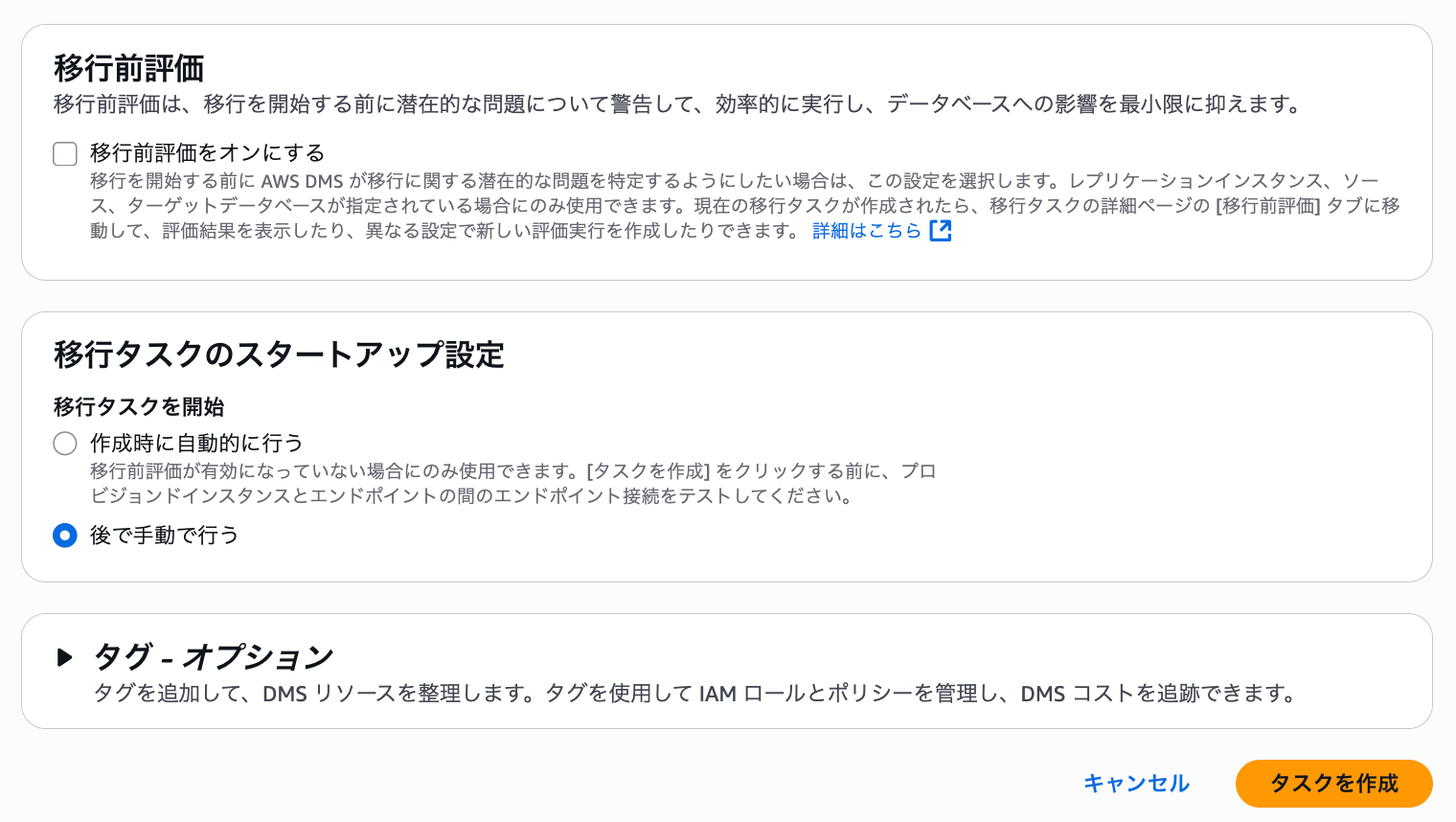
The pre-migration assessment is a feature that checks for errors before executing the migration task and saves the results to S3. We'll leave this disabled for now as we're not doing a pre-migration assessment.
Once the configuration is complete, select "Create task".
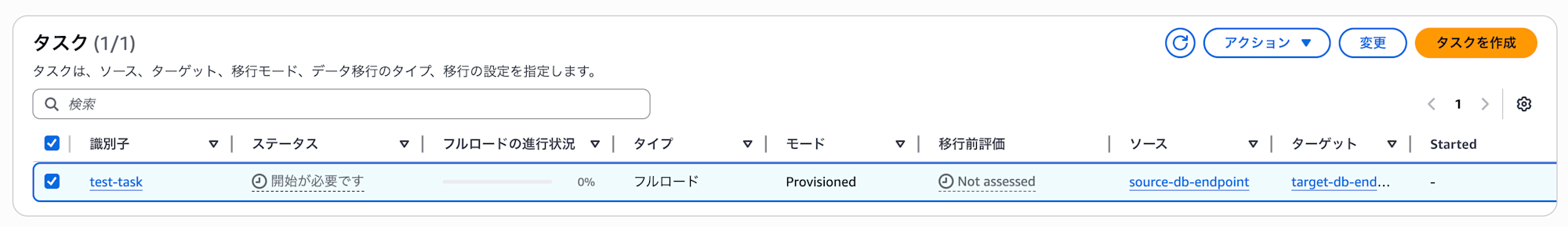
The task has been created successfully.
 ### Task Execution
### Task Execution
Let's execute the task we created in the previous section and actually try the migration.
Select the created task and click "Start" from the actions.
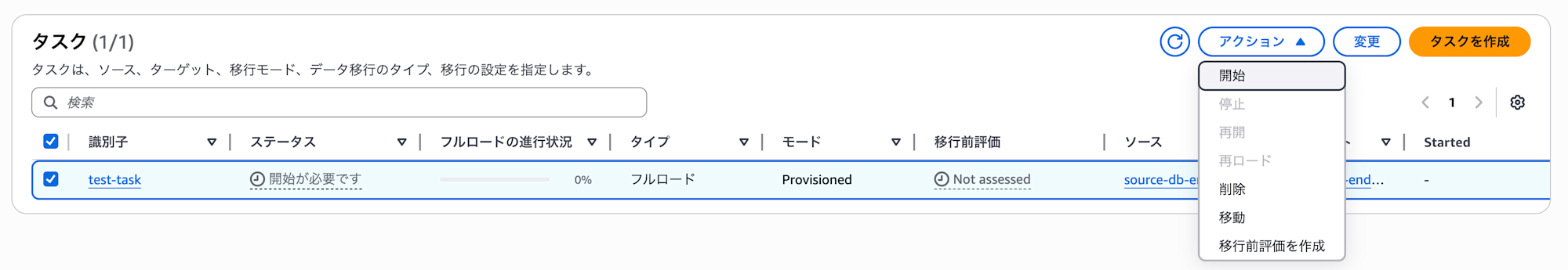
Once the task starts, the status will change to "Starting" as shown below.
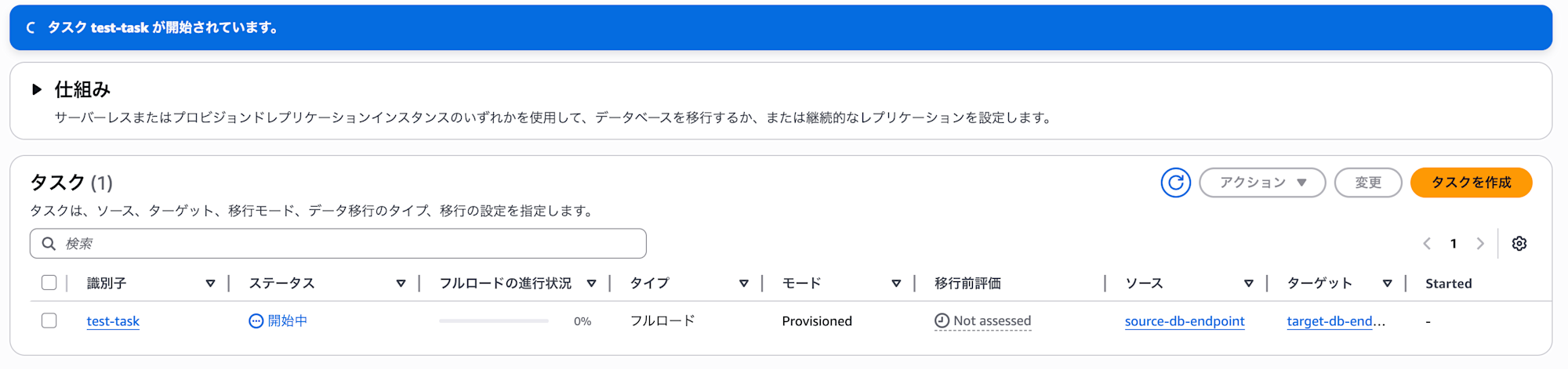
When completed, the status will change to complete.
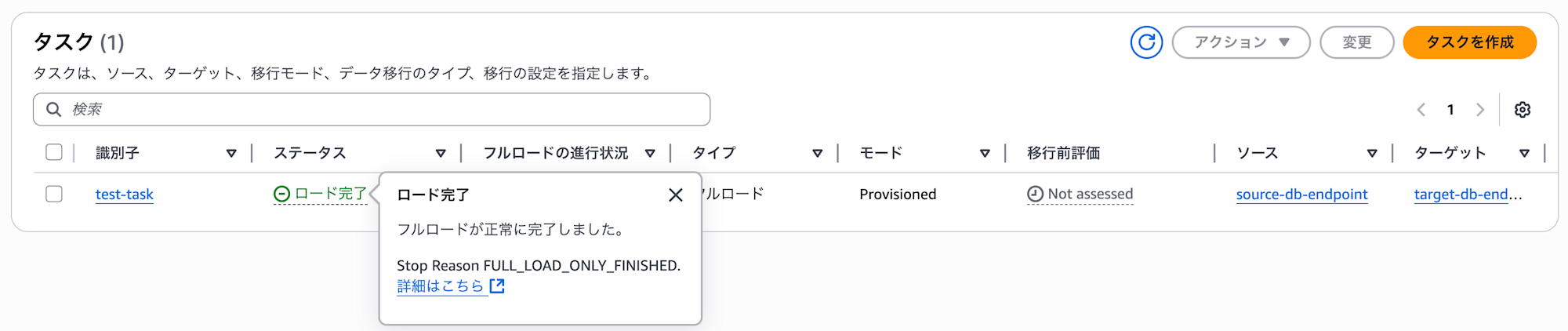
Now, let's log in to the target DB from the EC2 instance and verify that the migration was successful.
mysql -u admin -p -h <target DB cluster endpoint>
From the results below, we can confirm that the test_db database and user table created in the source DB have been properly migrated!
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| awsdms_control |
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
| test_db |
+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test_db.user;
+------+--------+---------+
| id | name | address |
+------+--------+---------+
| 1 | Yamada | Tokyo |
| 2 | Satou | Chiba |
| 3 | Kinjo | Okinawa |
+------+--------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Conclusion
This time I tried using DMS. I had been avoiding getting hands-on with DMS because it involves many components like endpoints and tasks, and you also need to prepare source and target databases, but when I actually tried it, it turned out to be relatively straightforward!
I did get stuck with errors due to not understanding how to configure security groups, but I think someone who works quickly could verify this content in about 1-2 hours. I hope this blog will be helpful for those who are trying DMS for the first time to get a general understanding of how DMS works.
References


