
Validating Zendesk SIP-IN from Linphone: Observing SIP and SDP with Wireshark
This page has been translated by machine translation. View original
Introduction
When considering a telephone response system, preparing carrier lines or a PBX for testing takes time. With Zendesk Talk's SIP-IN, you can receive incoming calls from external sources using SIP. This article confirms that calls can be made from a SIP client (Linphone) on Windows and received by Zendesk SIP-IN.
What is Zendesk
Zendesk is a customer service platform for handling inquiries. In addition to ticket management and help center capabilities, Zendesk Talk allows you to handle phone support from the same interface.
What is SIP
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) is a protocol for controlling calls. A call begins with a SIP message called INVITE. When the recipient is being called, 180 Ringing is returned, and when they answer, 200 OK is returned. After the call is established, voice is transmitted via RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol). SDP is the body included in SIP messages that determines voice conditions. Information such as which codec to use and which IP and port to receive voice on is written in the SDP.
Testing Environment
- Windows 11
- Linphone Desktop 5.2.6 (Core 5.3.72)
- Wireshark 4.6.3
Target Audience
- Those who want to quickly verify connectivity with Zendesk Talk SIP-IN
- Those who have heard SIP terminology but aren't confident in how to view it in Wireshark
- Those who want to get a basic understanding of operation before production implementation
References
Overall Process and Preparation
Create a SIP-IN line on the Zendesk side and make a call from Linphone to the SIP URI. After establishing the call, verify SIP and SDP with Wireshark.
Prerequisites
- Access to a Zendesk account with Zendesk Talk
- Administrative rights to operate the Admin Center
- A SIP account that can be used with Linphone
Zendesk Preparation
-
Create a SIP-IN line in Admin Center
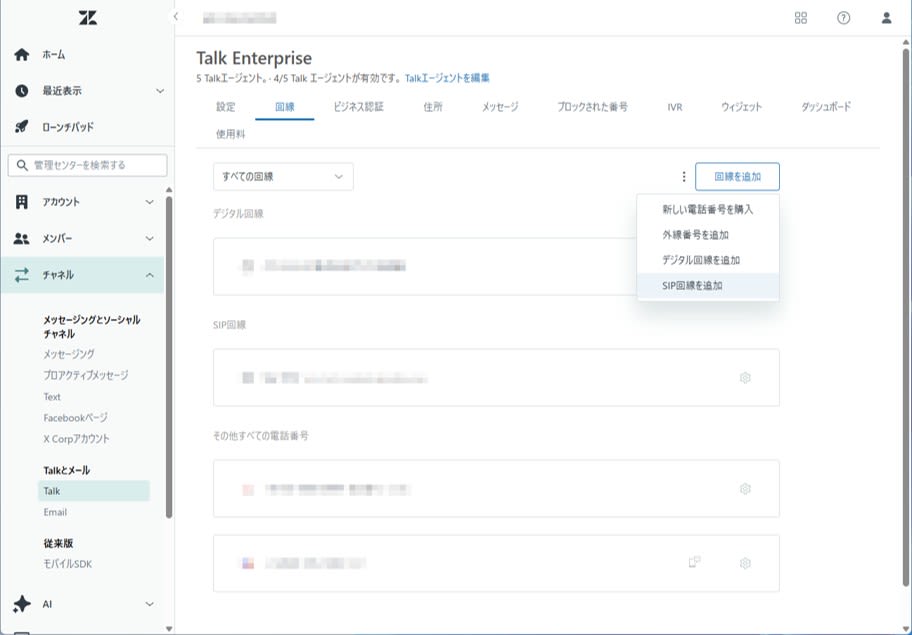
-
Enter configuration items
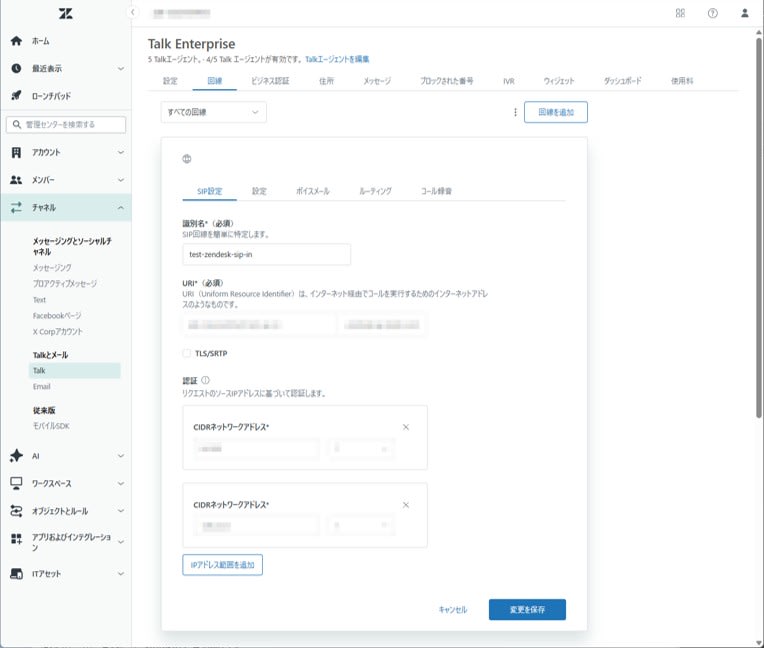
-
Note the SIP domain (e.g.,
example.com) (which you'll use asZENDESK_SIP_HOSTin later steps)
Wireshark Preparation
- Install Wireshark
- Select your normal network connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet) as the interface to capture
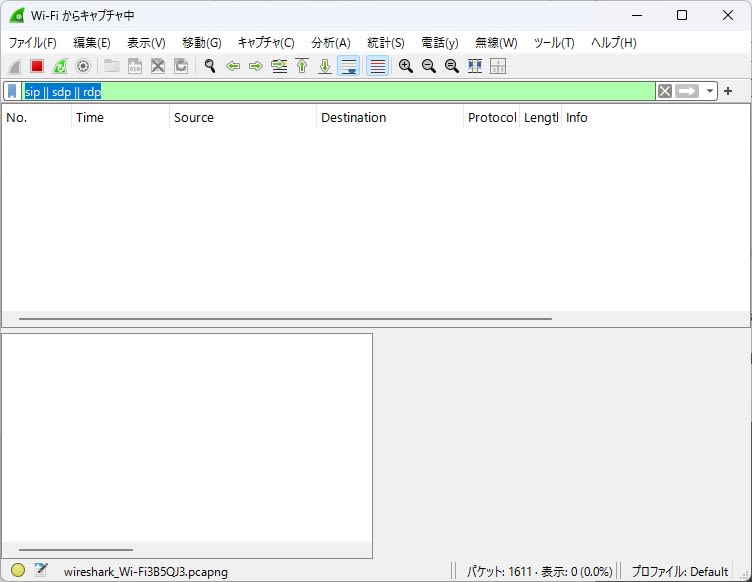
- Enter
sip || sdp || rtpin the display filter
Making a Call from Linphone to Zendesk's SIP URI
Verify that the SIP client can reach the SIP-IN entrance.
Linphone Preparation
Sign in to a SIP account in Linphone to make a call. If you already have a SIP account, use it. If not, set up a test SIP account. The account doesn't need to be related to Zendesk.
Making the Call
- Start Wireshark capture
- In the Linphone dialer, enter
sip:ZENDESK_SIP_HOST;transport=tcp(e.g.,sip:example.com;transport=tcp)
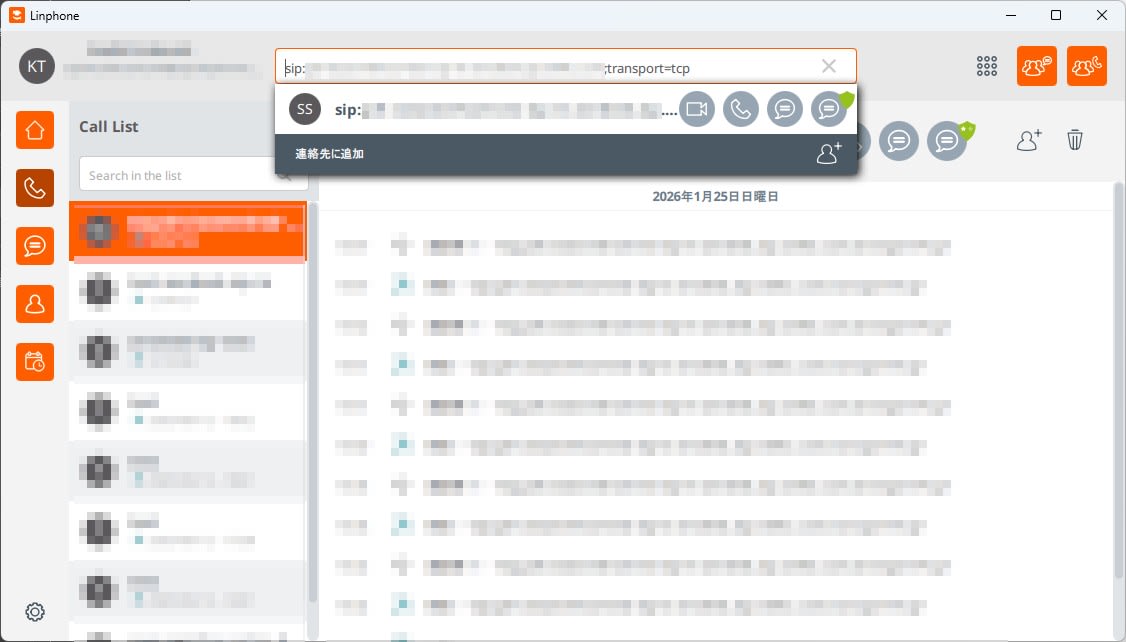
- Make the call
- Confirm that an incoming call appears on the Zendesk side
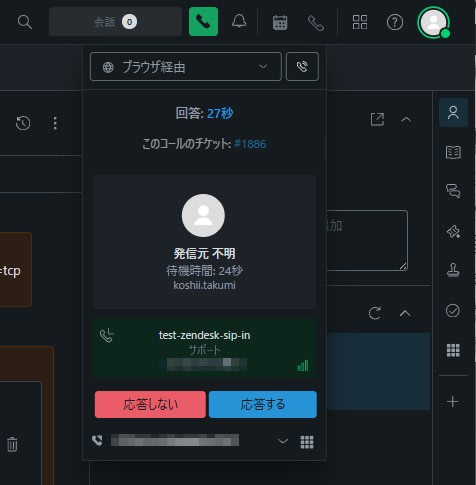
- Answer and confirm that the call is established
- End the call and stop the Wireshark capture
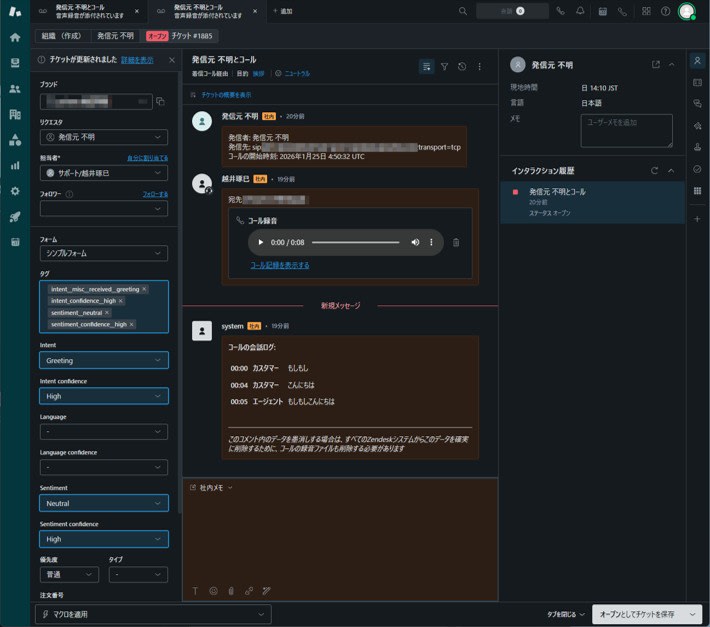
- After the call, confirm that transcription is generated in Zendesk
Observations
The following logs were observed in Wireshark:
| No. | Time | Protocol | Info |
|---|---|---|---|
| 237319 | 2523.911765 | SIP/SDP | Request: INVITE sip:example.com;transport=tcp |
| 237323 | 2524.101194 | SIP | Status: 100 trying -- your call is important to us |
| 237326 | 2524.188949 | SIP | Status: 180 Ringing |
| 237339 | 2524.717327 | SIP/SDP | Status: 200 OK (INVITE) |
| 237358 | 2525.101638 | SIP | Request: ACK sip:***.***.***.***:5060 |
| 237370 | 2525.217146 | SIP/SDP | Status: 200 OK (INVITE) |
| 237379 | 2525.254622 | SIP | Request: ACK sip:***.***.***.***:5060 |
| 240221 | 2547.625427 | SIP | Request: BYE sip:***.***.***.***:5060 |
| 240235 | 2547.820101 | SIP | Status: 200 OK (BYE) |
The following was confirmed:
- INVITE was sent
- 100 Trying was returned
- 180 Ringing was returned
- 200 OK was returned
Next, examine the SDP content returned from the Zendesk side.
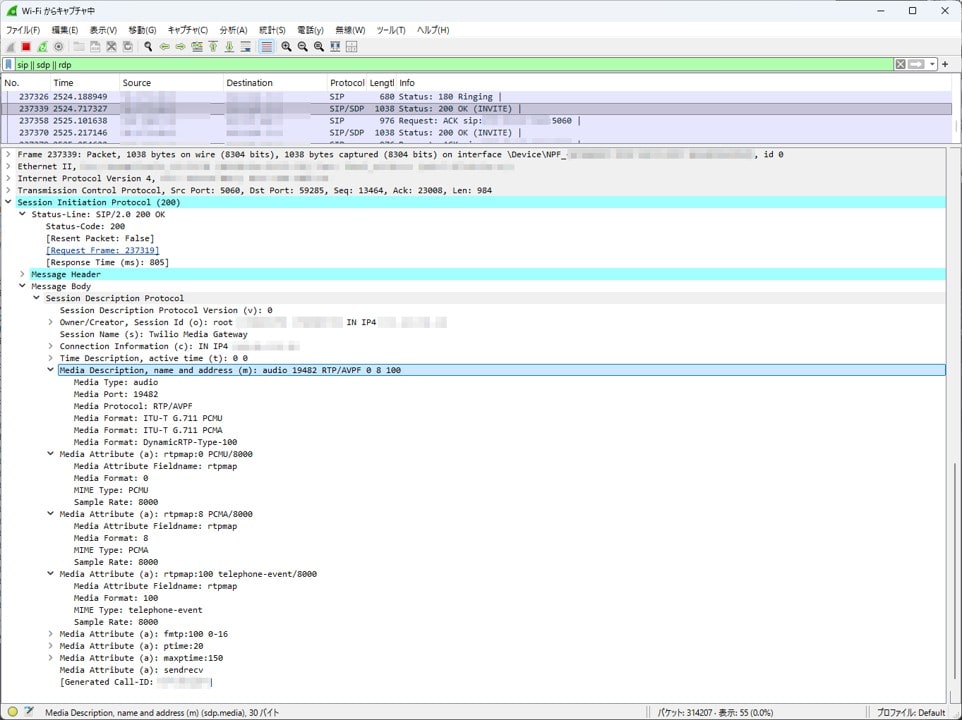
Zendesk officially documents support for G.711 μ-law (PCMU) and A-law (PCMA). Looking at the actual SDP content, the 200 OK (INVITE) SDP includes a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000 and a=rtpmap:8 PCMA/8000. This confirms that the Zendesk side accepts G.711 μ-law (PCMU) and A-law (PCMA).
Findings from the Test
In this test environment, SIP responses were not observed when initiating via UDP. However, when specifying transport=tcp, everything from 100 Trying to 200 OK was received, and the call was established. When verifying SIP connectivity, protocol differences may impact results even when connecting to the same destination.
When the agent status was offline, the system routed to voicemail, and no incoming call was generated for the agent. Even if SIP logs appear normal, the operational status on the Zendesk side can affect the outcome, so it's necessary to check the Talk status when troubleshooting.
Conclusion
In this article, we tested Zendesk SIP-IN. We made a direct call from Linphone to a SIP URI and confirmed that the SIP-IN entrance was functioning. We also observed SIP and SDP in Wireshark and documented evidence of success. The test revealed that specifying TCP enabled successful call establishment and that Zendesk accepts G.711 (PCMU/PCMA).



