
I Tried Using the MCP Toolbox for Databases with Claude Code to Operate BigQuery in Natural Language
I am Hanzawa from the Data Business Division.
Have you ever wanted to operate BigQuery through an MCP server?
At the time of writing, Google Cloud doesn't officially provide an MCP server, but the official documentation introduces a method using a third-party tool called MCP Toolbox for Databases.
In this blog, I'd like to try operating BigQuery using natural language through MCP Toolbox for Databases from Claude Code.
Operating Environment
- OS: macOS Sequoia 15.5 (Apple M1 / arm64)
- Client: Claude Code
- Target Service: BigQuery
What is MCP Toolbox for Databases?
MCP Toolbox for Databases is an open-source MCP server for databases published by Google. It handles complex processes such as connections and authentication, making tool development easier, faster, and more secure.
In this article, we'll use BigQuery as our integrated service, but it also supports various other database services such as Cloud Spanner and Bigtable.
Let's Try It
Let's immediately try operating BigQuery using MCP Toolbox for Databases from Claude Code.
This time, instead of hosting an MCP server ourselves, we'll use pre-built tools.
What are Pre-built Tools?
MCP Toolbox for Databases provides several pre-built tools for each service.
For BigQuery, the following pre-built tools are provided:
| Name | Overview |
|---|---|
bigquery-conversational-analytics |
Ask questions about data in natural language |
bigquery-execute-sql |
Execute SQL |
bigquery-forecast |
Predict time series data |
bigquery-get-dataset-info |
Get dataset metadata |
bigquery-get-table-info |
Get table metadata |
bigquery-list-dataset-ids |
Display a list of datasets |
bigquery-list-table-ids |
Display a list of tables |
bigquery-sql |
Execute predefined SQL |
These tools can be used immediately without having to build an MCP server yourself.
Let's confirm while actually using them.### Setup
First, we will authenticate to access Google Cloud.
Here, we will use a user account for authentication.
gcloud auth application-default login
Make sure the account used for authentication has permissions to access BigQuery in the Google Cloud project you are operating on.
Next, create a working directory and navigate to it.
mkdir mcp-bigquery
cd mcp-bigquery
Then, download the binary and grant execution permission.
curl -O https://storage.googleapis.com/genai-toolbox/v0.13.0/darwin/arm64/toolbox
chmod +x toolbox
Finally, verify that the installation was successful.
./toolbox --version
> toolbox version 0.13.0+binary.darwin.arm64.1a6dfe8d37d0f42fb3fd3f75c50988534dbc1b85
We have confirmed that the installation was successful.
Configuration for using the tool with Claude Code
Now we'll configure the prebuilt tool for use with Claude Code.
Create a configuration file called .mcp.json in your working directory and include the following content.
If this file already exists, you can simply add the BigQuery configuration to it.
{
"mcpServers": {
"bigquery": {
"command": "./toolbox",
"args": ["--prebuilt", "bigquery", "--stdio"],
"env": {
"BIGQUERY_PROJECT": "<PROJECT_ID>",
"GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT": "<PROJECT_ID>"
}
}
}
}
```### Verification with Claude Code
Now that we've completed the configuration, let's open Claude Code to check if the BigQuery tools are available.

As shown in the capture above, the list of available tools is displayed.
For this demonstration, I've copied the BigQuery public dataset `samples` to my environment.
First, let's check what tables are included in this dataset.
Here we'll use the `bigquery-list-table-ids` tool.
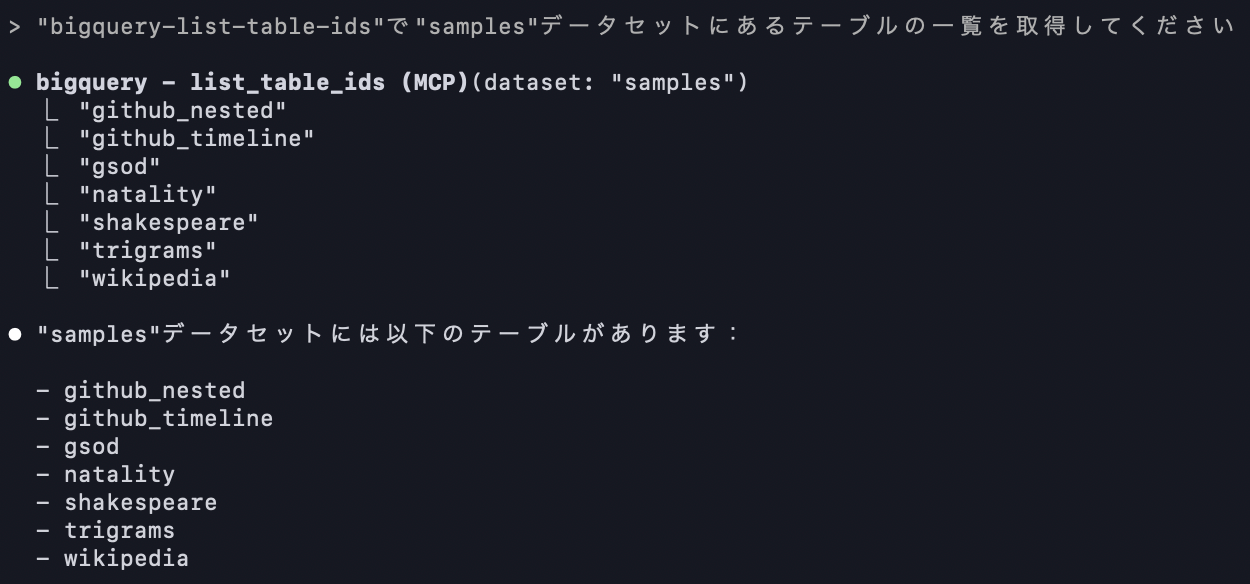
Next, let's check what kind of data is stored in the `gsod` table within the `samples` dataset.
For this operation, we'll use the `bigquery-get-table-info` tool.
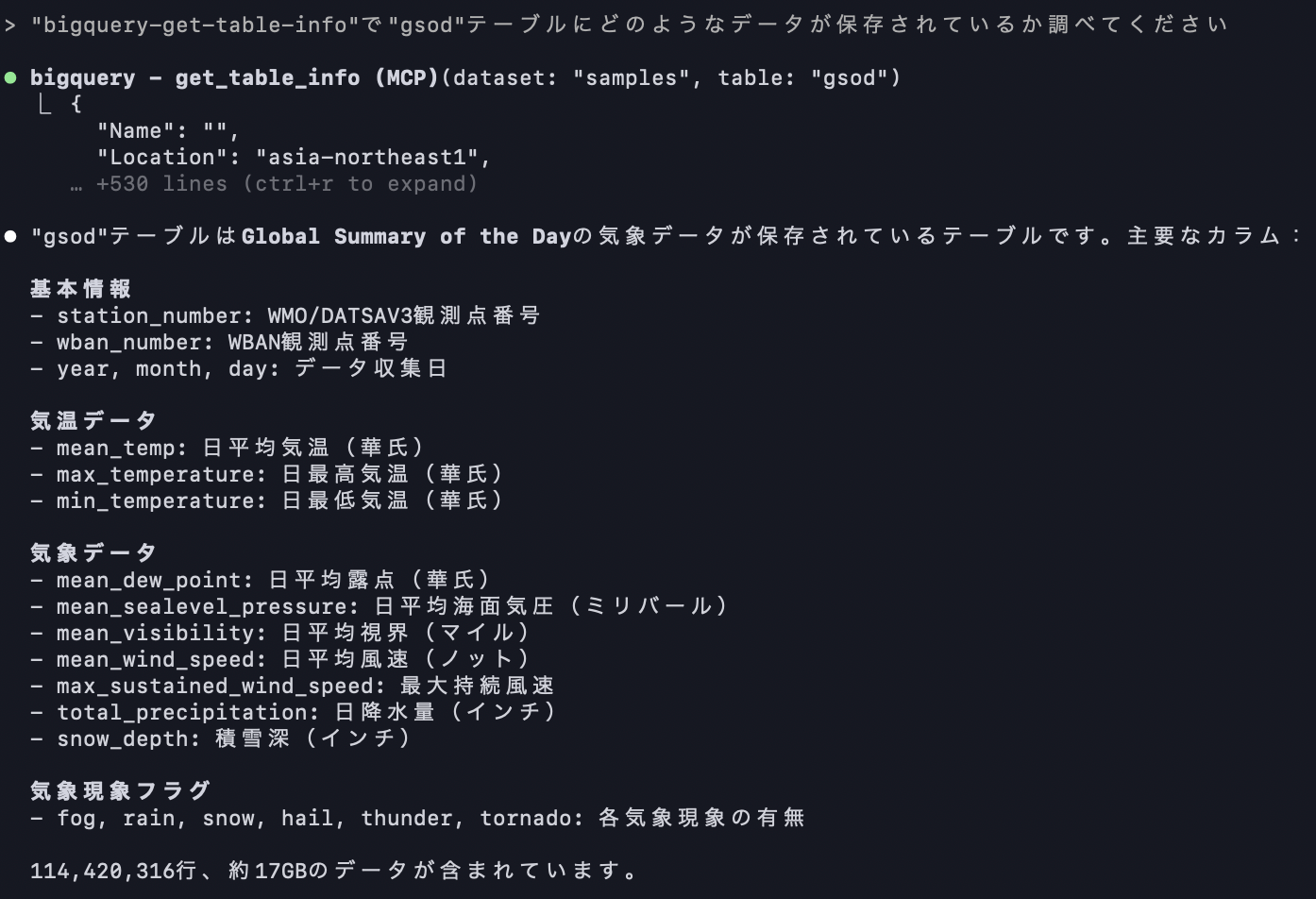
Finally, let's run a query using the `gsod` table data to aggregate the count by `year` and get the top 5 results.
Here we're using the `bigquery-execute-sql` tool to run an arbitrary SQL query.
The query content is displayed beforehand, so let's check it and execute if there are no issues.
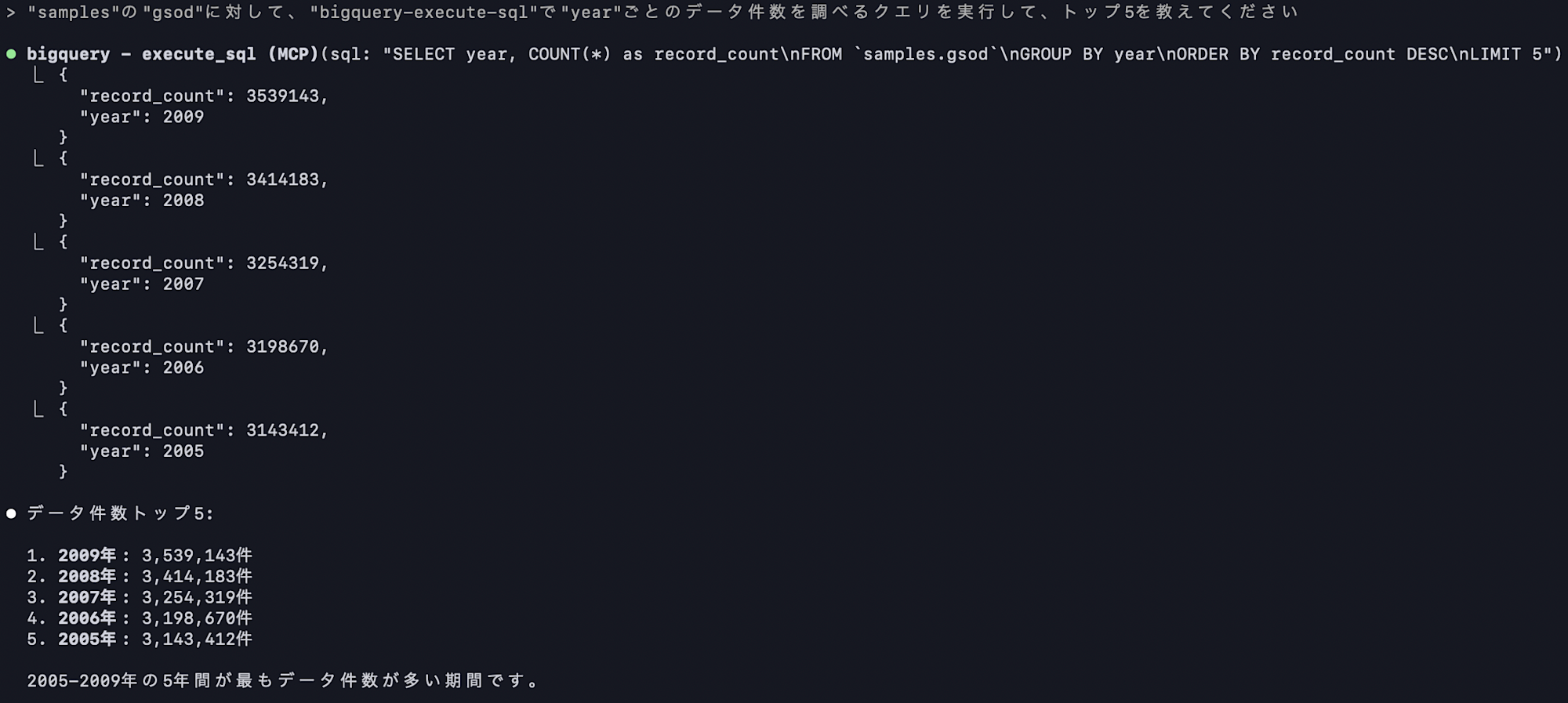
We got the expected results!
## Summary
In this article, we tried operating BigQuery using natural language through MCP Toolbox for Databases from Claude Code.
By using the pre-built tools provided, we were able to operate BigQuery easily without having to build our own MCP server.
Note that MCP Toolbox also allows you to host your own custom tools on an MCP server and use them from the client side.
If the pre-built tools aren't enough for your needs, please give this a try as well.
https://googleapis.github.io/genai-toolbox/samples/bigquery/mcp_quickstart/
Also, although we didn't go into much detail, there are risks associated with natural language operations.
There's a possibility of running high-cost queries or destructive queries.
To prevent such accidents, I think it's effective to minimize account permissions and restrict accessible projects and datasets.
Additionally, since natural language operations may generate unintended queries, I felt it's important to have mechanisms for checking queries before execution and reviewing them as needed.
https://www.yasuhisay.info/entry/2025/08/31/144559#google_vignette




![[新機能]dbt CloudでホストされたRemote MCP Serverがパブリックベータとしてリリースされました](https://images.ctfassets.net/ct0aopd36mqt/wp-thumbnail-f846b6052d1f7b983172226c6b1ed44b/6b4729aabfb5b7a3359acc27dc6b5453/dbt-1200x630-1.jpg)
