
I tried running a simple AI workflow using AWS Lambda Durable Function #AWSreInvent
This page has been translated by machine translation. View original
Hello, this is Morita.
AWS Lambda Durable Function, which was announced below, is a feature that enables long-running workflows that have traditionally been difficult to implement.
In this article, I'd like to actually implement this Durable Function in Python and verify its behavior.
Trying it out
Creating a Lambda
Durable Function is currently only available in the us-east-2 (Ohio) region as of December 2025.
When creating a Lambda in the AWS Management Console, you must enable Durable execution.
(I spent a bit of time here because it won't work if you miss this setting...! Be sure to check this when creating it.)

Checking the default code
When you successfully create a Lambda, the following Python code is provided by default.
from aws_durable_execution_sdk_python.config import Duration
from aws_durable_execution_sdk_python.context import DurableContext, StepContext, durable_step
from aws_durable_execution_sdk_python.execution import durable_execution
@durable_step
def my_step(step_context: StepContext, my_arg: int) -> str:
step_context.logger.info("Hello from my_step")
return f"from my_step: {my_arg}"
@durable_execution
def lambda_handler(event, context) -> dict:
msg: str = context.step(my_step(123))
context.wait(Duration.from_seconds(10))
context.logger.info("Waited for 10 seconds without consuming CPU.")
return {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": msg,
}
In this code, the handler is defined with the @durable_execution decorator, and internally it uses context.wait(Duration.from_seconds(10)) to pause execution for 10 seconds.
Running the default code and verifying the behavior
Let's run a test with this code as is.
After execution completes, you can check the final output results, just like with a regular Lambda.

However, this screen only shows the final result.
To check detailed processing such as execution pauses and resumptions, use the "Durable executions" tab in Lambda.
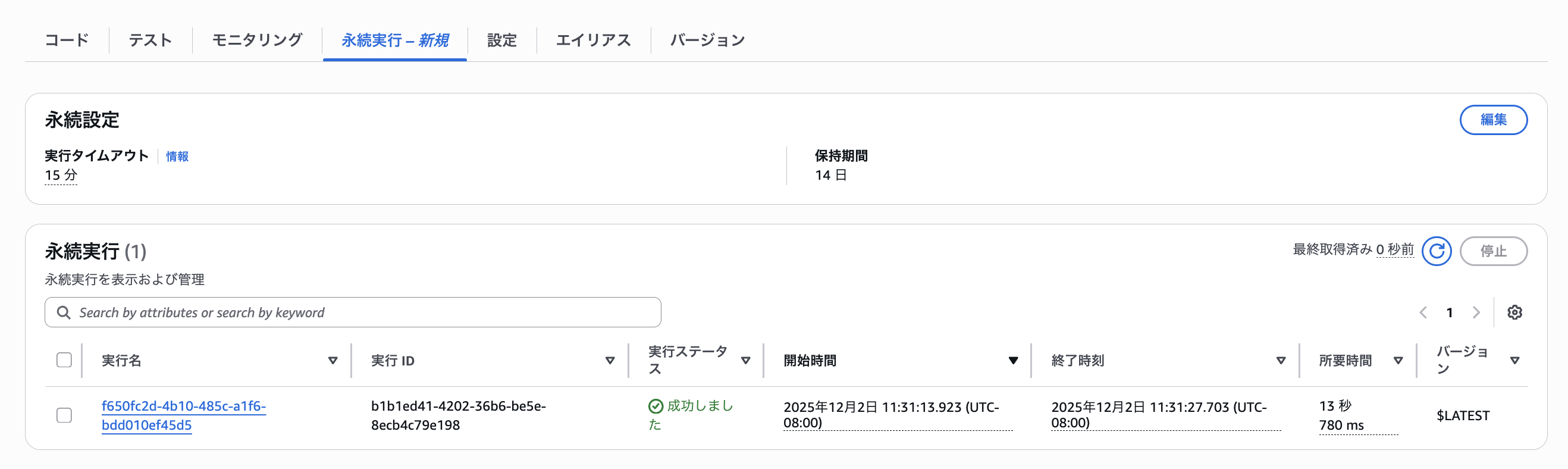
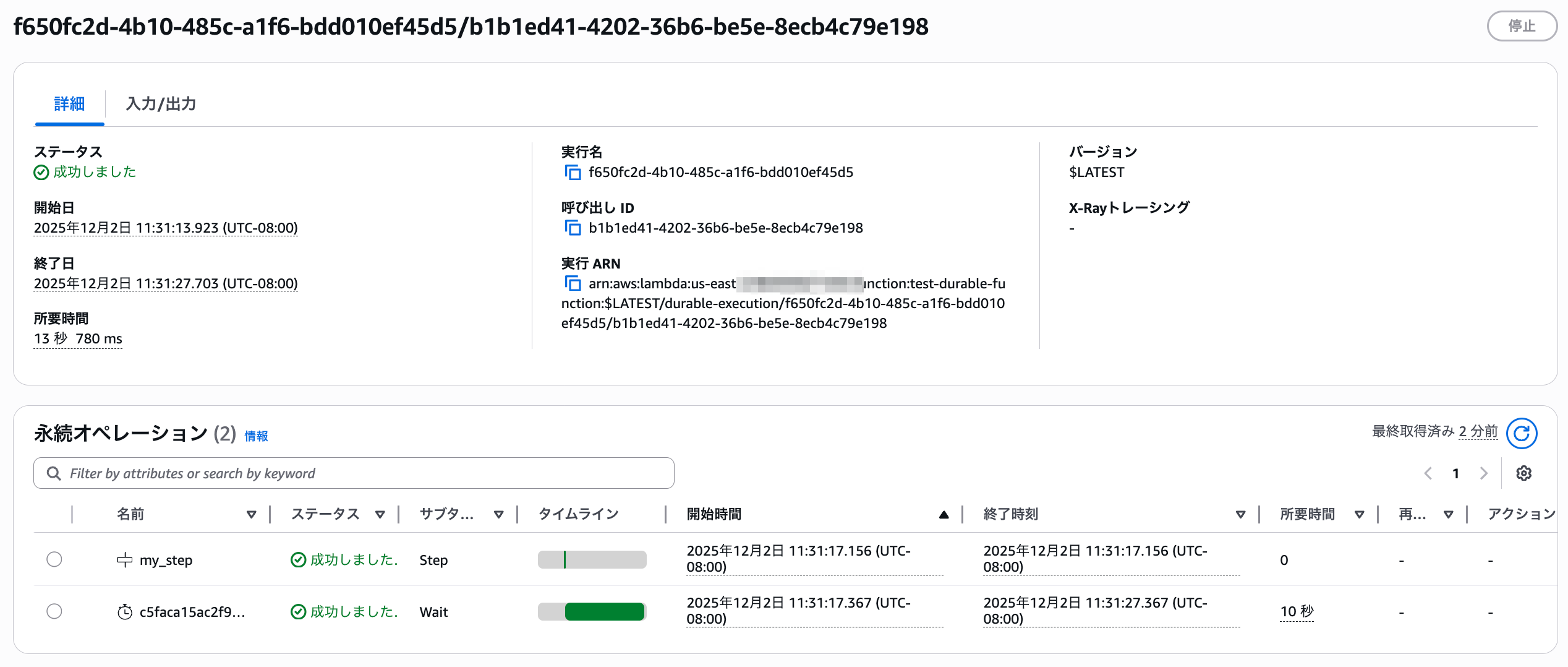
Clicking on the execution name opens the detailed screen as shown below, allowing you to track event information.
Callbacks
The above was simply a process that waits, but it supports various other processing cases as well.
Let's implement one of them - callbacks.
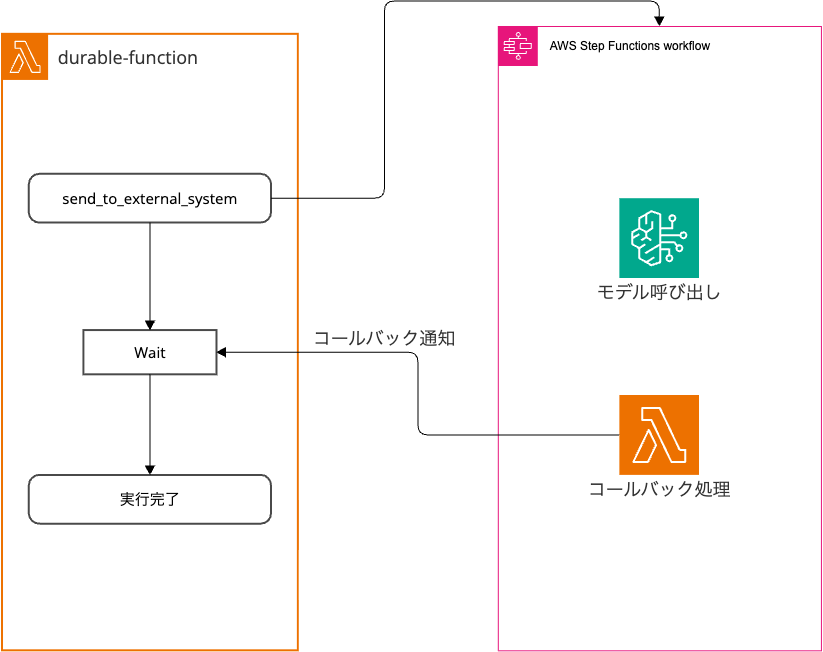
Using callbacks allows you to pause and wait for Lambda execution until a long-running external process completes.
import json
import os
import boto3
from typing import Any
from aws_durable_execution_sdk_python import DurableContext, durable_execution
from aws_durable_execution_sdk_python.config import CallbackConfig, Duration
# State machine ARN
state_machine_arn = os.getenv('STATE_MACHINE_ARN')
def send_to_external_system(data: dict) -> None:
sfn = boto3.client('stepfunctions')
response = sfn.start_execution(
stateMachineArn=state_machine_arn,
input=json.dumps(data)
)
@durable_execution
def lambda_handler(event: Any, context: DurableContext) -> dict:
"""Create a callback and wait for external system response."""
# Step 1: Create the callback
callback_config = CallbackConfig(
timeout=Duration.from_minutes(2),
heartbeat_timeout=Duration.from_seconds(60),
)
callback = context.create_callback(
name="example_callback",
config=callback_config,
)
# Step 2: Send callback ID to external system
# In a real scenario, you'd send this to a third-party API,
# message queue, or webhook endpoint
send_to_external_system({
"callback_id": callback.callback_id,
"text": event.get("text")
})
# Step 3: Wait for the result - execution suspends here
result = callback.result()
# Step 4: Execution resumes when result is received
return {
"status": "completed",
"result": result,
}
In the code above, the send_to_external_system function uses Step Functions as an external system.
It waits at result = callback.result() until it receives the execution result.
Step Functions
The Step Function is configured to call a Bedrock model and execute Callback processing (Lambda) as follows.
(Currently, Step Function actions don't support operations like send_durable_execution)
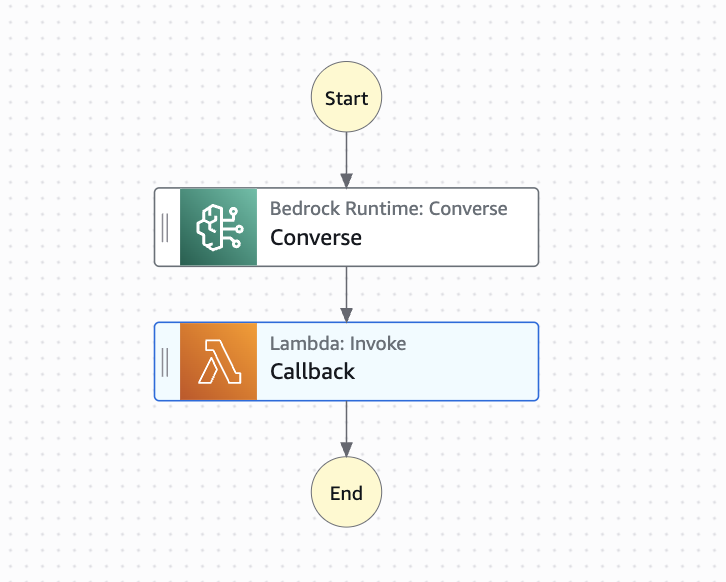
Overall Architecture
Callback Processing (Lambda)
import json
import boto3
lambda_client = boto3.client('lambda')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
callback_id = event['callback_id']
status = event['status']
result_data = event['result_data']
if status == 'success':
lambda_client.send_durable_execution_callback_success(
CallbackId=callback_id,
Result=result_data
)
else:
lambda_client.send_durable_execution_callback_failure(
CallbackId=callback_id,
Error={
'ErrorType': 'Error',
'ErrorMessage': result_data
}
)
# TODO implement
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps('Hello from Lambda!')
}
Execution Results
When we run it, this time it's recognized with the subtype Callback.
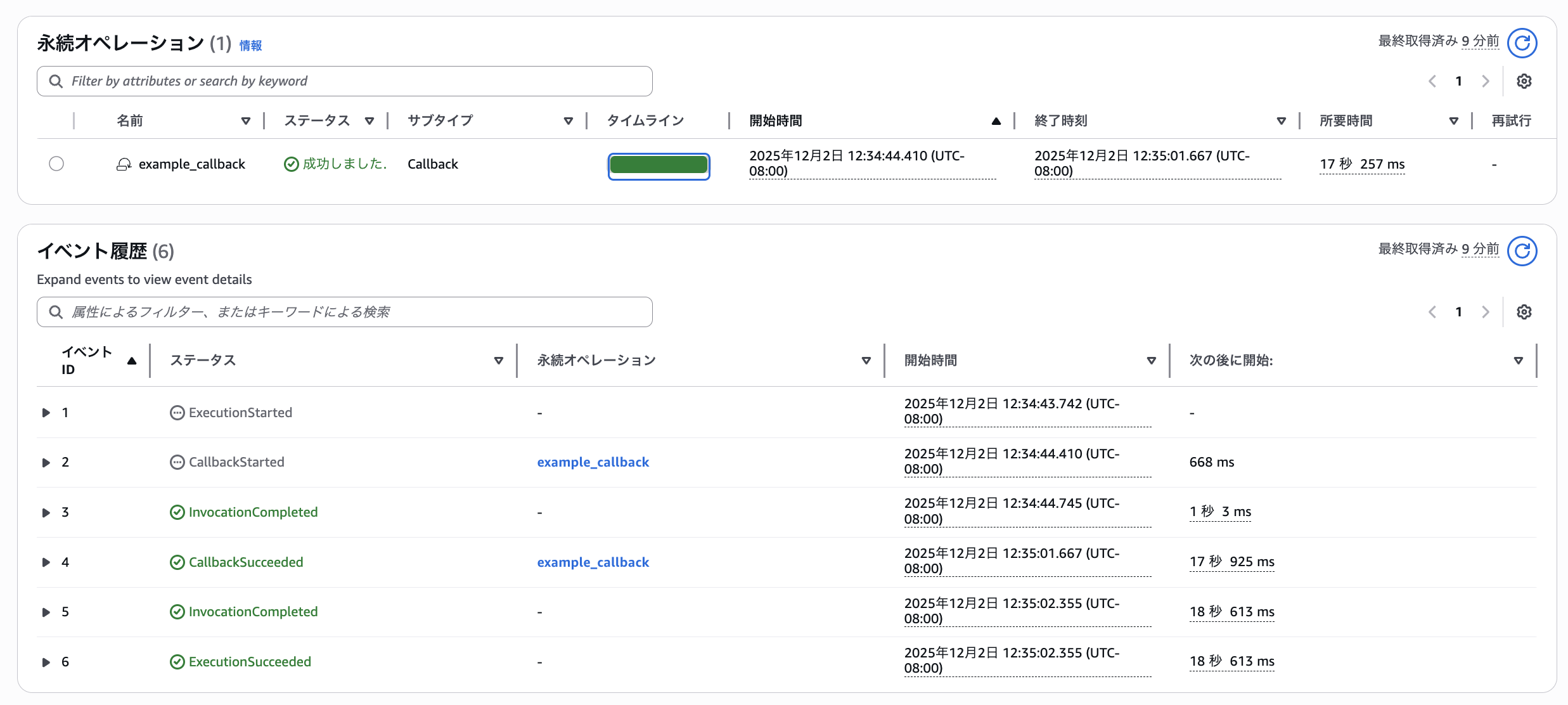
The execution results are also obtained successfully.
{
"status": "completed",
"result": "# AWSサービスのおすすめポイント\n\n## 1. 圧倒的なスケーラビリティ\n\nAWSの最大の魅力は、ビジネスの成長に合わせて柔軟にリソースを拡張できる点です。スタートアップの小規模なWebサイトから、数百万ユーザーを抱える大規模サービスまで、需要に応じて自動的にサーバー容量を調整できます。急なアクセス増加にも即座に対応でき、ビジネスチャンスを逃しません。\n\n## 2. 従量課金制によるコスト最適化\n\n従来のオンプレミス環境では、高額な初期投資が必要でした。AWSでは使った分だけ支払う従量課金制を採用しており、初期費用を大幅に削減できます。また、リザーブドインスタンスやスポットインスタンスを活用すれば、さらなるコスト削減も可能です。無駄なリソースを持つ必要がなく、経営効率の向上に直結します。\n\n## 3. 豊富なサービスラインナップ\n\nAWSは200以上のサービスを提供しており、あらゆるニーズに対応できます。コンピューティング(EC2)、ストレージ(S3)、データベース(RDS、DynamoDB)、機械学習(SageMaker)、IoT、セキュリティなど、必要な機能をすぐに利用開始できます。これにより、開発期間の短縮とイノベーションの加速が実現します。\n\n## 4. 高いセキュリティと信頼性\n\nAWSは世界中の政府機関や金融機関も採用する、業界最高水準のセキュリティを誇ります。データセンターは物理的なセキュリティから、暗号化、アクセス管理まで多層的に保護されています。また、複数のアベイラビリティゾーンを活用することで、99.99%以上の可用性を実現し、障害時も事業継続が可能です。\n\n## 5. グローバル展開の容易さ\n\n世界30以上のリージョンにデータセンターを持つAWSなら、海外展開も簡単です。数クリックで世界各地にサービスを展開でき、現地ユーザーに低遅延でサービスを提供できます。グローバルビジネスを目指す企業にとって、これは大きなアドバンテージとなります。\n\n## 6. 充実したサポートとエコシステム\n\nAWSには豊富なドキュメント、トレーニング、認定資格プログラムが用意されています。また、世界中のパートナー企業やコミュニティからのサポートも受けられます。技術的な課題に直面しても、解決策を見つけやすい環境が整っています。\n\n## まとめ\n\nAWSは、コスト効率、拡張性、セキュリティ、グローバル対応のすべてを兼ね備えたクラウドプラットフォームです。デジタルトランスフォーメーションを推進し、競争力を高めたい企業にとって、AWSは最適な選択肢といえるでしょう。"
}
Conclusion
In this article, I tried running the default Durable Function and callbacks, and I feel it's a service that can be applied to various use cases.
It also seems to support parallel processing and other features, so I'd like to try those out when I have the opportunity.



