
dbtの公式MCPサーバーを使ってモデルの情報を取得してみる
こんばんは、製造ビジネステクノロジー部の夏目です。
dbtが公式MCPサーバーを公開したので使ってみます。
dbt-mcp
dbtが公式に出したMCPサーバーです。
モデルの定義の取得などができます。
プロジェクトのディレクトリとdbtのCLI Toolへのパスを渡すとCLI Toolを実行することも可能なようです。
今回はCLI Toolなしで使える部分を試してみます。
使ってみる
dbtのMCPサーバーを使ってみます。
- 事前準備
- MCPサーバーをインストールする
- MCPサーバーの設定値に追加の設定を行う
- MCPサーバーを登録する
- 使ってみる
1. 事前準備
dbtのアカウントとデータを用意する必要があります。
今回はdbt cloudにアカウントを作り、公式のQuickstartを使ってデータを準備します。
- Quickstart for dbt Cloud and Redshift | dbt Developer Hub
- Quickstart for the dbt Cloud Semantic Layer and Snowflake | dbt Developer Hub
Semantic LayerのQuickstartはSnowflakeとタイトルについていますが、RedshiftでもできるとQuickstartに記載があったので、Redshiftで作成しました。
少々量があるので、今回はアカウントの作成とQuickstartの手順はここには書きません。
2. MCPサーバーをインストールする
Want to get going quickly?
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dbt-labs/dbt-mcp/refs/heads/main/install.sh)"The installer also serves as an updater, simply run it again and it will detect your exisiting dbt-mcp installation and offers to update it.
https://github.com/dbt-labs/dbt-mcp?tab=readme-ov-file#installation
MCPサーバーのREADME.mdによると、こちらのコマンドでインストールできるようです。
$ /bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dbt-labs/dbt-mcp/refs/heads/main/install.sh)"
(pipを使いインストールしている文章が流れる)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
We need a couple of details about your dbt project to get started.
You can always adjust the configuration later in <HOMEディレクトリ>/.dbt-mcp/.env
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Your dbt Cloud instance hostname.
This will look like an `Access URL` found at https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/cloud/about-cloud/access-regions-ip-addresses. If you are using Multi-cell, do not include the `ACCOUNT_PREFIX` here.
Enter DBT_HOST [cloud.dbt.com]: us1.dbt.com
Your personal access token or service token. Service token is required when using the Semantic Layer.
Enter DBT_TOKEN: dbtc_xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Your dbt Cloud user ID.
Enter DBT_USER_ID: 00000000000000
The path to your dbt project directory.
Enter DBT_PROJECT_DIR:
Your dbt Cloud production environment ID.
Enter DBT_PROD_ENV_ID: 00000000000000
Your dbt Cloud development environment ID.
Enter DBT_DEV_ENV_ID: 00000000000000
The path to your dbt Core or dbt Cloud CLI executable. You can find your dbt executable by running `which dbt`.
Enter DBT_PATH:
If you are using Multi-cell, set this to your `ACCOUNT_PREFIX`. If you are not using Multi-cell, do not set this environment variable. You can learn more here : https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/cloud/about-cloud/access-regions-ip-addresses.
Enter MULTICELL_ACCOUNT_PREFIX: dv000
Great! That's all we needed for now.
You can always adjust the configuration later in <HOMEディレクトリ>/.dbt-mcp/.env
Installation and configuration complete!
Have a great day!
基本的な値はインストールの際に入力し、 <HOMEディレクトリ>/.dbt-mcp/.env に書き込まれます。
必要な値を集める過程も書いていきます。
DBT_HOST
Your dbt Cloud instance hostname.
This will look like an `Access URL` found at https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/cloud/about-cloud/access-regions-ip-addresses. If you are using Multi-cell, do not include the `ACCOUNT_PREFIX` here.
Enter DBT_HOST [cloud.dbt.com]: us1.dbt.com
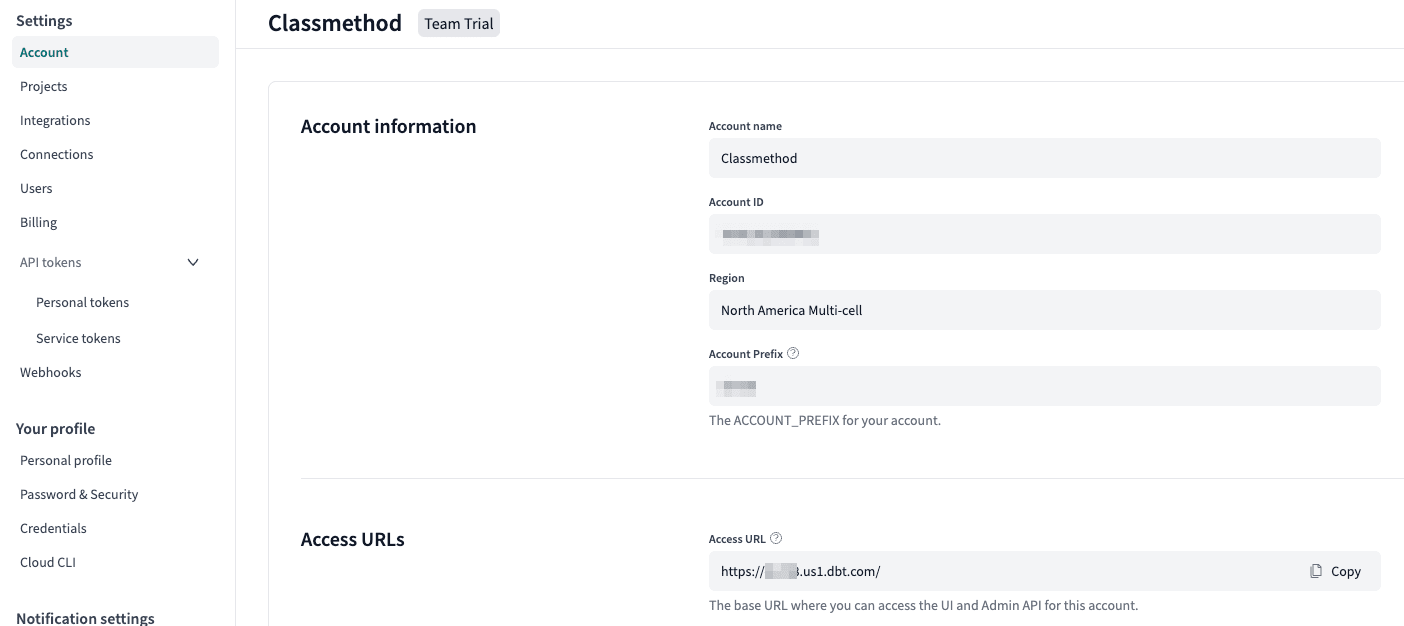
こちらにはホストネームを入力します。
この値を探します。
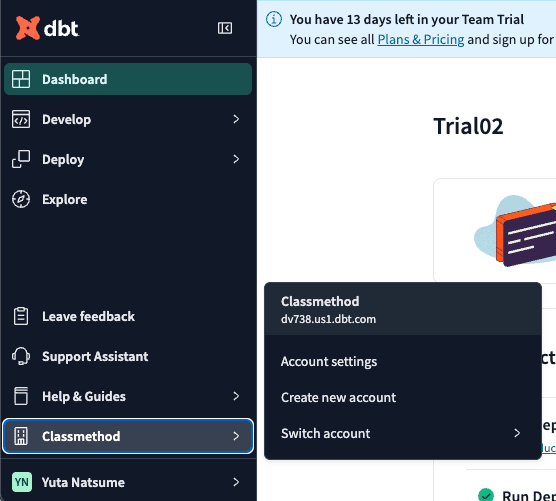
左下の会社名(ここでは Classmethod )をクリックし、 Account settings を
クリックします。
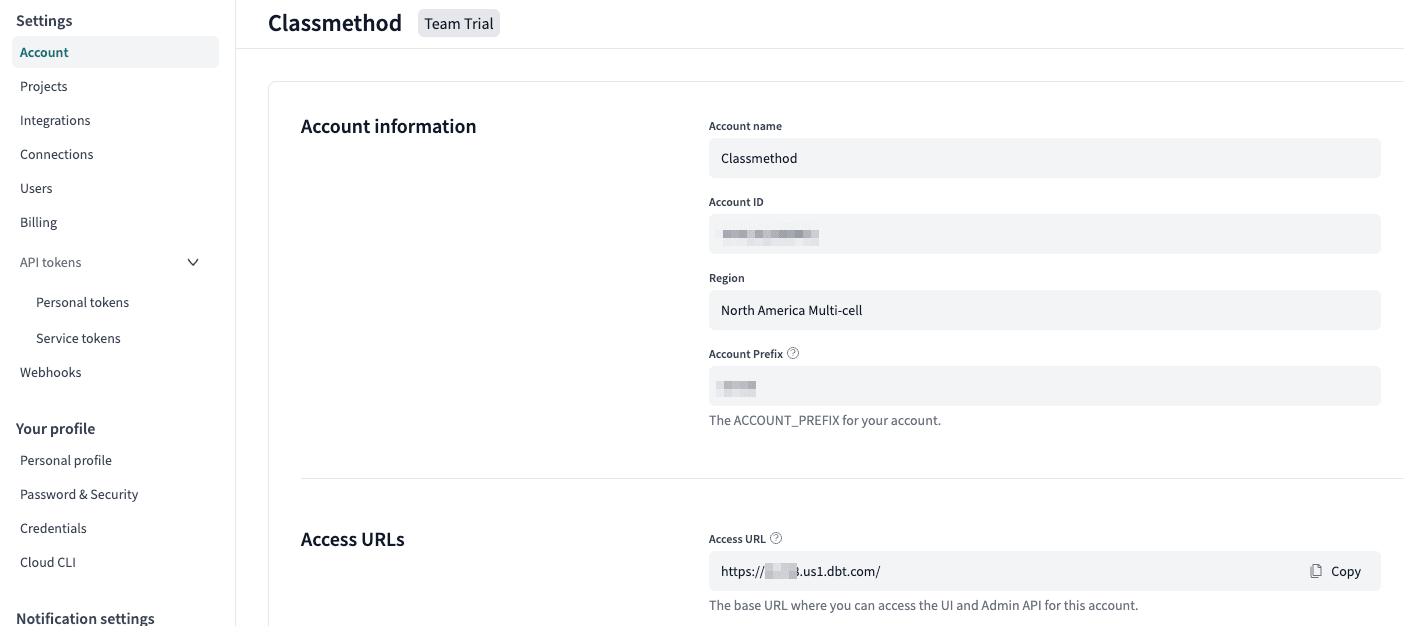
Access URLs の Access URL を見ます。
このアカウントはMulti-cellのRegionなので、 Account Prefix を除く us1.dbt.com を DBT_HOST に設定します。
DBT_TOKEN
Your personal access token or service token. Service token is required when using the Semantic Layer.
Enter DBT_TOKEN: dbtc_xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
今回はService Tokenを作成して、使用します。
左の API tokens 配下の Service tokens をクリックします。
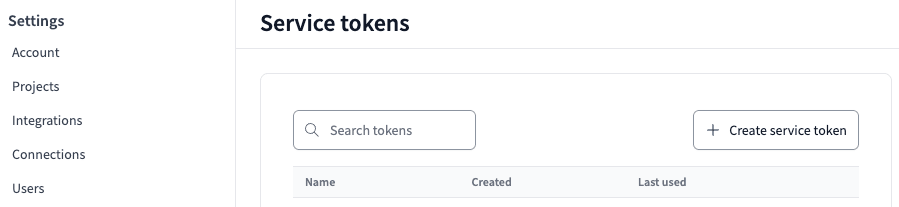
Create service token をクリックします。
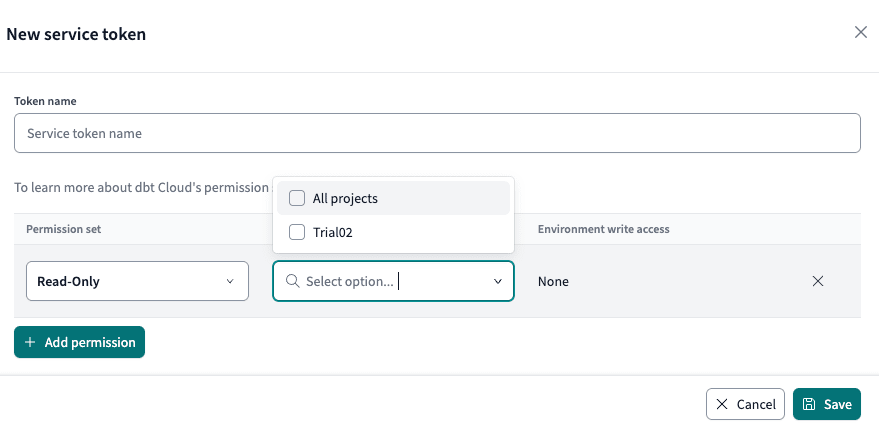
Add permission をクリックして権限を追加します。
今回は Read Only を設定します。
対象のプロジェクトとして All projects にすることもできますし、特定のプロジェクトだけにすることもできます。
Token name に任意の名前を入力します。
右下の Save をクリックします。
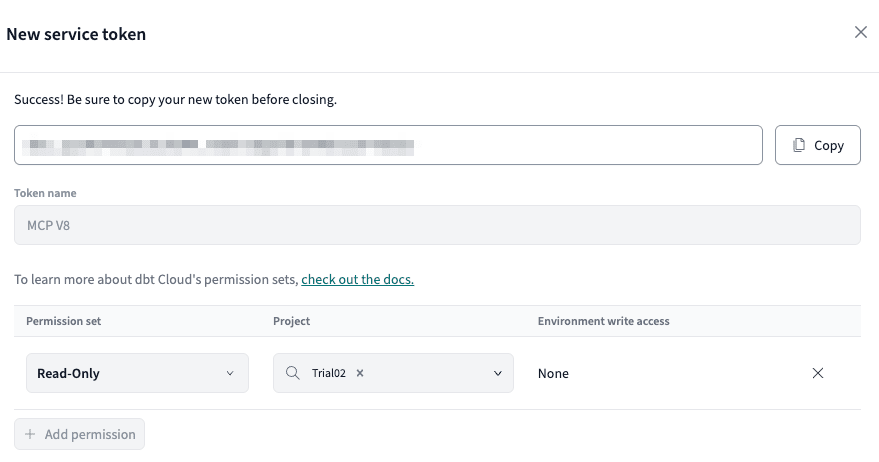
Service Tokenが発行されました。
この画面を閉じるとTokenは見えなくなるので、注意してください。
DBT_USER_ID
Your dbt Cloud user ID.
Enter DBT_USER_ID: 00000000000000
ユーザーIDを取得します。
左の Users をクリックします。
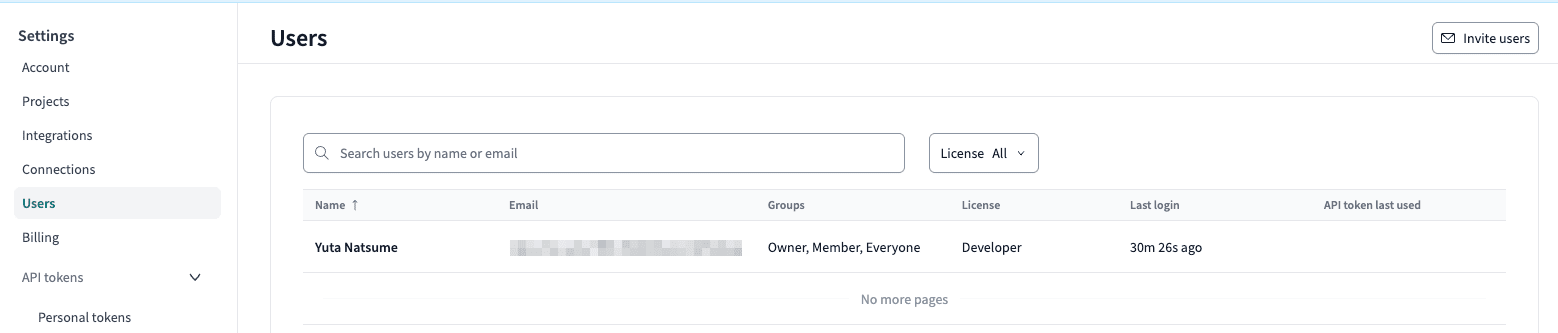
自分の名前の行をクリックします。
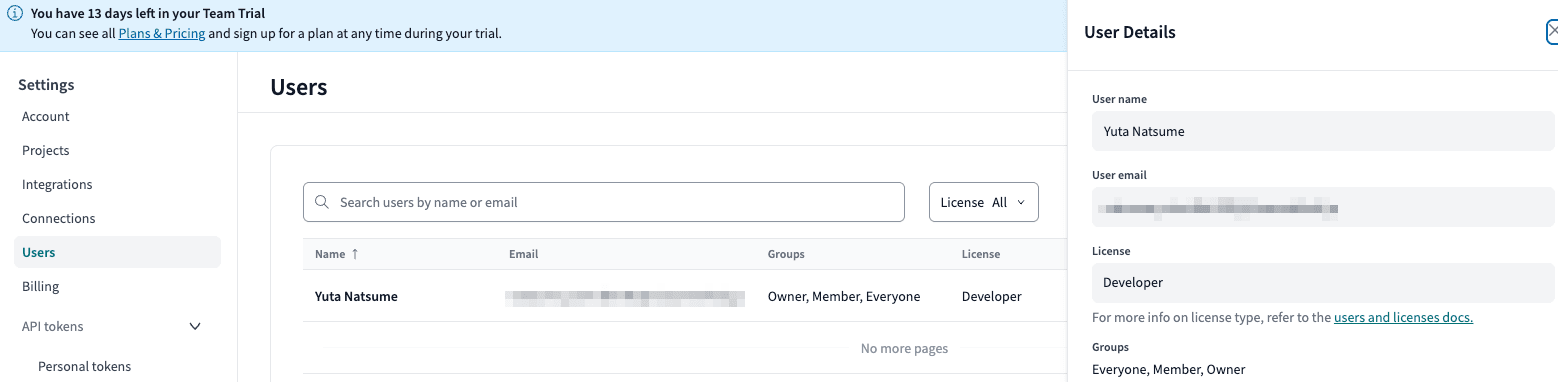
画面右側にユーザーの詳細が表示されます。
このときのURLにユーザーIDが含まれています。
https://dv000.us1.dbt.com/settings/accounts/00000000000000/pages/users/99999999999999
99999999999999 と書いた部分がユーザーIDです。
DBT_PROJECT_DIR
The path to your dbt project directory.
Enter DBT_PROJECT_DIR:
今回はdbtのCLI Toolを使わないので、空のままEnterを押します。
DBT_PROD_ENV_ID, DBT_DEV_ENV_ID
Your dbt Cloud production environment ID.
Enter DBT_PROD_ENV_ID: 00000000000000
Your dbt Cloud development environment ID.
Enter DBT_DEV_ENV_ID: 00000000000000
dbtのEnvironmentのIDを集めてきます。
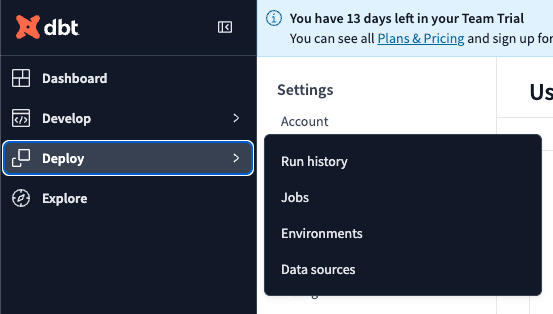
先ほどのユーザーIDと同様にEnvironmentのIDもURLに含まれます。
Deploy をクリックし、出てきた窓の Environments をクリックします。
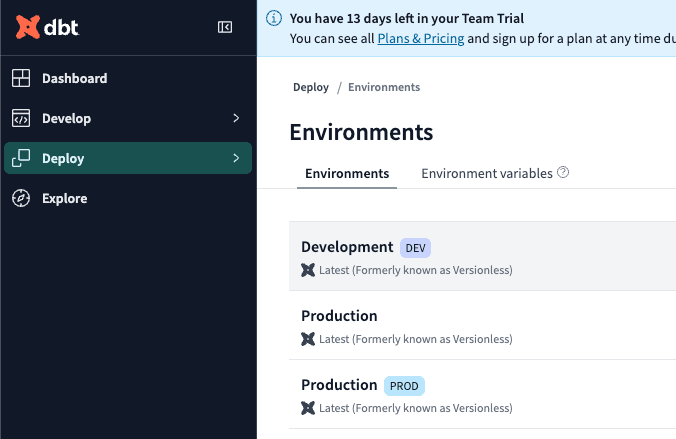
まず DBT_PROD_ENV_ID の値を求めるので、 PROD のマークがついた Production の行をクリックします。
(検証中Environmentを作る際に間違えて二つ Productionがあります。わかりにくくてすみません)
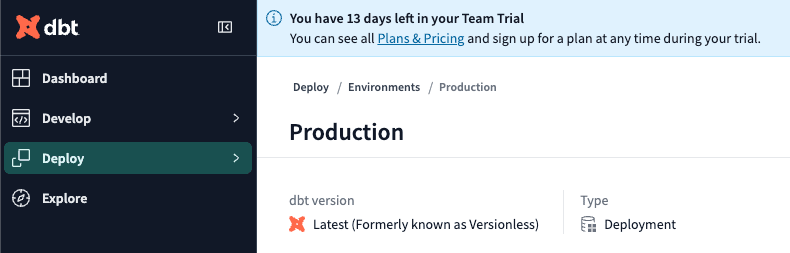
Environmentの画面になりました。
このときのURLにEnvironmentのIDが含まれています。
https://dv000.us1.dbt.com/deploy/00000000000000/projects/00000000000000/environments/99999999999999
99999999999999 と書いたところがEnvironmentのIDです。
同様にして、 DBT_DEV_ENV_ID の値を取得します。
DBT_PATH
The path to your dbt Core or dbt Cloud CLI executable. You can find your dbt executable by running `which dbt`.
Enter DBT_PATH:
dbtのCLI Toolは今回使用しないので、空のままEnterを押します。
MULTICELL_ACCOUNT_PREFIX
If you are using Multi-cell, set this to your `ACCOUNT_PREFIX`. If you are not using Multi-cell, do not set this environment variable. You can learn more here : https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/cloud/about-cloud/access-regions-ip-addresses.
Enter MULTICELL_ACCOUNT_PREFIX: dv000
このアカウントはMulti-cellだったので、値を入力します。
DBT_HOST を取得するのに見た、 Account settings を見ます。
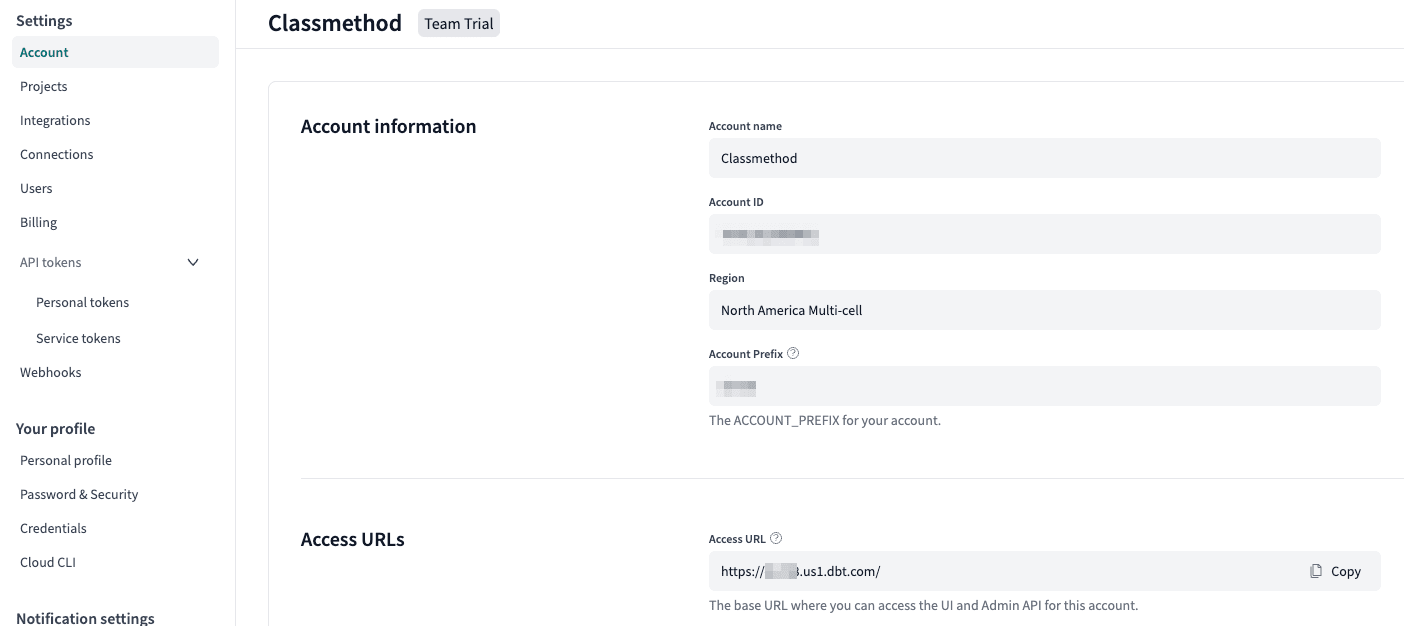
Account Prefix に書かれている値を使用します。
3. MCPサーバーの設定値に追加の設定を行う
今回試すにはもう少し設定をいじる必要があるので、 .envファイルに追記をします。
DBT_HOST="us1.dbt.com"
DBT_TOKEN="dbtc_VS_xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
DBT_PROD_ENV_ID="00000000000000"
DBT_DEV_ENV_ID="00000000000000"
DBT_USER_ID="00000000000000"
DBT_PROJECT_DIR=""
DBT_PATH=""
MULTICELL_ACCOUNT_PREFIX="dv000"
# 追記分
DISABLE_REMOTE="false"
DISABLE_DBT_CLI="true"
DISABLE_REMOTE と DISABLE_DBT_CLI を追記しています。
今回はローカルのプロジェクトを使用しないのでこれらを追記する必要があります。
4. MCPサーバーを登録する
{
"mcpServers": {
"dbt": {
"command": "<HOMEディレクトリ>/.dbt-mcp/dbt-mcp",
"args": [],
}
}
}
MCPサーバーをクライエントに登録します。
<HOMEディレクトリ> はそれぞれの環境にあわせて書いてください。
5. 使ってみる
モデルの一覧を取得する

プロンプト
dbtのモデル一覧を取得してください
結果
dbtのモデル一覧を取得します。dbtに登録されているすべてのモデルを確認しましょう。
get_all_models
リクエスト{}レスポンス{"name": "agg_customers", "description": "One record per customer"}レスポンス{"name": "dim_customers", "description": ""}レスポンス{"name": "fct_orders", "description": ""}レスポンス{"name": "metricflow_time_spine", "description": ""}レスポンス{"name": "stg_customers", "description": "This model cleans up customer data"}レスポンス{"name": "stg_orders", "description": "This model cleans up order data"}レスポンス{"name": "stg_sl_customers", "description": ""}レスポンス{"name": "stg_sl_orders", "description": ""}レスポンス{"name": "stg_sl_payments", "description": ""}dbtに登録されている全モデルのリストを取得しました。以下が現在のdbt環境に存在するモデルです:
- agg_customers - 顧客ごとに1レコード
- dim_customers - 説明なし
- fct_orders - 説明なし
- metricflow_time_spine - 説明なし
- stg_customers - このモデルは顧客データをクリーニングします
- stg_orders - このモデルは注文データをクリーニングします
- stg_sl_customers - 説明なし
- stg_sl_orders - 説明なし
- stg_sl_payments - 説明なし
モデルはステージングモデル(stg_)、ディメンションモデル(dim_)、ファクトモデル(fct_)、集計モデル(agg_)など、dbtの一般的な命名規則に従って整理されていることがわかります。特定のモデルについて詳細情報が必要であれば、お知らせください。
モデルの一覧を取得できました。
RedshiftのQuickstartでドキュメントを整備したモデルは説明を取得できています。
(逆にSemantic LayerのQuickstartで作成したモデルは、ドキュメントの整備をしていないので、説明なしになっています)
モデルの詳細を取得してみる
プロンプト
agg_customersの詳細を取得してください
結果
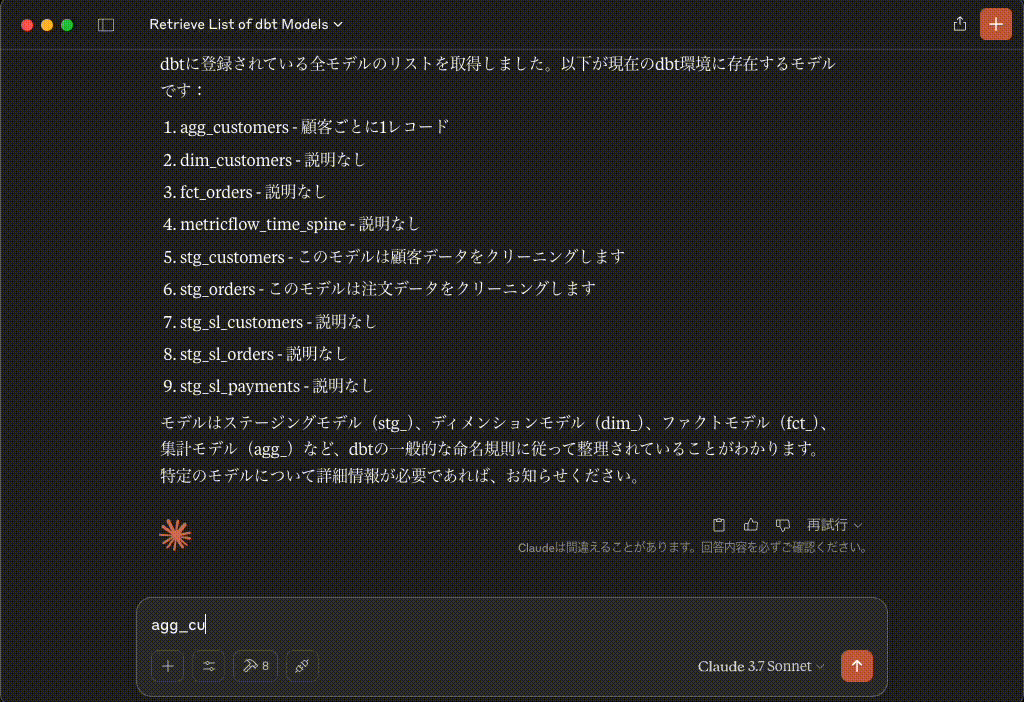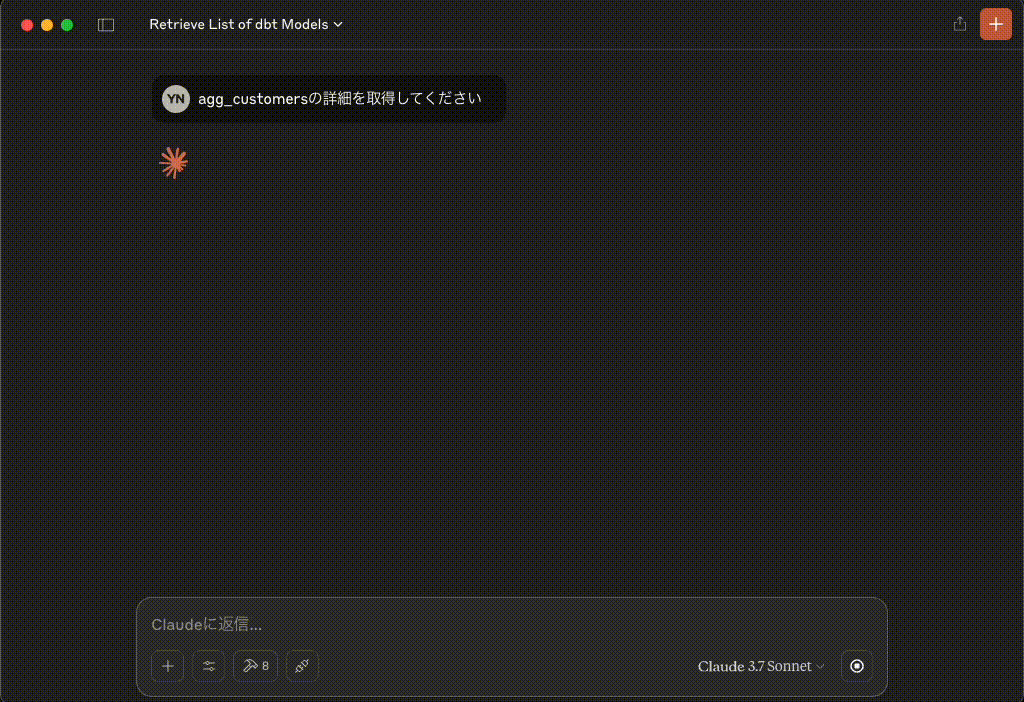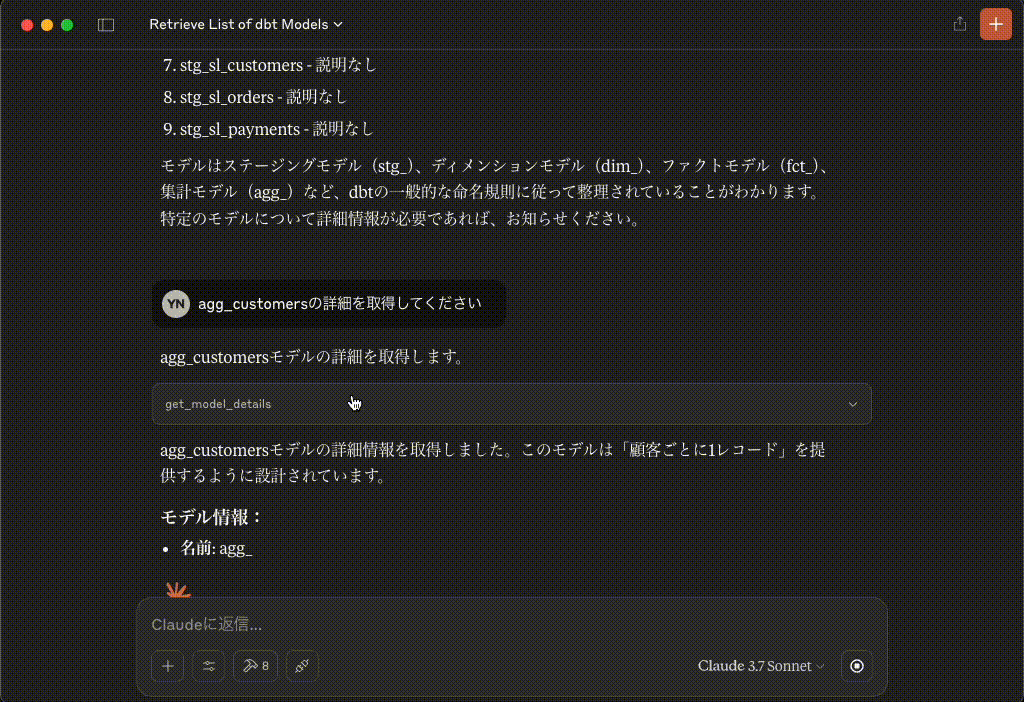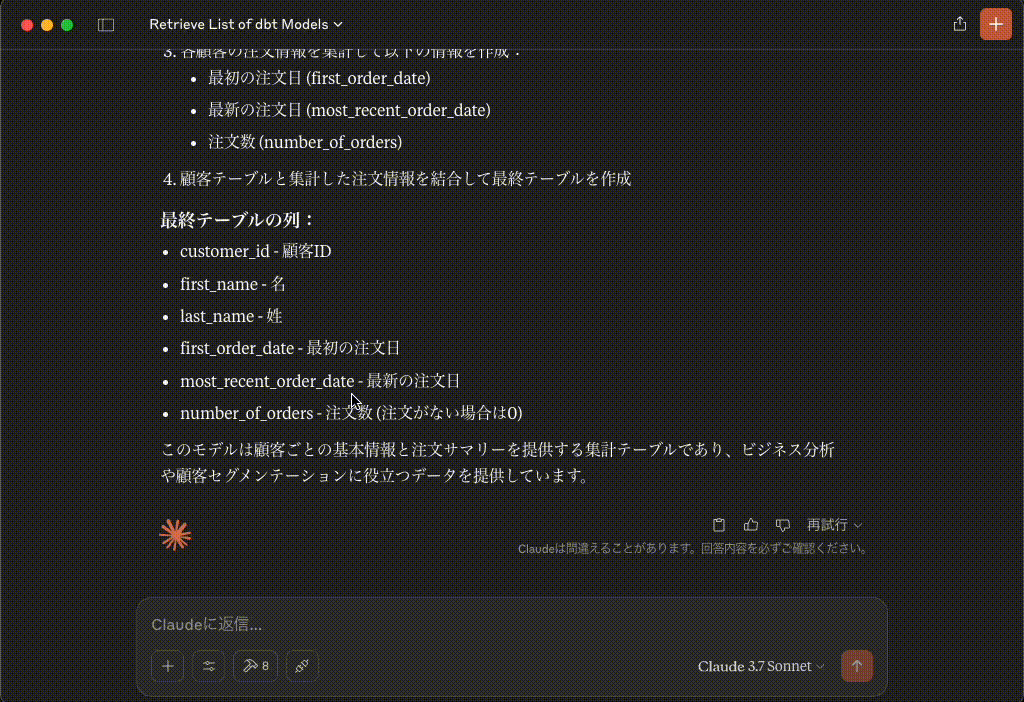
agg_customersモデルの詳細を取得します。
get_model_details
リクエスト{ `model_name`: `agg_customers` }レスポンス{"name": "agg_customers", "compiledCode": "\n\nwith customers as (\n\n select * from \"dbtworkshop\".\"dbt_production_v3\".\"stg_customers\"\n\n),\n\norders as (\n\n select * from \"dbtworkshop\".\"dbt_production_v3\".\"stg_orders\"\n\n),\n\ncustomer_orders as (\n\n select\n customer_id,\n\n min(order_date) as first_order_date,\n max(order_date) as most_recent_order_date,\n count(order_id) as number_of_orders\n\n from orders\n\n group by 1\n\n),\n\nfinal as (\n\n select\n customers.customer_id,\n customers.first_name,\n customers.last_name,\n customer_orders.first_order_date,\n customer_orders.most_recent_order_date,\n coalesce(customer_orders.number_of_orders, 0) as number_of_orders\n\n from customers\n\n left join customer_orders using (customer_id)\n\n)\n\nselect * from final", "description": "One record per customer", "database": "dbtworkshop", "schema": "dbt_production_v3", "catalog": null}agg_customersモデルの詳細情報を取得しました。このモデルは「顧客ごとに1レコード」を提供するように設計されています。
モデル情報:
- 名前: agg_customers
- 説明: One record per customer (顧客ごとに1レコード)
- データベース: dbtworkshop
- スキーマ: dbt_production_v3
SQLコード解析:
このモデルは以下のような処理を行っています:
stg_customersテーブルから顧客データを取得stg_ordersテーブルから注文データを取得- 各顧客の注文情報を集計して以下の情報を作成:
- 最初の注文日 (first_order_date)
- 最新の注文日 (most_recent_order_date)
- 注文数 (number_of_orders)
- 顧客テーブルと集計した注文情報を結合して最終テーブルを作成
最終テーブルの列:
- customer_id - 顧客ID
- first_name - 名
- last_name - 姓
- first_order_date - 最初の注文日
- most_recent_order_date - 最新の注文日
- number_of_orders - 注文数 (注文がない場合は0)
このモデルは顧客ごとの基本情報と注文サマリーを提供する集計テーブルであり、ビジネス分析や顧客セグメンテーションに役立つデータを提供しています。
モデルの詳細を取得できました。
ドキュメントを整備したモデルだと色々データが取れます。
次に、ドキュメントを整備していないモデルを取得してみます。
プロンプト
fct_ordersの詳細を取得してください。
結果
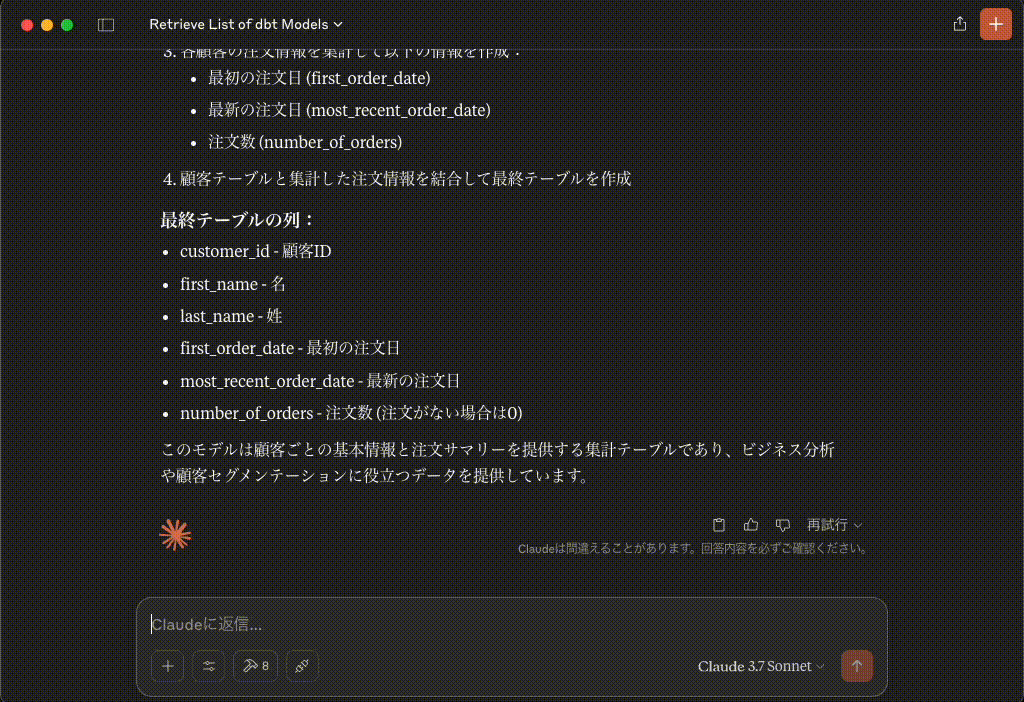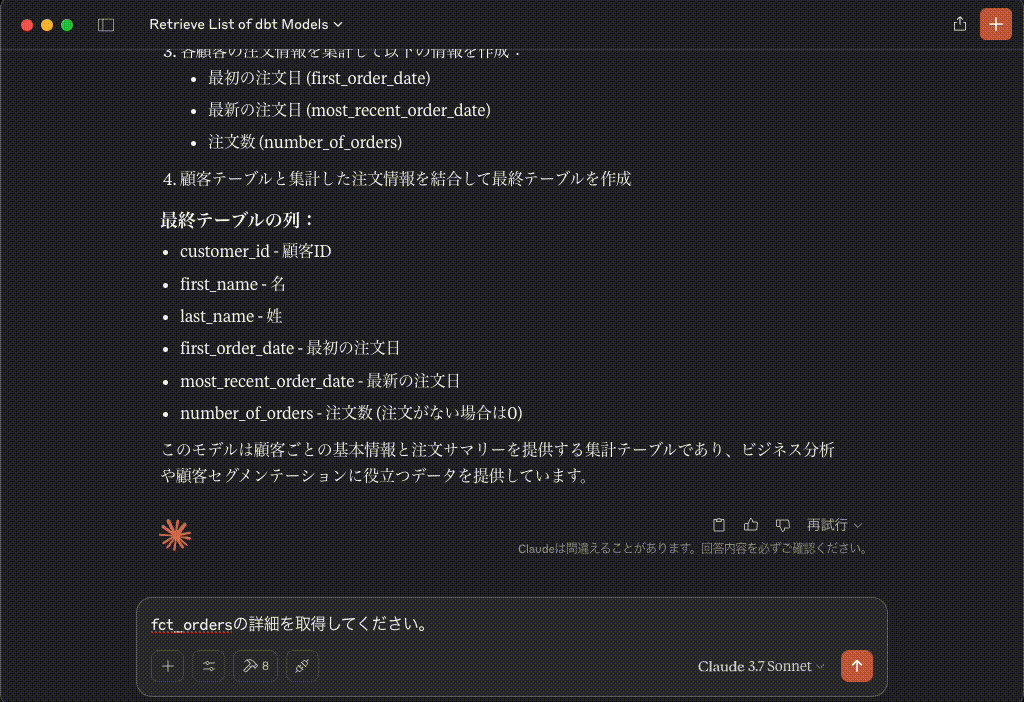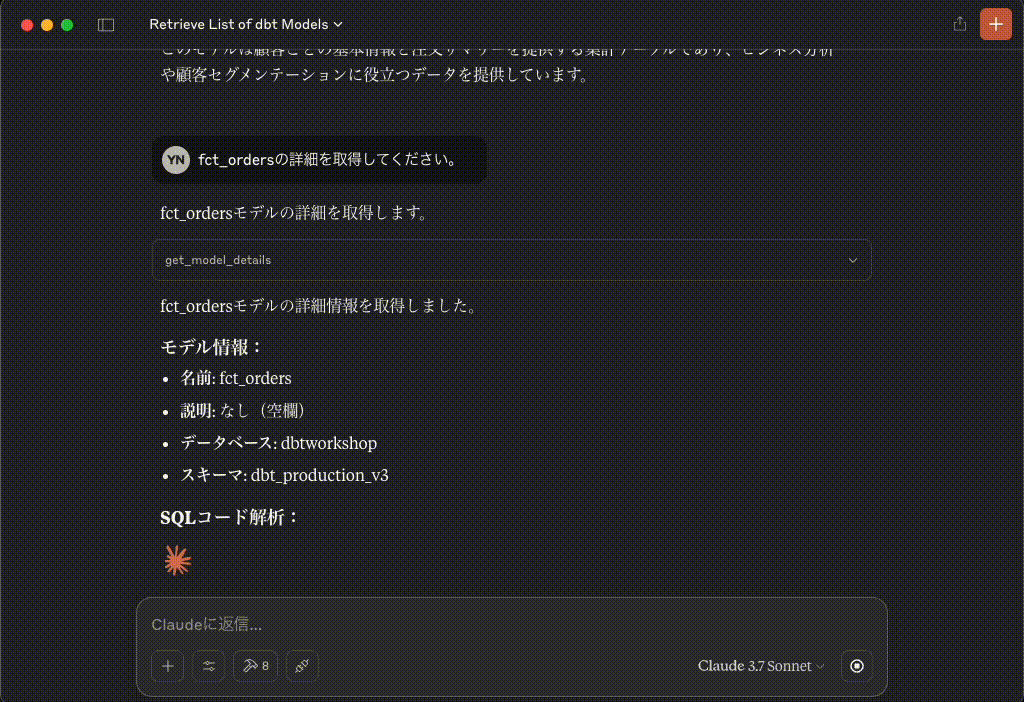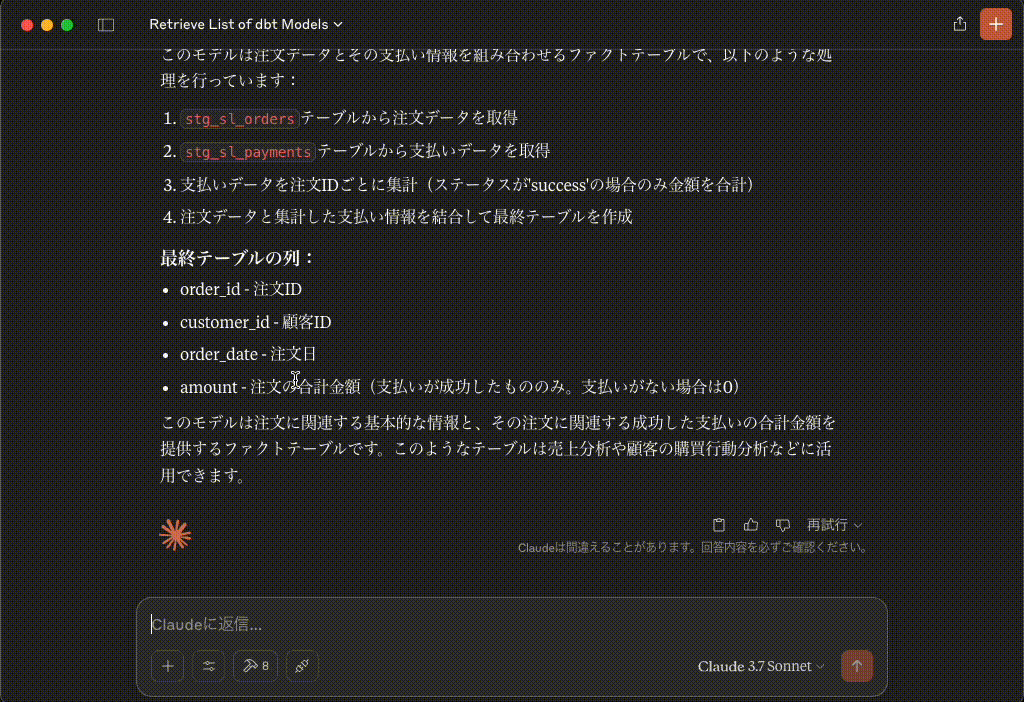
fct_ordersモデルの詳細を取得します。
get_model_details
リクエスト{ `model_name`: `fct_orders` }レスポンス{"name": "fct_orders", "compiledCode": "with orders as (\n select * from \"dbtworkshop\".\"dbt_production_v3\".\"stg_sl_orders\"\n),\n\n\npayments as (\n select * from \"dbtworkshop\".\"dbt_production_v3\".\"stg_sl_payments\"\n),\n\n\norder_payments as (\n select\n order_id,\n sum(case when status = 'success' then amount end) as amount\n\n\n from payments\n group by 1\n),\n\n\nfinal as (\n\n\n select\n orders.order_id,\n orders.customer_id,\n orders.order_date,\n coalesce(order_payments.amount, 0) as amount\n\n\n from orders\n left join order_payments using (order_id)\n)\n\n\nselect * from final", "description": "", "database": "dbtworkshop", "schema": "dbt_production_v3", "catalog": null}fct_ordersモデルの詳細情報を取得しました。
モデル情報:
- 名前: fct_orders
- 説明: なし(空欄)
- データベース: dbtworkshop
- スキーマ: dbt_production_v3
SQLコード解析:
このモデルは注文データとその支払い情報を組み合わせるファクトテーブルで、以下のような処理を行っています:
stg_sl_ordersテーブルから注文データを取得stg_sl_paymentsテーブルから支払いデータを取得- 支払いデータを注文IDごとに集計(ステータスが'success'の場合のみ金額を合計)
- 注文データと集計した支払い情報を結合して最終テーブルを作成
最終テーブルの列:
- order_id - 注文ID
- customer_id - 顧客ID
- order_date - 注文日
- amount - 注文の合計金額(支払いが成功したもののみ。支払いがない場合は0)
このモデルは注文に関連する基本的な情報と、その注文に関連する成功した支払いの合計金額を提供するファクトテーブルです。このようなテーブルは売上分析や顧客の購買行動分析などに活用できます。
特定のモデルの親モデルを取得する
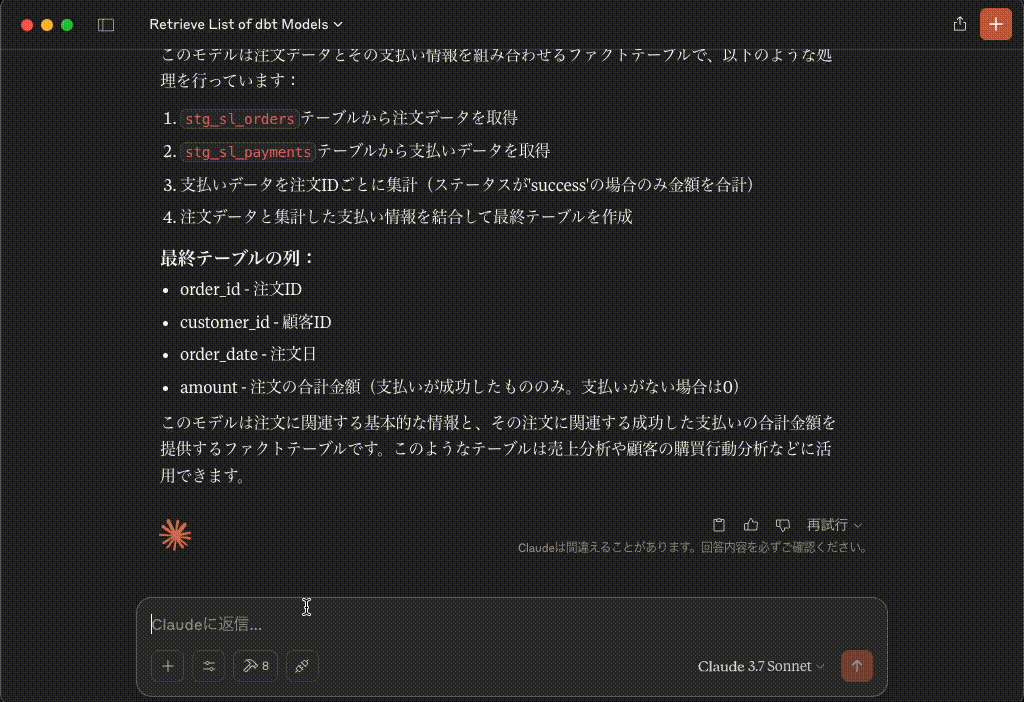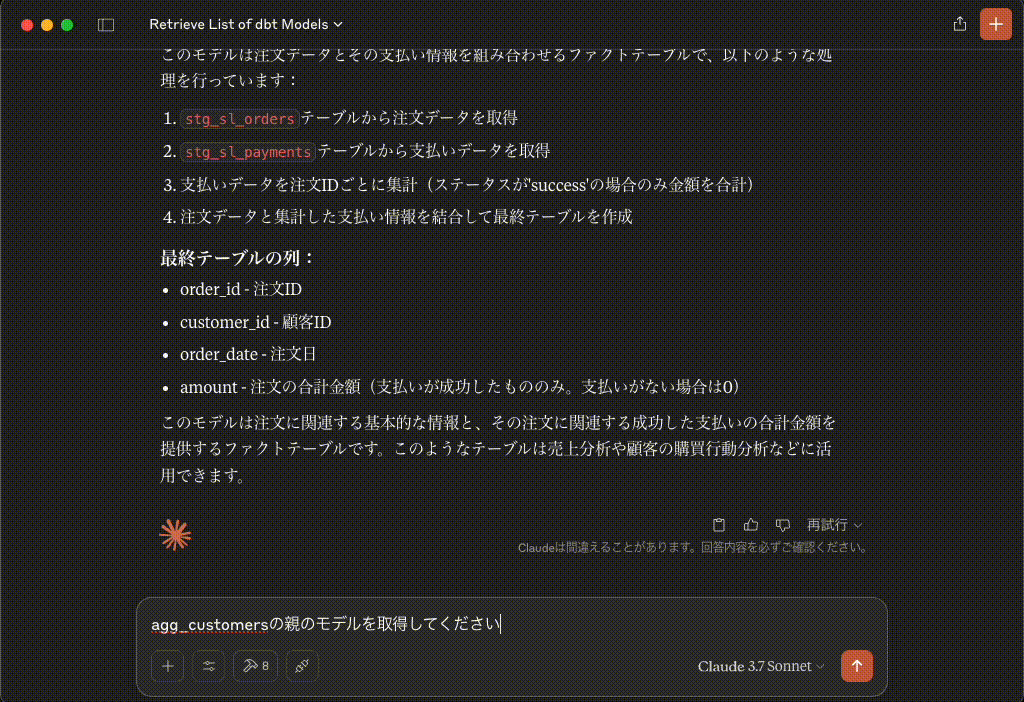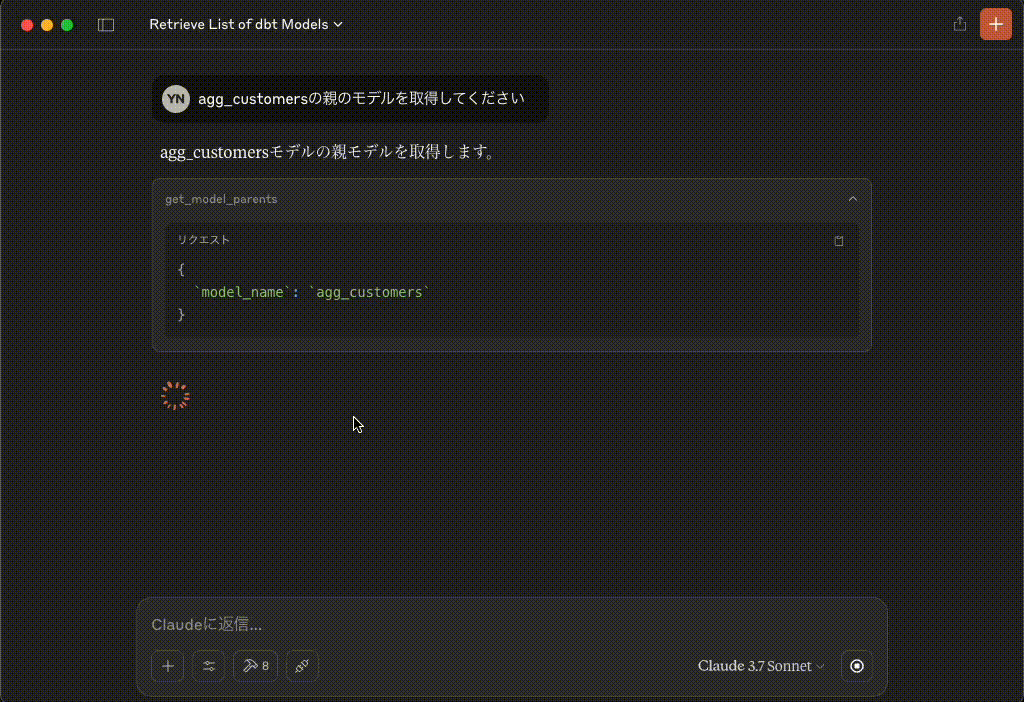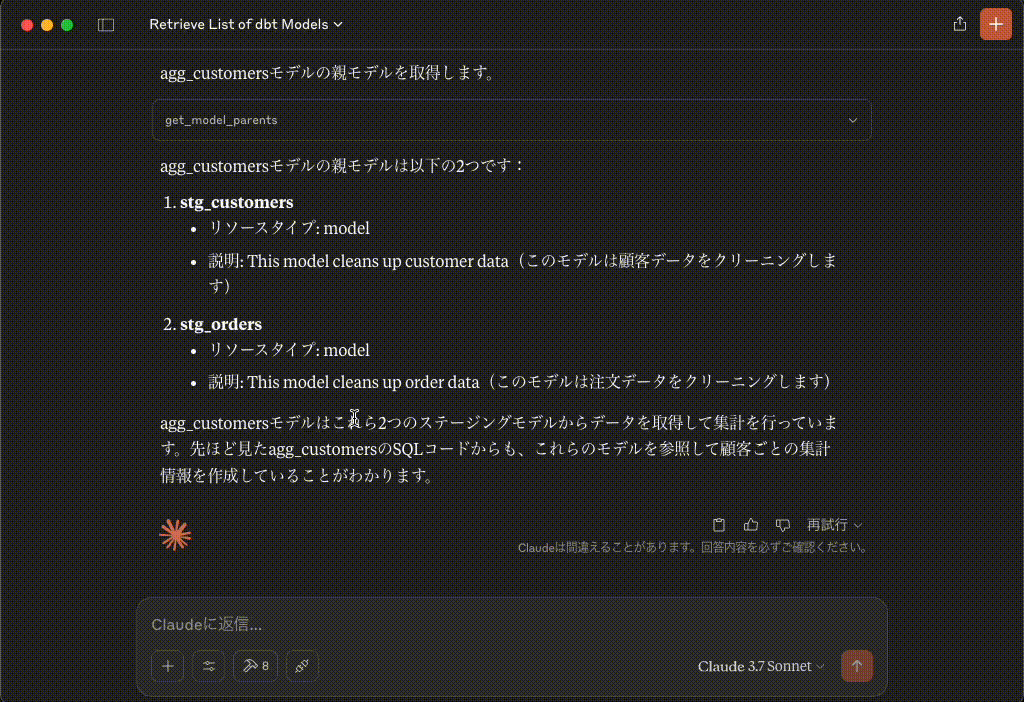
プロンプト
agg_customersの親のモデルを取得してください
結果
agg_customersモデルの親モデルを取得します。
get_model_parents
リクエスト{ `model_name`: `agg_customers` }レスポンス{"resourceType": "model", "name": "stg_customers", "description": "This model cleans up customer data"}レスポンス{"resourceType": "model", "name": "stg_orders", "description": "This model cleans up order data"}agg_customersモデルの親モデルは以下の2つです:
stg_customers
- リソースタイプ: model
- 説明: This model cleans up customer data(このモデルは顧客データをクリーニングします)
stg_orders
- リソースタイプ: model
- 説明: This model cleans up order data(このモデルは注文データをクリーニングします)
agg_customersモデルはこれら2つのステージングモデルからデータを取得して集計を行っています。先ほど見たagg_customersのSQLコードからも、これらのモデルを参照して顧客ごとの集計情報を作成していることがわかります。
親モデルの取得ができました。
ドキュメントを整備しているモデルが親になっているので、説明もあります。
メトリクスの一覧を取得する
プロンプト
dbtのメトリクスの一覧を取得してください
結果
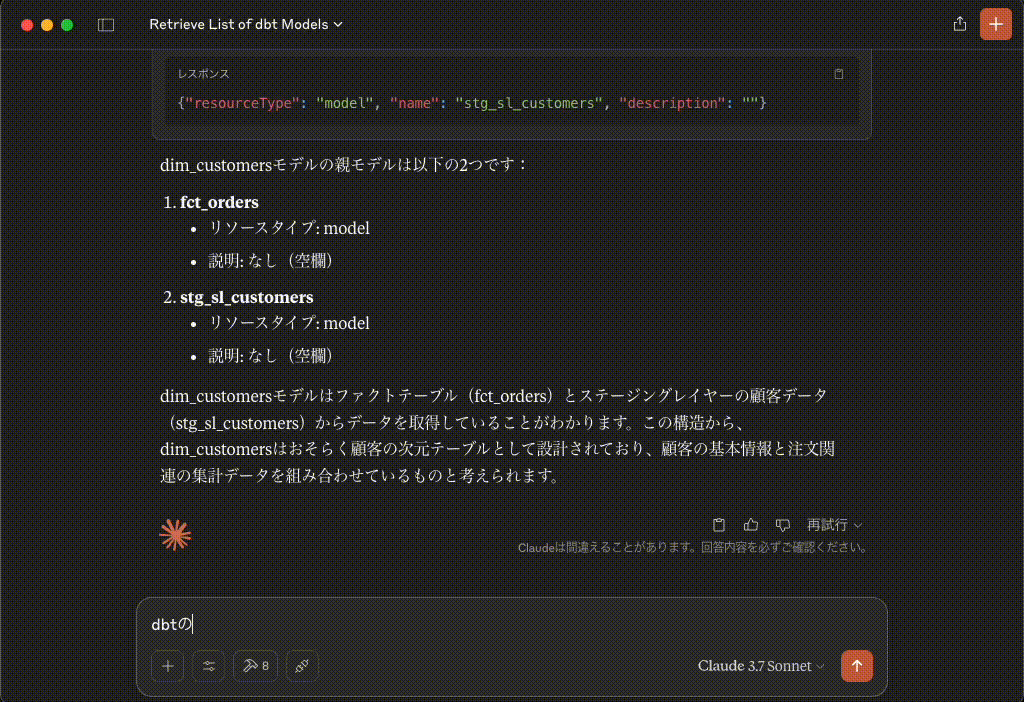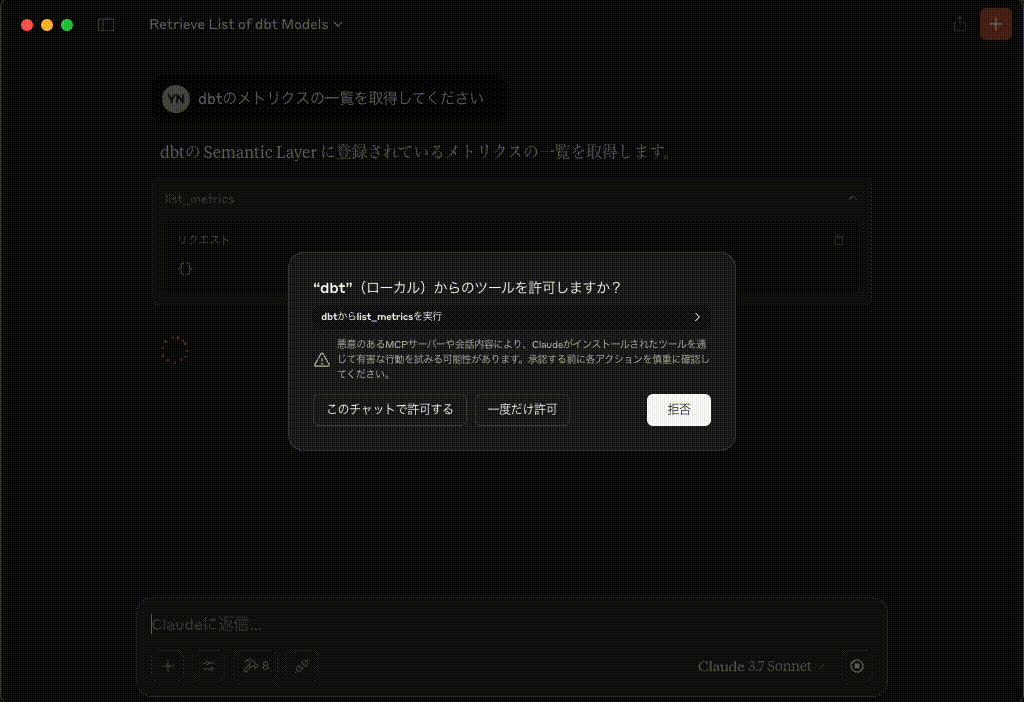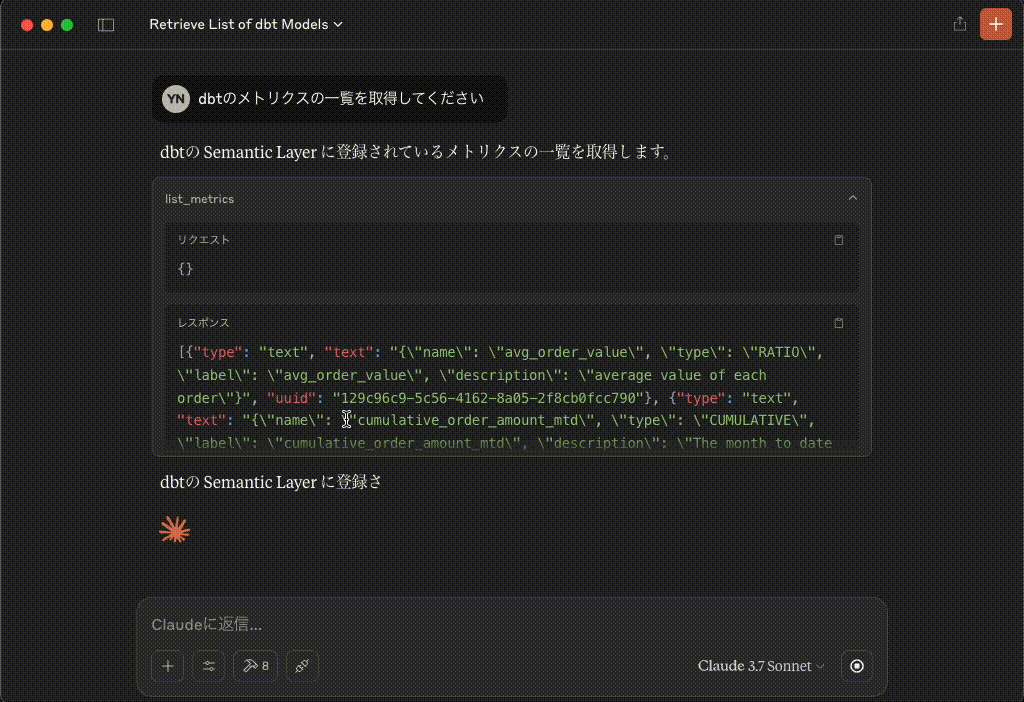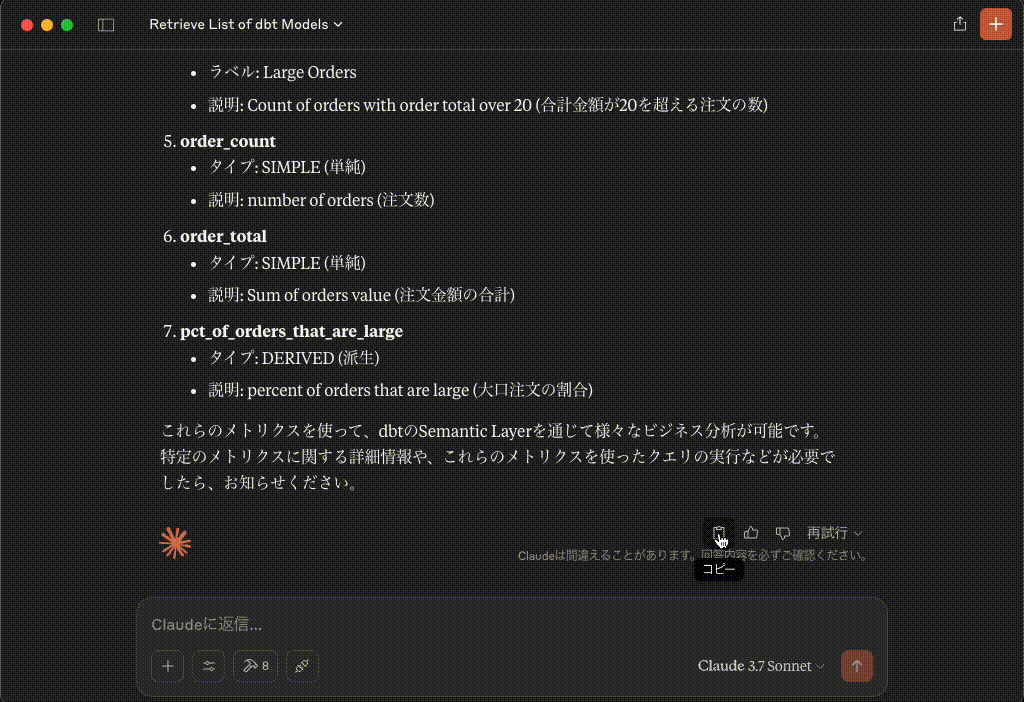
dbtの Semantic Layer に登録されているメトリクスの一覧を取得します。
list_metrics
リクエスト{}レスポンス{"name": "avg_order_value", "type": "RATIO", "label": "avg_order_value", "description": "average value of each order"}レスポンス{"name": "cumulative_order_amount_mtd", "type": "CUMULATIVE", "label": "cumulative_order_amount_mtd", "description": "The month to date value of all orders"}レスポンス{"name": "customers_with_orders", "type": "SIMPLE", "label": "customers_with_orders", "description": "Unique count of customers placing orders"}レスポンス{"name": "large_orders", "type": "SIMPLE", "label": "Large Orders", "description": "Count of orders with order total over 20."}レスポンス{"name": "order_count", "type": "SIMPLE", "label": "order_count", "description": "number of orders"}レスポンス{"name": "order_total", "type": "SIMPLE", "label": "order_total", "description": "Sum of orders value"}レスポンス{"name": "pct_of_orders_that_are_large", "type": "DERIVED", "label": "pct_of_orders_that_are_large", "description": "percent of orders that are large"}dbtの Semantic Layer に登録されているメトリクスの一覧は以下の通りです:
avg_order_value
- タイプ: RATIO (比率)
- 説明: average value of each order (各注文の平均金額)
cumulative_order_amount_mtd
- タイプ: CUMULATIVE (累積)
- 説明: The month to date value of all orders (当月の全注文の累計金額)
customers_with_orders
- タイプ: SIMPLE (単純)
- 説明: Unique count of customers placing orders (注文した顧客のユニーク数)
large_orders
- タイプ: SIMPLE (単純)
- ラベル: Large Orders
- 説明: Count of orders with order total over 20 (合計金額が20を超える注文の数)
order_count
- タイプ: SIMPLE (単純)
- 説明: number of orders (注文数)
order_total
- タイプ: SIMPLE (単純)
- 説明: Sum of orders value (注文金額の合計)
pct_of_orders_that_are_large
- タイプ: DERIVED (派生)
- 説明: percent of orders that are large (大口注文の割合)
これらのメトリクスを使って、dbtのSemantic Layerを通じて様々なビジネス分析が可能です。特定のメトリクスに関する詳細情報や、これらのメトリクスを使ったクエリの実行などが必要でしたら、お知らせください。
メトリクスの一覧を取得できました。
メトリクスのエンティティを取得してみる
プロンプト
avg_order_valueのエンティティを取得してください
結果
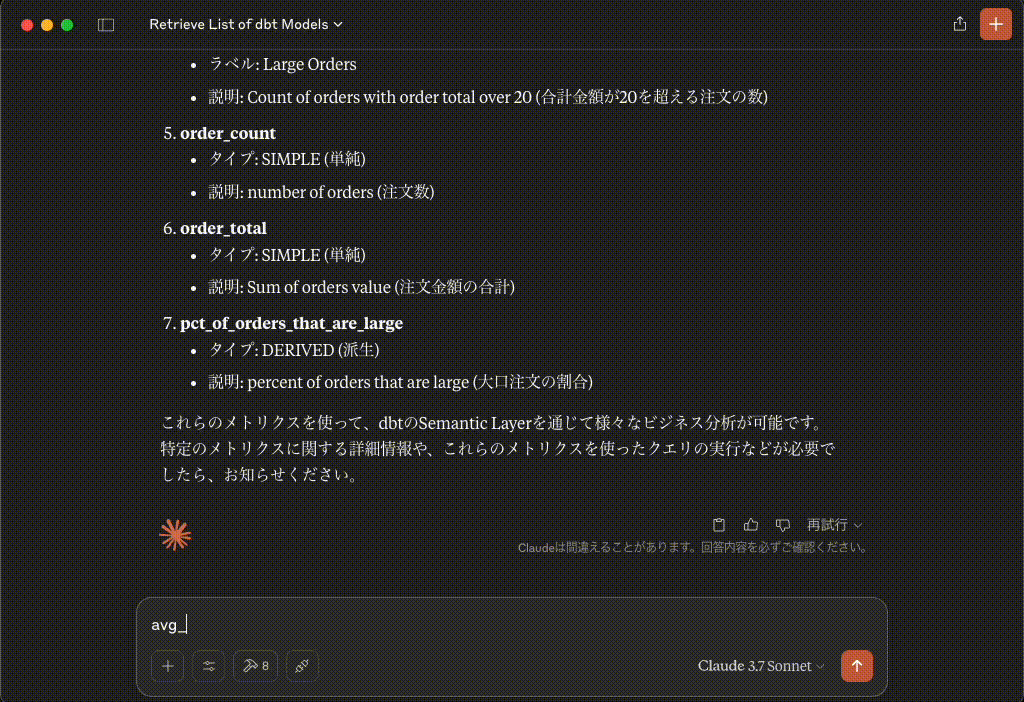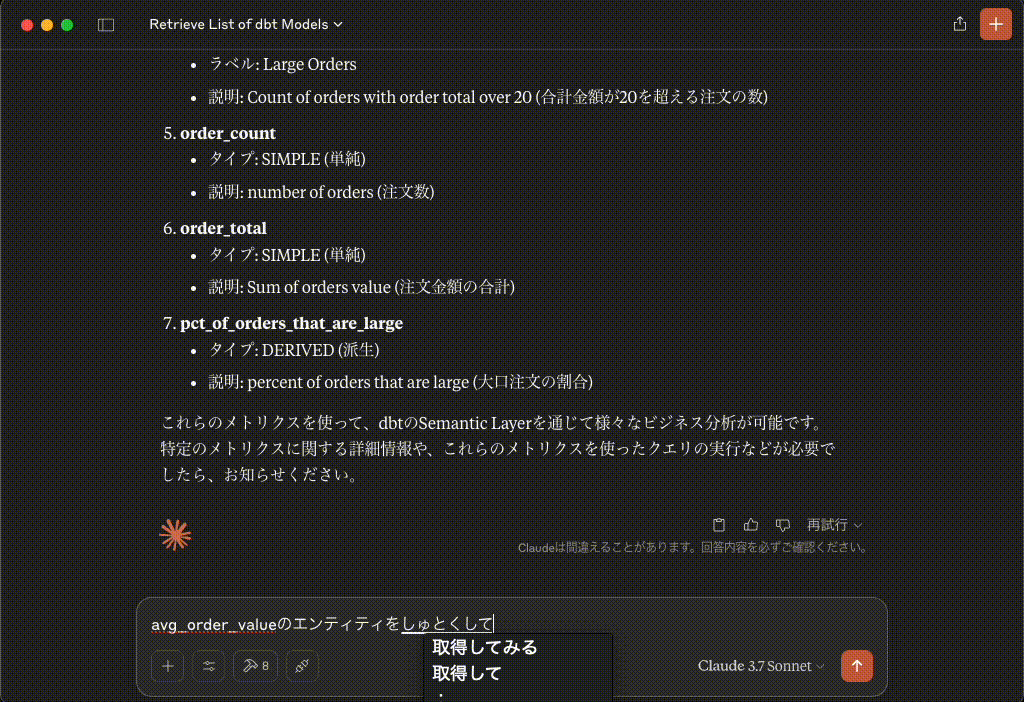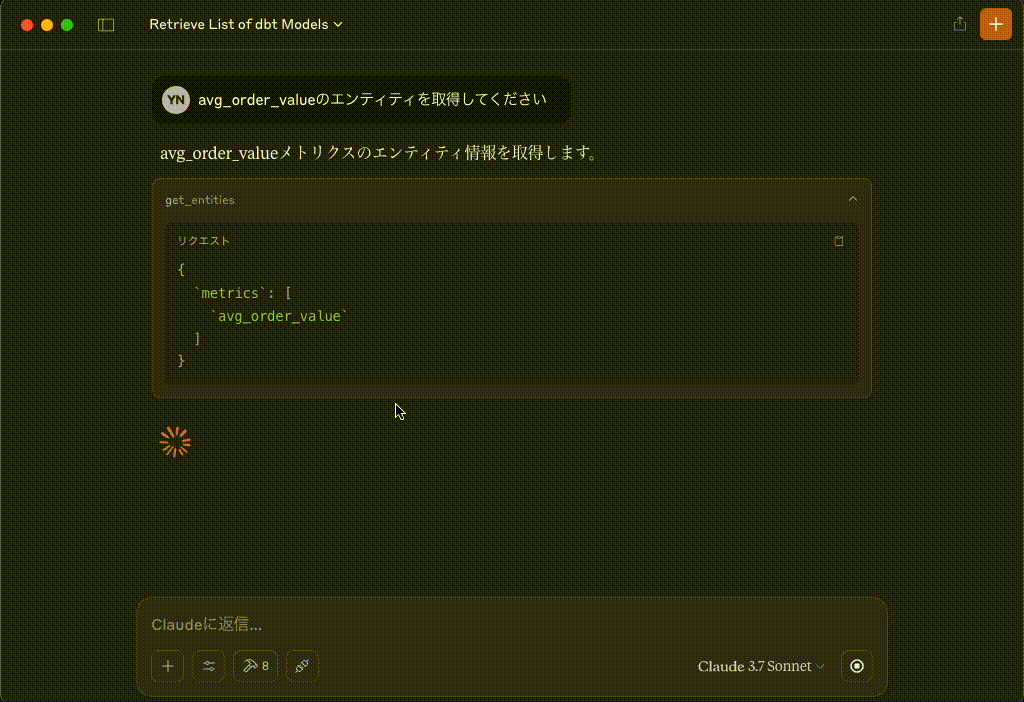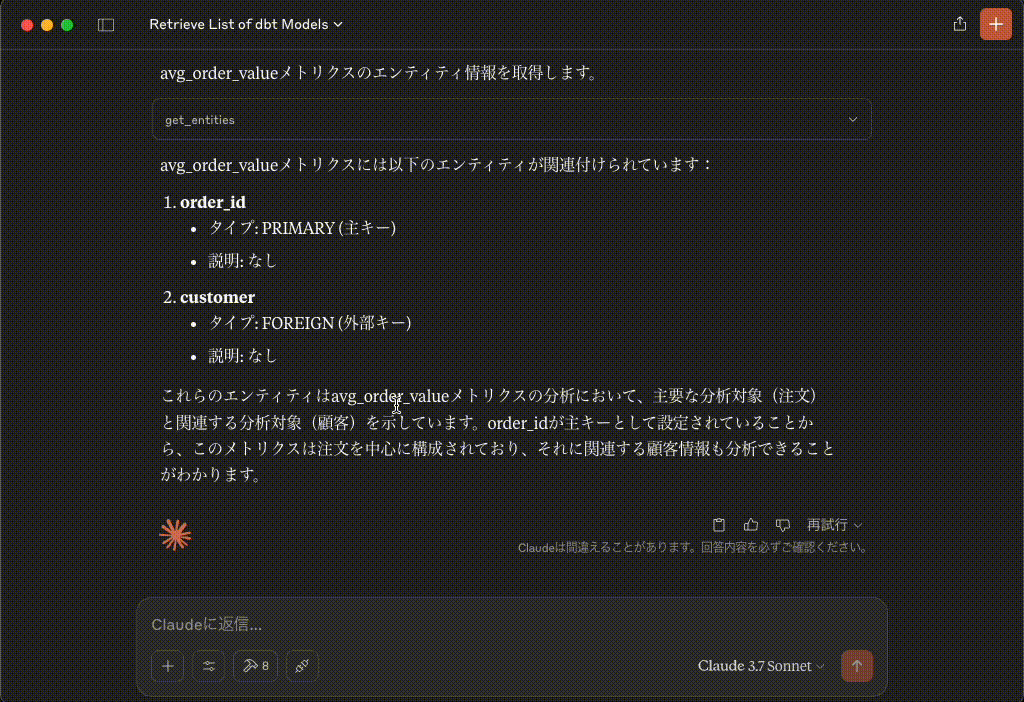
avg_order_valueメトリクスのエンティティ情報を取得します。
get_entities
リクエスト{ `metrics`: [ `avg_order_value` ] }レスポンス{"name": "order_id", "type": "PRIMARY", "description": null}レスポンス{"name": "customer", "type": "FOREIGN", "description": null}avg_order_valueメトリクスには以下のエンティティが関連付けられています:
order_id
- タイプ: PRIMARY (主キー)
- 説明: なし
customer
- タイプ: FOREIGN (外部キー)
- 説明: なし
これらのエンティティはavg_order_valueメトリクスの分析において、主要な分析対象(注文)と関連する分析対象(顧客)を示しています。order_idが主キーとして設定されていることから、このメトリクスは注文を中心に構成されており、それに関連する顧客情報も分析できることがわかります。
エンティティについて取得することができました。
まとめ
以上、dbtの公式MCPサーバーを試してみました。
きちんとドキュメントを整備していると便利に使えそうです。
謝罪
実は検証の際、メトリクスから値を取得しようとしたのですが何故か権限が足りないと言われてうまくいきませんでした。
管理者権限を付けたService Tokenを使ってもダメだったので、何でダメなのかもわかりません。








