AWS IoT TwinMakerで走行するトラックのデジタルツインを作って可視化してみた
こんにちは、CX 事業本部 IoT 事業部の若槻です。
AWS IoT TwinMaker では、Motion indicatorを使うことにより 3D model でデジタルツインの挙動を表現することができます。

この Motion indicator の設定方法について調べていたところ次の workshop を見つけました。AWS IoT TwinMaker で走行するトラックのデジタルツインを Motion indicator を使いつつ作るというものです。
というわけで今回は上記 workshop に沿って、走行するトラックのデジタルツインを作って可視化してみました。
やってみた
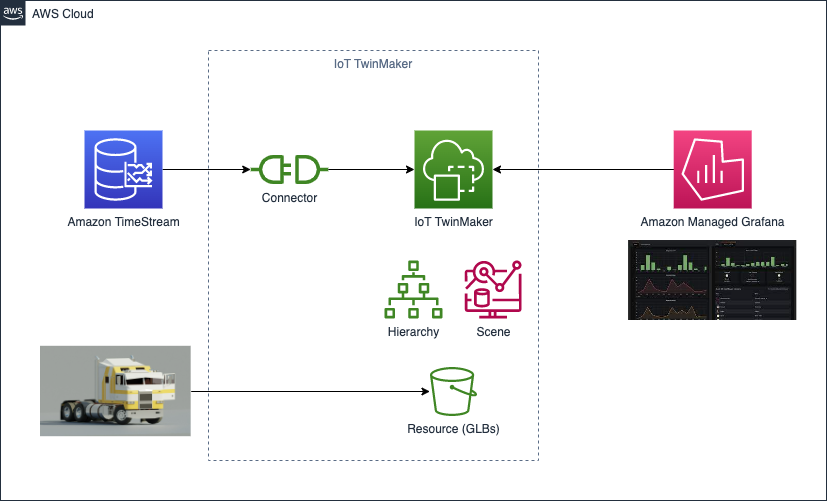
次のような構成を作成します。(図は workshop 手順より引用)
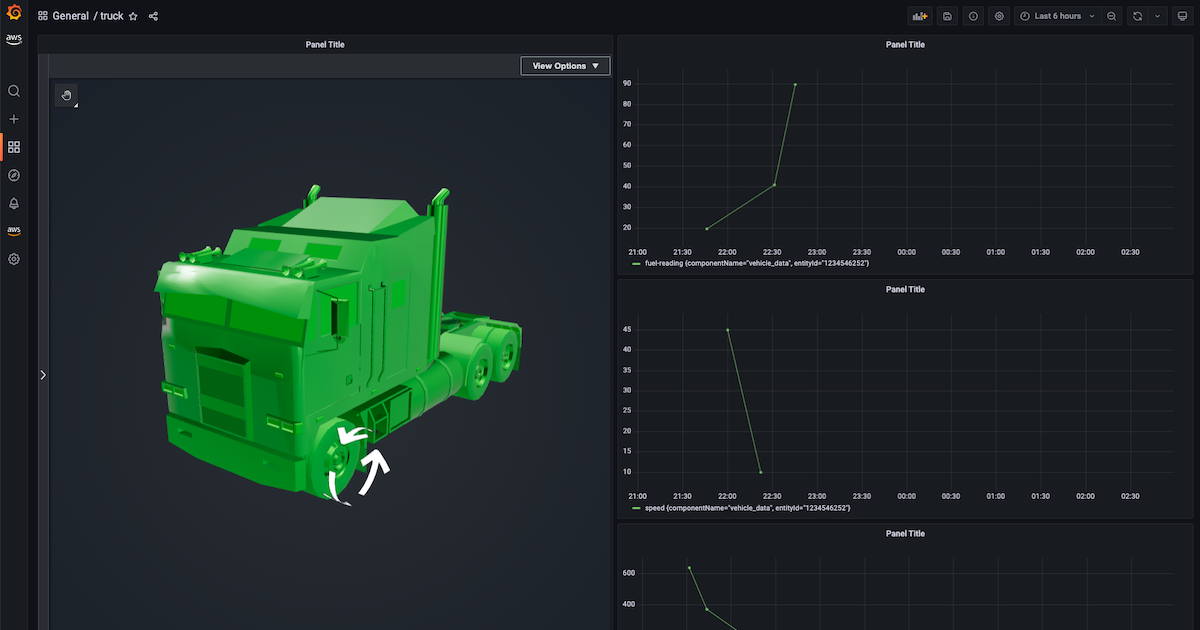
dashboard 上ではトラックが次のように可視化されます。走行速度に応じて矢印の回転速度が変化し、また燃料残量に応じて 3D model の色が変化します。

Create AWS Cloud9
開発環境に使用する AWS Cloud9 environment を作成します。
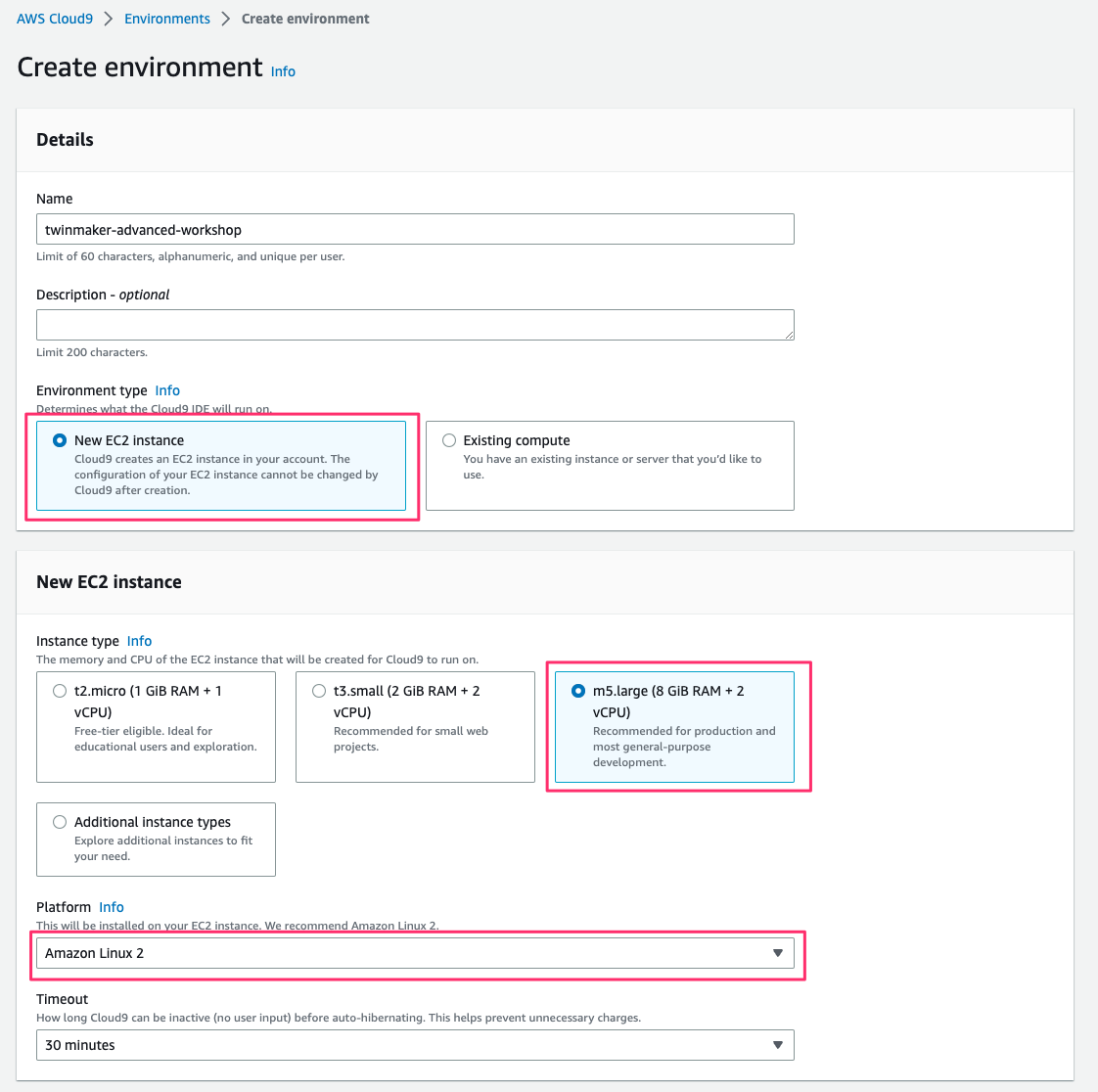
AWS Management Console でAWS Cloud9 > Environments > Create environmentにアクセスし、パラメータを次の通り指定して[Create]をクリックし作成を完了します。
- Name:任意の environment 名
- Environment type:
New EC2 instance - Instance type:
m5.large (8 GiB RAM + 2 vCPU) - Platform:
Amazon Linux 2
作成した environment を開きます。
以降のコマンド実行の実施は Cloud9 環境上で行います。
次の記事を参考に Cloud9 environment のボリュームサイズを 100GiB に拡張します。
以前紹介していた方法
# resize.shをダウンロード wget https://sehyul-us-east-1.s3.amazonaws.com/scripts/resize.sh # resize.shの実行権限を付与 chmod +x resize.sh # 引数にサイズ(GiB)を指定してresize.shを実行 ./resize.sh 100 # 拡張後は不要なので削除 rm resize.sh
拡張できました。
$ df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on devtmpfs 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /dev tmpfs 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 3.8G 460K 3.8G 1% /run tmpfs 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/nvme0n1p1 100G 5.6G 95G 6% / tmpfs 777M 0 777M 0% /run/user/1000
Create Sample Database
サンプルデータを保持する領域として Amazon TimeStream の database を作成します。
Timestream > Databases > Create databaseにアクセスし、パラメータを次の通り指定して[Create database]をクリックし作成を完了します。
- configuration:
Sample database - Name:
fleetdb - sample data sets:
IoT - type of time series records:
Single-measure records
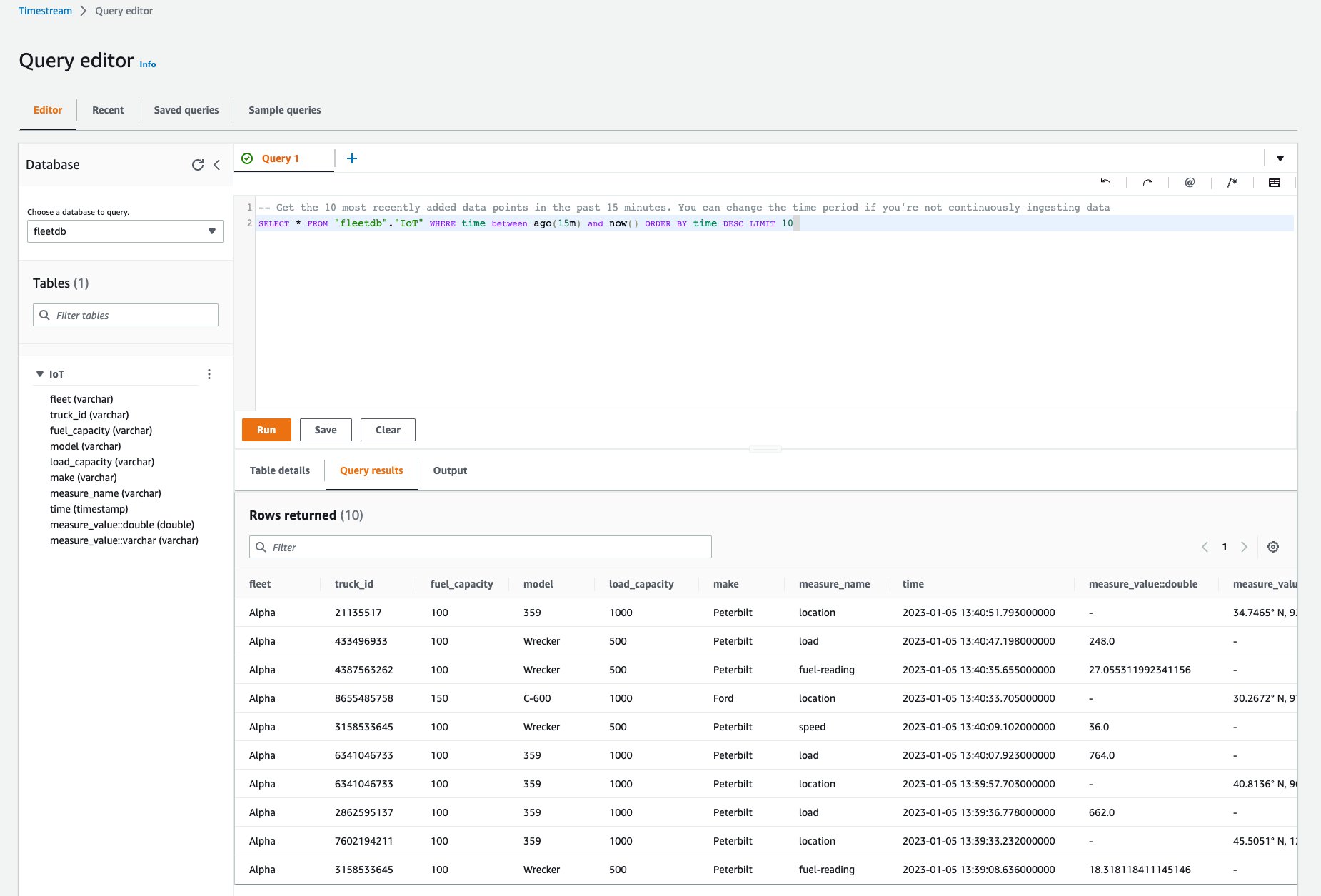
作成した table にクエリするとサンプル IoT データが取得できています。
Grafana
AWS IoT TwinMaker で作成するデジタルツインを可視化する Grafana workspace は、以前に次のエントリで作成した workspace を使用します。
Amazon Grafana Workspacesで、作成済みのワークスペースの[IAM role]を確認しておきます。
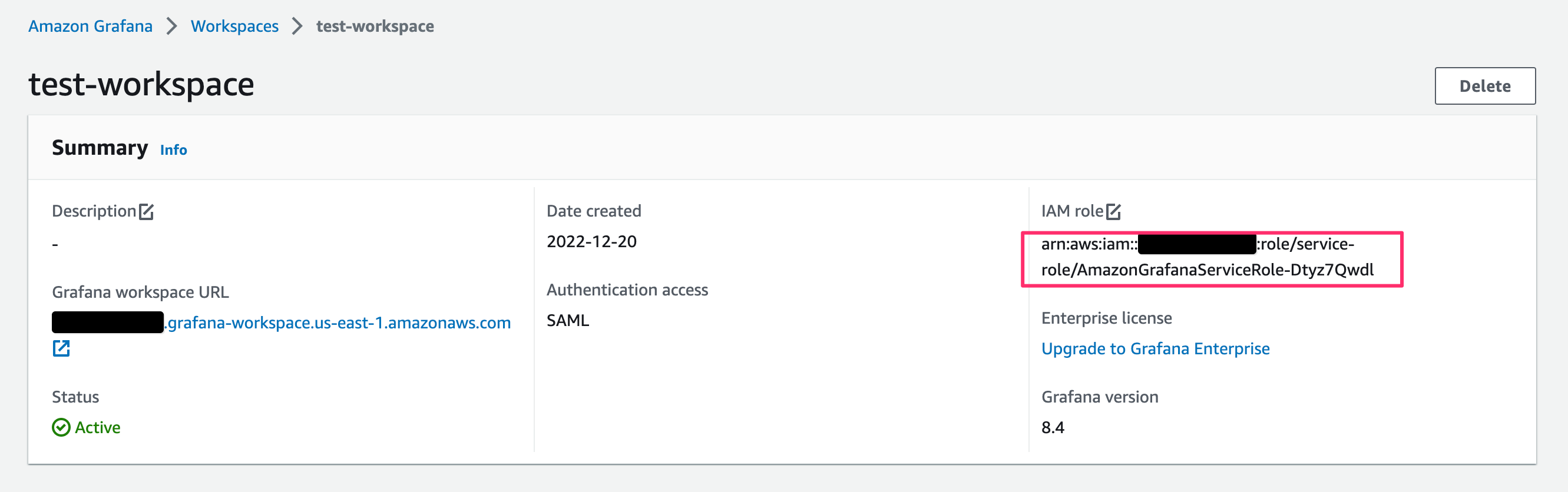
Create an IoT TwinMaker Workspace
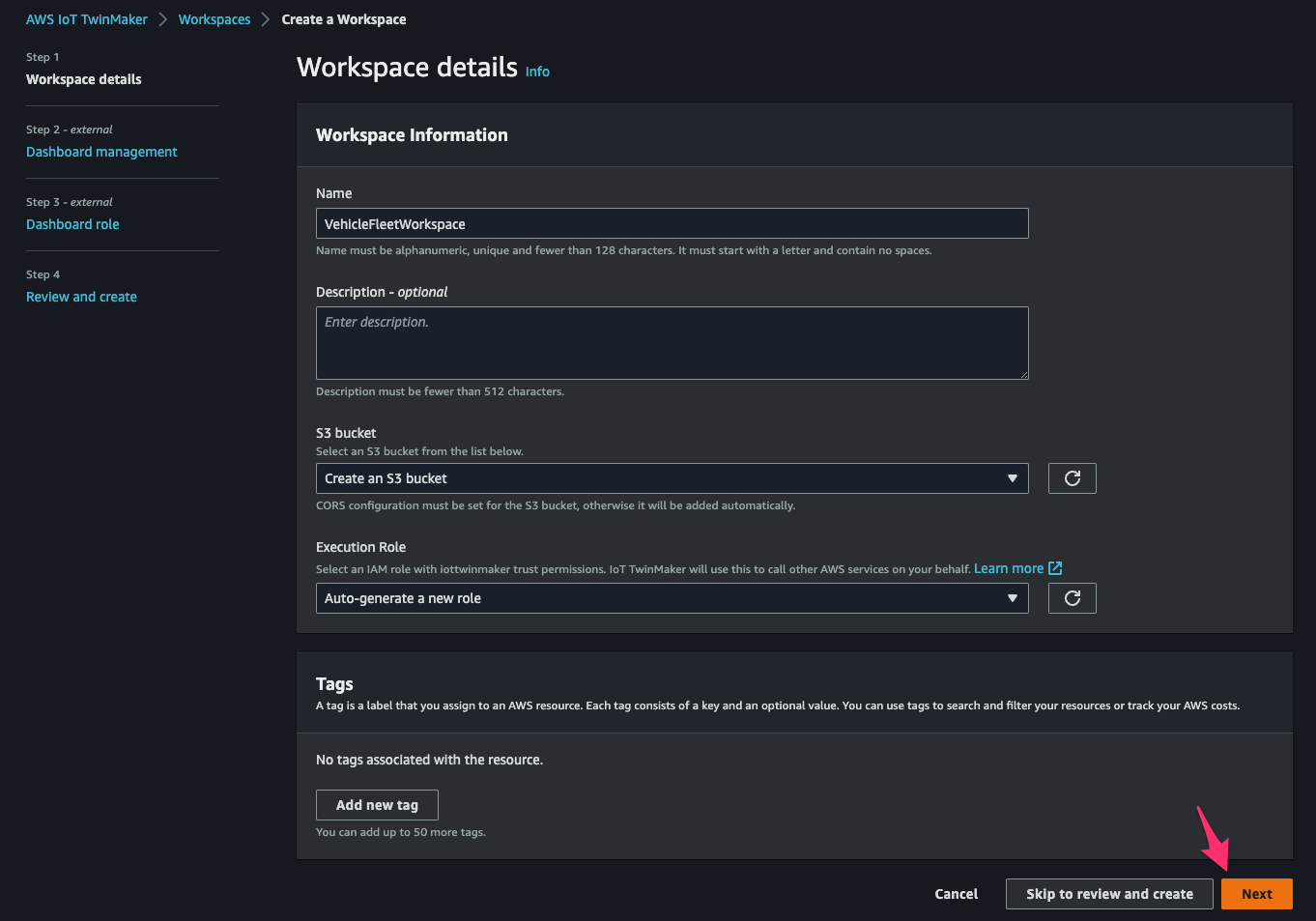
AWS IoT TwinMaker > Workspaces > Create a Workspaceにアクセスし、[Step 1]でパラメータを次の通り指定して[Next]をクリック。
- Name:
VehicleFleetWorkspace - S3 bucket:
Create an S3 bucket - Execution Role:
Auto-generate a new role
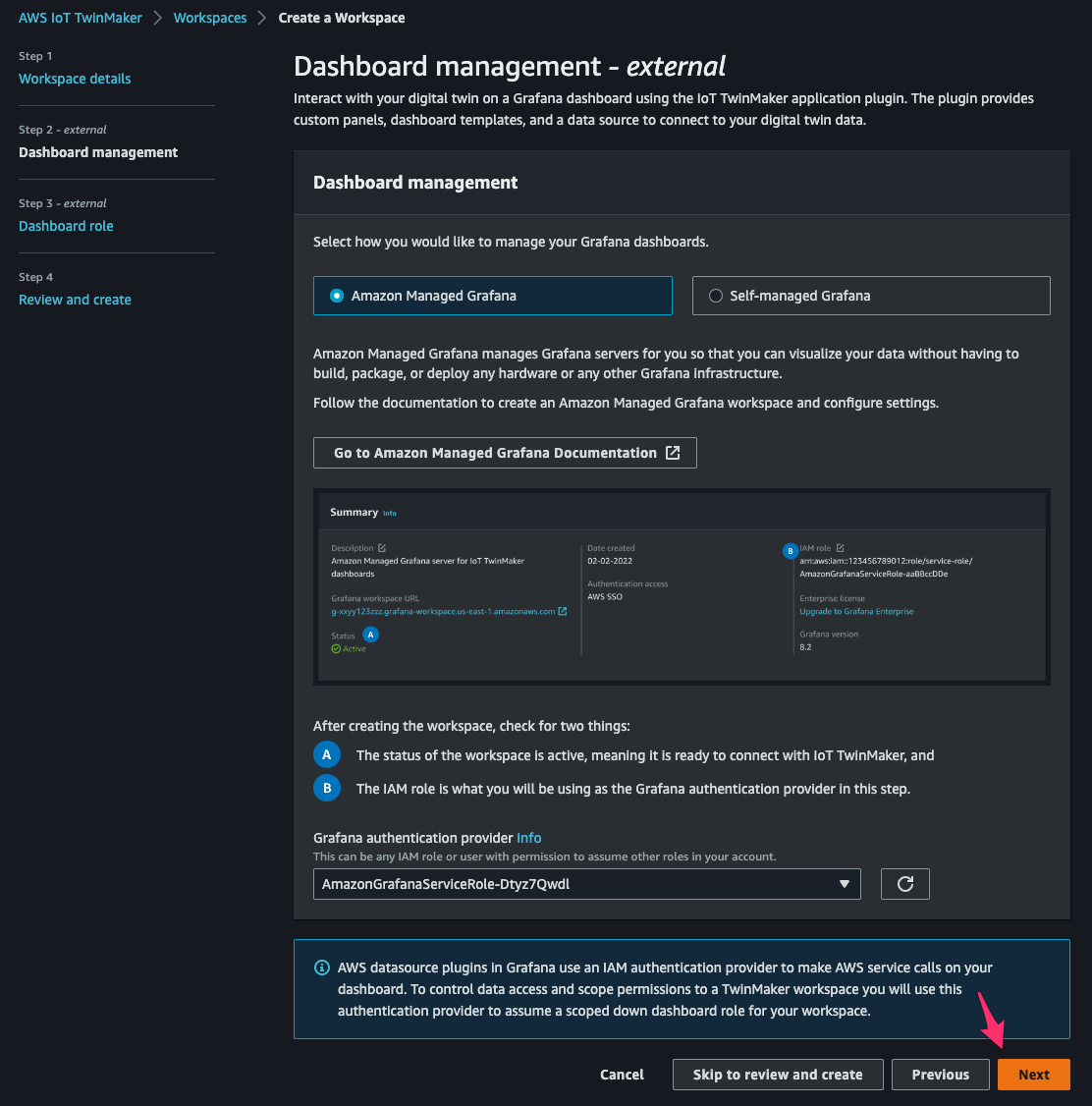
[Step 2]でパラメータを次の通り指定して[Next]をクリック。
- how you would like to manage your Grafana dashboards:
Amazon Managed Grafana - Grafana authentication provider:先程確認した Grafana workspace の IAM role
[Step 3]で permission の構文をコピーし、[Create policy in IAM]をクリック。
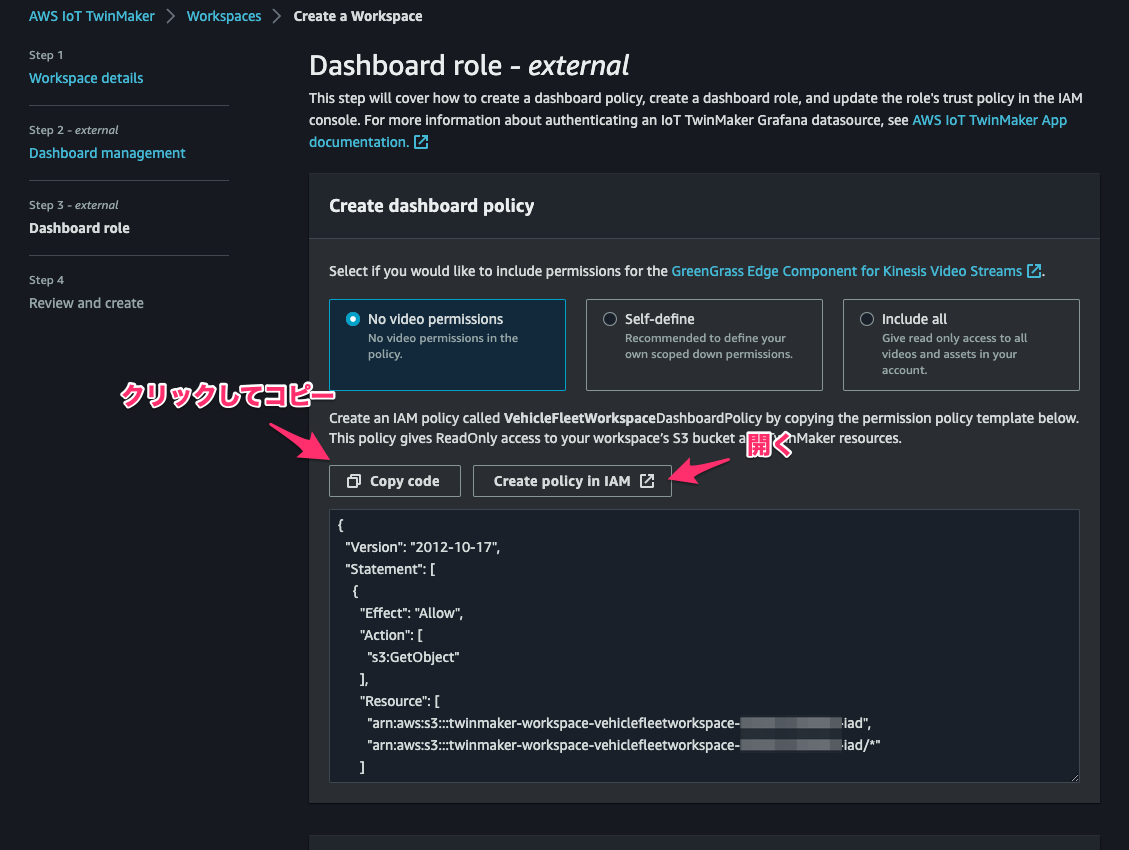
先程コピーした permission を指定したVehicleFleetWorkspaceDashboardPolicyという名前の IAM policy を作成します。
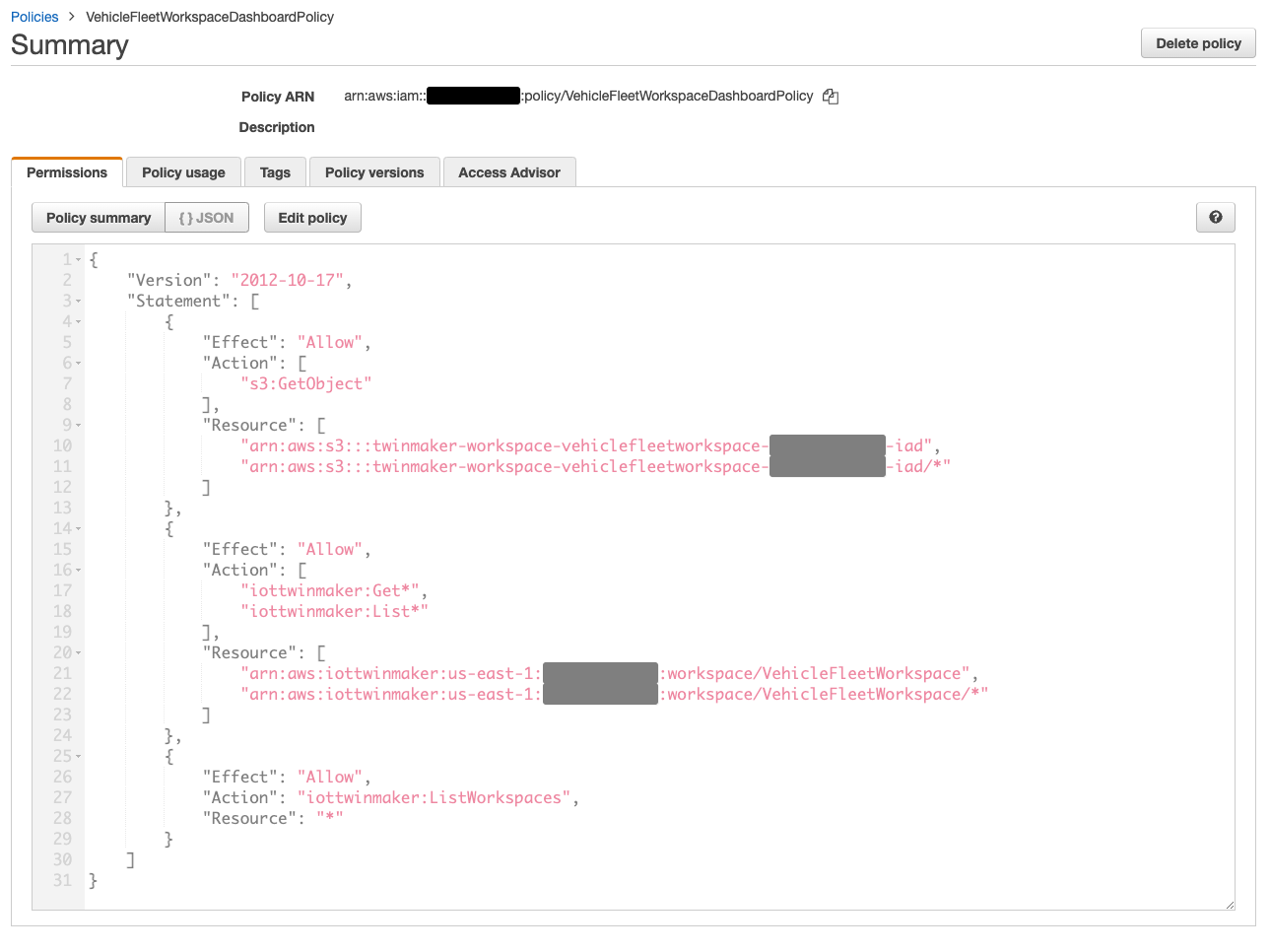
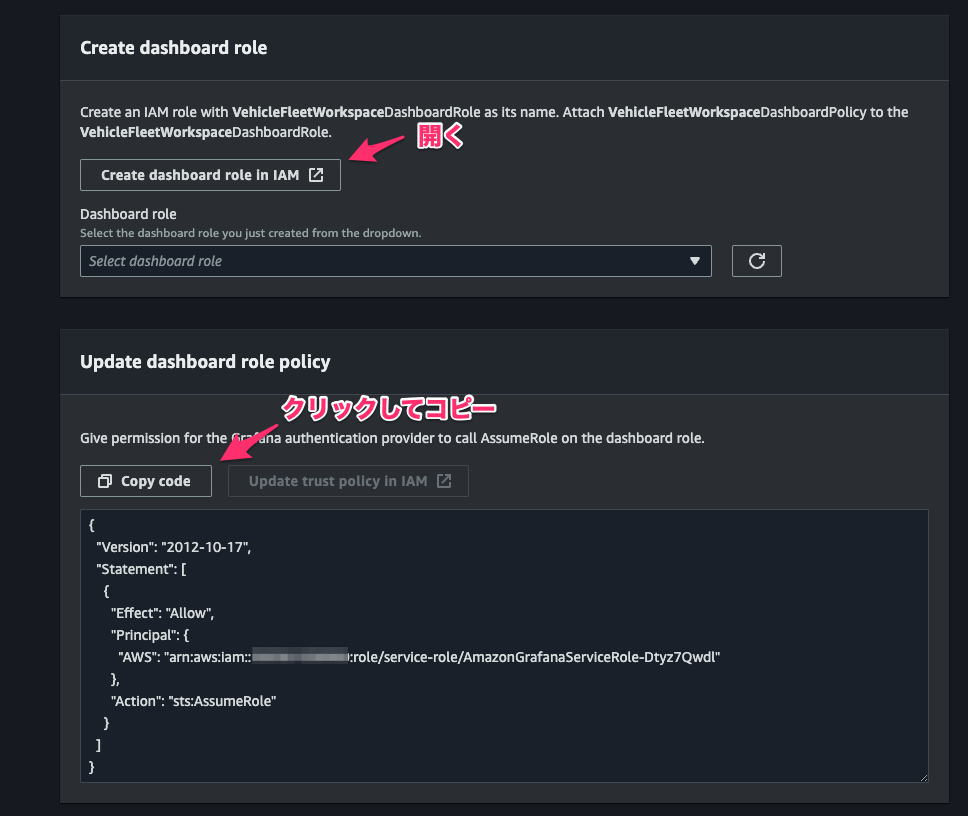
[Create a Workspace]コンソールに戻り、Grafana dashboard の AssumeRole 用の permission をコピーし、[Create dashboard role in IAM]をクリック。
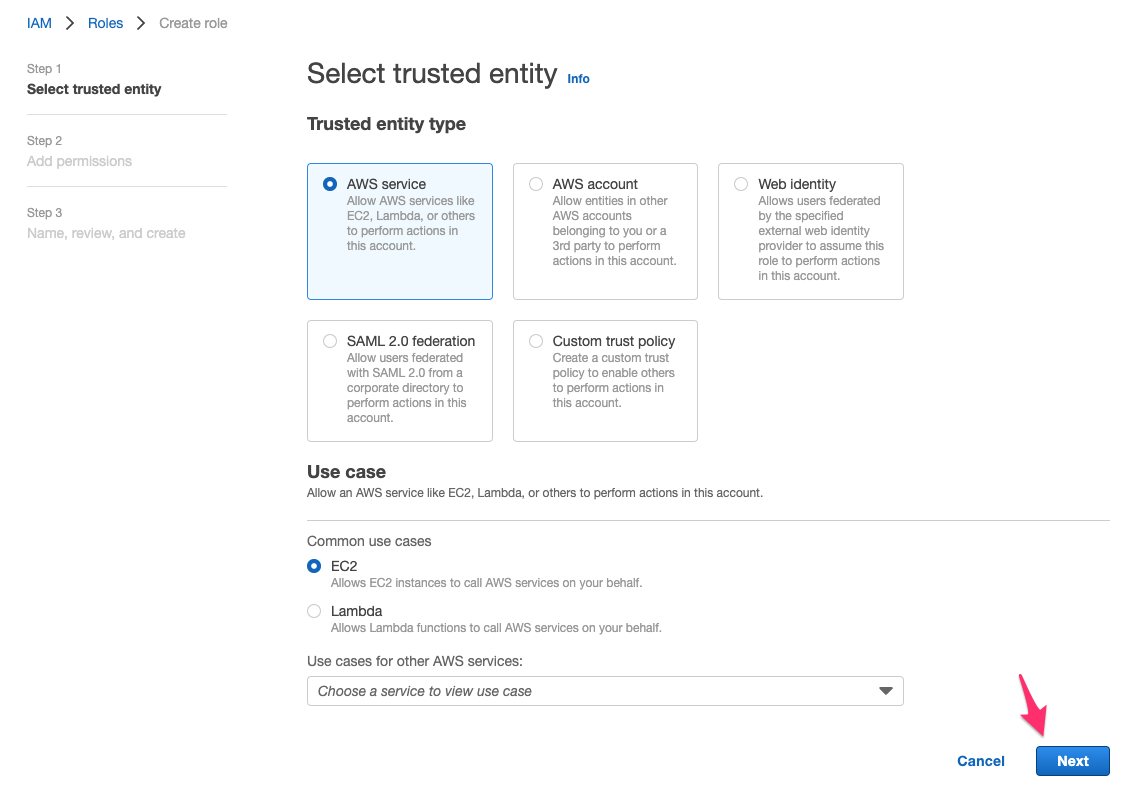
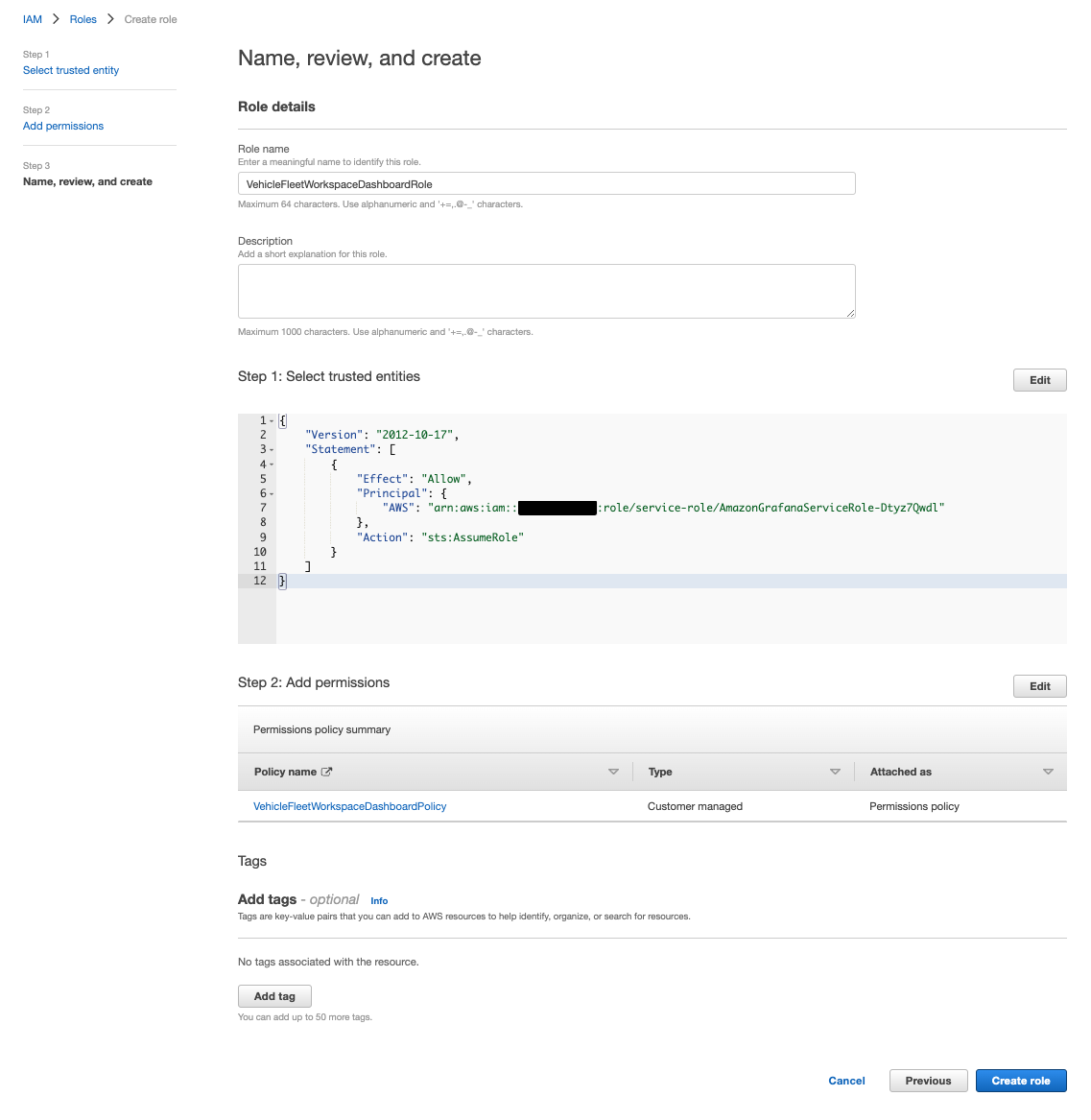
IAM role の作成コンソールが開くので、[Step 1]で次の通り指定して[Next]をクリック。
- Trusted entity type:
Custom trust policy - Custom trust policy:先程コピーした AscumeRole 用の permission
[Step 2]で先程作成した policy を指定して[Next]をクリック。
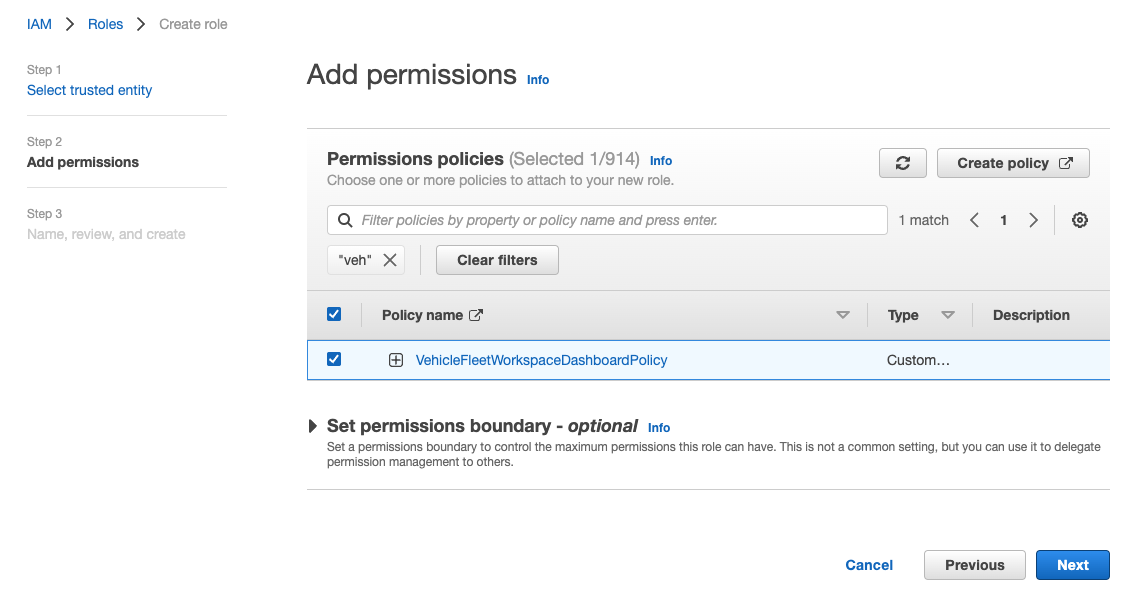
[Role name]にVehicleFleetWorkspaceDashboardRoleを指定して、[Create role]をクリックし作成を完了します。
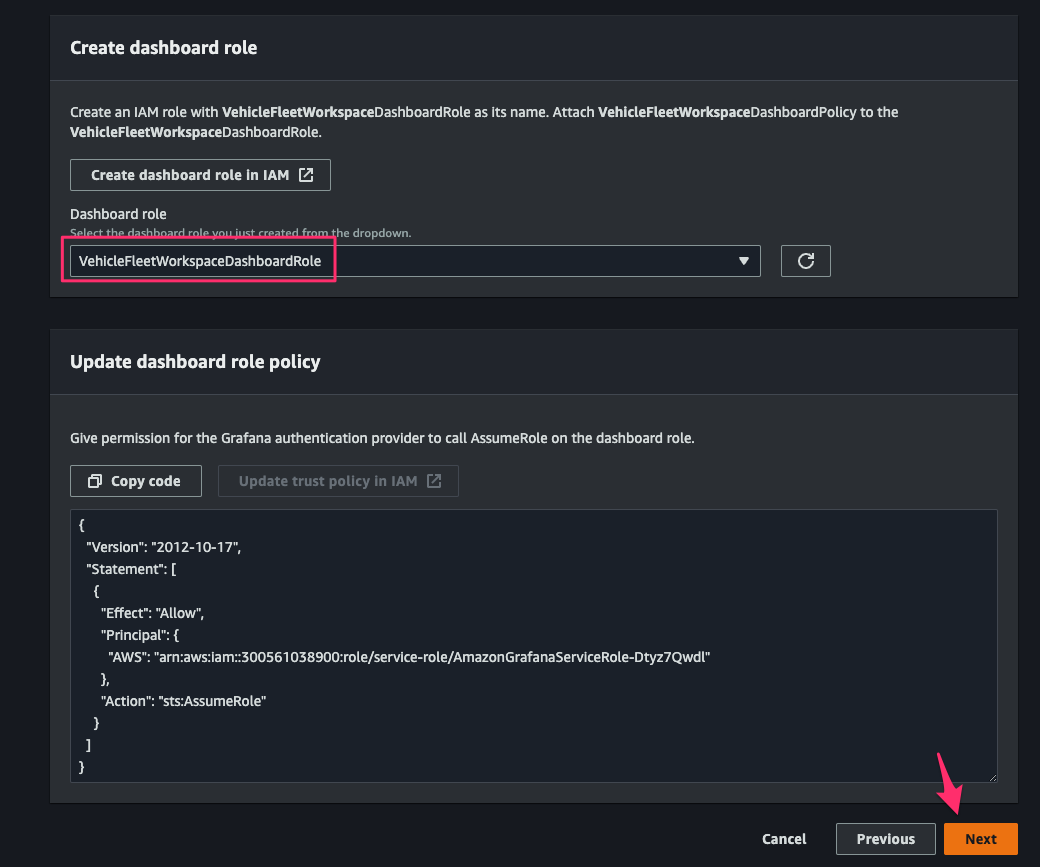
[Create a Workspace]コンソールに戻り、[Dashboard role]で先程作成した roleVehicleFleetWorkspaceDashboardRoleを指定して[Next]をクリック。
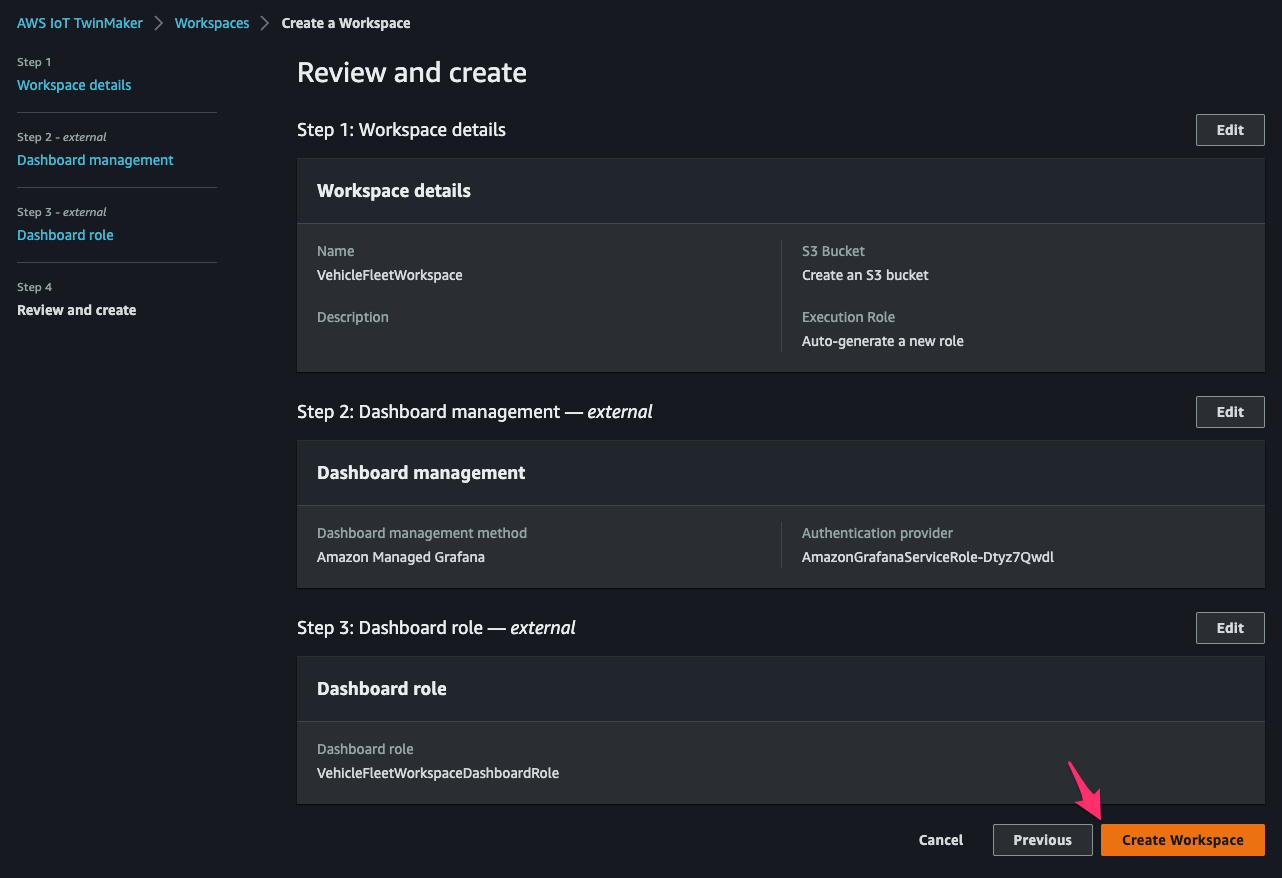
[Create Workspace]をクリックして workspace の作成を完了します。
Create an IoT TwinMaker Component
Install the Amazon TimeStream Data Reader Function
ここでは Amazon TimeStream からデータを取得する component に必要な resource を作成します。
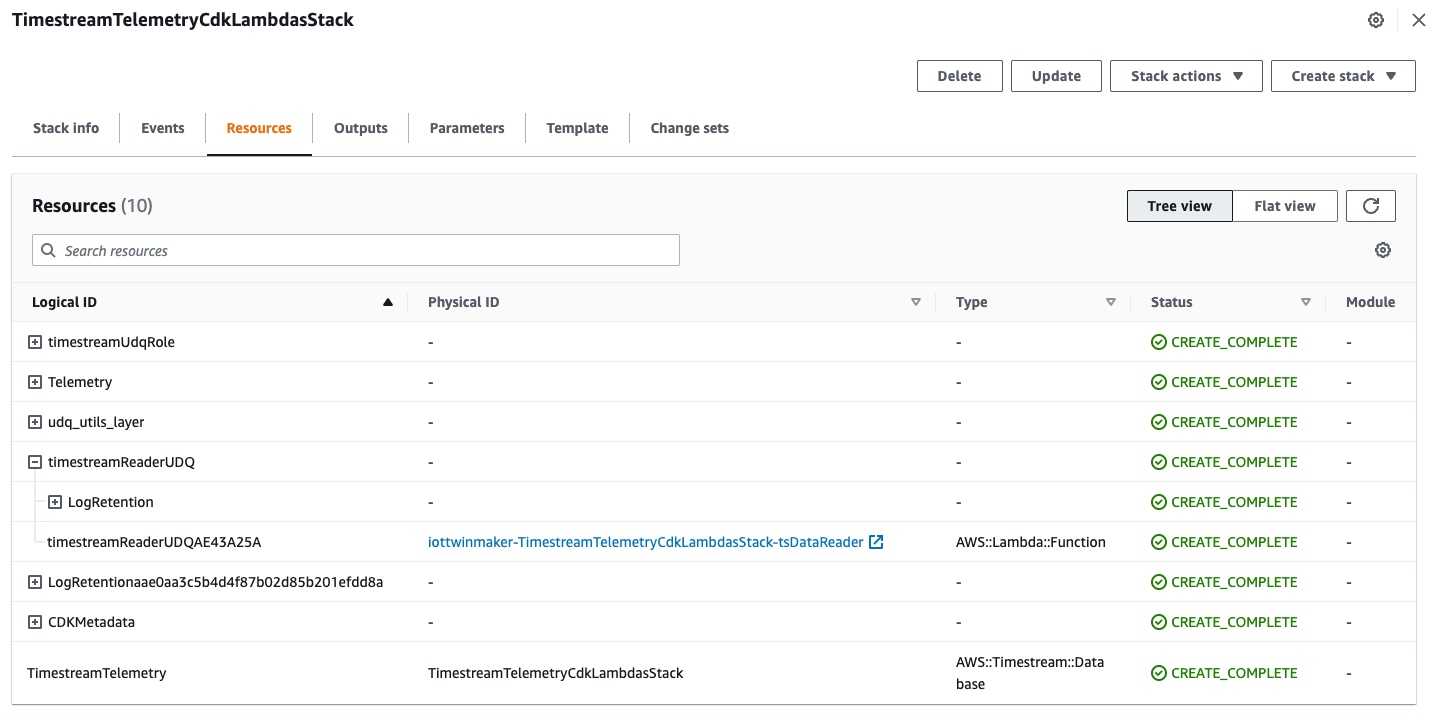
Cloud9 environment に戻り、次のコマンドを実行して AWS CDK により resource を作成します。
git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/aws-iot-twinmaker-samples.git cd aws-iot-twinmaker-samples/src/modules/timestream_telemetry/cdk/ npm install # cdk bootstrap 必要に応じて cdk deploy --require-approval never
Lambda function などのリソースを作成できました。
コンソールでLambda > Functions > iottwinmaker-TimestreamTelemetryCdkLambdasStack-tsDataReaderにアクセスし、[Code]より fileudq_data_reader.pyを次のコードで置き換え、[Deploy]をクリックしてデプロイします。これにより指定した truck id に基づき database をクエリするようになります。
# Copyright Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. 2021
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
import logging
import os
import sys
from datetime import datetime
import boto3
from udq_utils.udq import SingleEntityReader, MultiEntityReader, IoTTwinMakerDataRow, IoTTwinMakerUdqResponse
from udq_utils.udq_models import IoTTwinMakerUDQEntityRequest, IoTTwinMakerUDQComponentTypeRequest, OrderBy, IoTTwinMakerReference, \
EntityComponentPropertyRef, ExternalIdPropertyRef
from udq_utils.sql_detector import SQLDetector
LOGGER = logging.getLogger()
LOGGER.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Sample implementation of an AWS IoT TwinMaker UDQ Connector against AWS Timestream
# consists of the EntityReader and IoTTwinMakerDataRow implementations
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
class TimestreamReader(SingleEntityReader, MultiEntityReader):
"""
The UDQ Connector implementation for our Timestream table
It supports both single-entity queries and multi-entity queries and contains 2 utility functions to read from Timestream
and convert the results into a IoTTwinMakerUdqResponse object
"""
def __init__(self, query_client, database_name, table_name):
self.query_client = query_client
self.database_name = database_name
self.table_name = table_name
self.sqlDetector = SQLDetector()
# overrides SingleEntityReader.entity_query abstractmethod
def entity_query(self, request: IoTTwinMakerUDQEntityRequest) -> IoTTwinMakerUdqResponse:
"""
This is a entityId.componentName.propertyId type query.
The entityId and componentName is resolved into the externalId's for this component so we are getting truck_id passed in
We are selecting all entries matching the passed in truck_id and additional filters
"""
LOGGER.info("TimestreamReader entity_query")
selected_property = request.selected_properties[0]
property_filter = request.property_filters[0] if request.property_filters else None
filter_clause = f"AND measure_value::varchar {property_filter['operator']} '{property_filter['value']['stringValue']}'" if property_filter else ""
truck_id = request.udq_context['properties']['truck_id']['value']['stringValue']
if property_filter:
sample_query = f"""SELECT truck_id, measure_name, time, measure_value::double, measure_value::varchar FROM {self.database_name}.{self.table_name} WHERE time > from_iso8601_timestamp('2021-10-18T21:42:58') AND time <= from_iso8601_timestamp('2021-10-18T21:43:35') AND truck_id = 'test' AND measure_name = 'load' AND measure_value::varchar {property_filter['operator']} 'abc' ORDER BY time ASC"""
else:
sample_query = f"""SELECT truck_id, measure_name, time, measure_value::double, measure_value::varchar FROM {self.database_name}.{self.table_name} WHERE time > from_iso8601_timestamp('2021-10-18T21:42:58') AND time <= from_iso8601_timestamp('2021-10-18T21:43:35') AND truck_id = 'test' AND measure_name = 'load' ORDER BY time ASC"""
query_string = f"SELECT truck_id, measure_name, time, measure_value::double, measure_value::varchar" \
f" FROM {self.database_name}.{self.table_name} " \
f" WHERE time > from_iso8601_timestamp('{request.start_time}')" \
f" AND time <= from_iso8601_timestamp('{request.end_time}')" \
f" AND truck_id = '{truck_id}'" \
f" AND measure_name = '{selected_property}'" \
f" {filter_clause} " \
f" ORDER BY time {'ASC' if request.order_by == OrderBy.ASCENDING else 'DESC'}"
self.sqlDetector.detectInjection(sample_query, query_string)
page = self._run_timestream_query(query_string, request.next_token, request.max_rows)
return self._convert_timestream_query_page_to_udq_response(page, request.entity_id, request.component_name, truck_id)
# overrides MultiEntityReader.component_type_query abstractmethod
def component_type_query(self, request: IoTTwinMakerUDQComponentTypeRequest) -> IoTTwinMakerUdqResponse:
"""
This is a componentTypeId query.
The componentTypeId is resolved into the (partial) externalId's for this component type so we are getting a truck_id passed in.
We are selecting all entries matching the passed in truck_id and additional filters
"""
LOGGER.info("TimestreamReader component_type_query")
selected_property = request.selected_properties[0]
property_filter = request.property_filters[0] if request.property_filters else None
filter_clause = f"AND measure_value::varchar {property_filter['operator']} '{property_filter['value']['stringValue']}'" if property_filter else ""
truck_id = request.udq_context['properties']['truck_id']['value']['stringValue']
if property_filter:
sample_query = f"""SELECT truck_id, measure_name, time, measure_value::double, measure_value::varchar FROM {self.database_name}.{self.table_name} WHERE time > from_iso8601_timestamp('2021-10-18T21:42:58') AND time <= from_iso8601_timestamp('2021-10-18T21:43:35') AND truck_id = 'test' AND measure_name = 'load' AND measure_value::varchar {property_filter['operator']} 'abc' ORDER BY time ASC"""
else:
sample_query = f"""SELECT truck_id, measure_name, time, measure_value::double, measure_value::varchar FROM {self.database_name}.{self.table_name} WHERE time > from_iso8601_timestamp('2021-10-18T21:42:58') AND time <= from_iso8601_timestamp('2021-10-18T21:43:35') AND truck_id = 'test' AND measure_name = 'load' ORDER BY time ASC"""
query_string = f"SELECT truck_id, measure_name, time, measure_value::double, measure_value::varchar" \
f" FROM {self.database_name}.{self.table_name} " \
f" WHERE time > from_iso8601_timestamp('{request.start_time}')" \
f" AND time <= from_iso8601_timestamp('{request.end_time}')" \
f" AND measure_name = '{selected_property}'" \
f" {filter_clause} " \
f" ORDER BY time {'ASC' if request.order_by == OrderBy.ASCENDING else 'DESC'}"
self.sqlDetector.detectInjection(sample_query, query_string)
page = self._run_timestream_query(query_string, request.next_token, request.max_rows)
return self._convert_timestream_query_page_to_udq_response(page, request.entity_id, request.component_name, truck_id)
def _run_timestream_query(self, query_string, next_token, max_rows) -> dict:
"""
Utility function: handles executing the given query_string on AWS Timestream. Returns an AWS Timestream Query Page
see https://boto3.amazonaws.com/v1/documentation/api/latest/reference/services/timestream-query.html#TimestreamQuery.Client.query
"""
LOGGER.info("Query string is %s , next token is %s", query_string, next_token)
try:
# Timestream SDK returns error if None is passed for NextToken and MaxRows
if next_token and max_rows:
page = self.query_client.query(QueryString=query_string, NextToken=next_token, MaxRows=max_rows)
elif next_token:
page = self.query_client.query(QueryString=query_string, NextToken=next_token)
elif max_rows:
page = self.query_client.query(QueryString=query_string, MaxRows=max_rows)
# skip empty pages returned by Timestream
# passing in MaxRows but no NextToken, if we have more than MaxRows available we get back a NextToken and no results, and reissue the query
while 'NextToken' in page and len(page['Rows']) == 0:
page = self.query_client.query(QueryString=query_string, NextToken=page['NextToken'], MaxRows=max_rows)
else:
page = self.query_client.query(QueryString=query_string)
return page
except Exception as err:
LOGGER.error("Exception while running query: %s", err)
raise err
@staticmethod
def _convert_timestream_query_page_to_udq_response(query_page, entity_id, component_name, truck_id):
"""
Utility function: handles converting an AWS Timestream Query Page into a IoTTwinMakerUdqResponse object
For each IoTTwinMakerDataRow, we include:
- the raw row data from Timestream
- the column schema from Timestream we can later use to interpret the row
- and the entity_id, component_name, and truck_id as context for constructing the entityPropertyReference
"""
LOGGER.info("Query result is %s", query_page)
result_rows = []
schema = query_page['ColumnInfo']
for row in query_page['Rows']:
result_rows.append(TimestreamDataRow(row, schema, entity_id, component_name, truck_id))
return IoTTwinMakerUdqResponse(result_rows, query_page.get('NextToken'))
class TimestreamDataRow(IoTTwinMakerDataRow):
"""
The AWS IoT TwinMaker data row implementation for our Timestream data
It supports the IoTTwinMakerDataRow interface to:
- calculate the IoTTwinMakerReference ("entityPropertyReference") for a Timestream row
- extract the timestamp from a Timestream row
- extract the value from a Timestream row
"""
def __init__(self, timestream_row, timestream_column_schema, entity_id=None, component_name=None, _truck_id=None):
self._timestream_row = timestream_row
self._timestream_column_schema = timestream_column_schema
self._row_as_dict = self._parse_row(timestream_column_schema, timestream_row)
self._entity_id = entity_id
self._component_name = component_name
self._truck_id = _truck_id
# overrides IoTTwinMakerDataRow.get_iottwinmaker_reference abstractmethod
def get_iottwinmaker_reference(self) -> IoTTwinMakerReference:
"""
This function calculates the IoTTwinMakerReference ("entityPropertyReference") for a Timestream row
For single-entity queries, the entity_id and component_name values are passed in, use those to construct the 'EntityComponentPropertyRef'
For multi-entity queries, we don't have the IoT TwinMaker entity_id so we return back the property identifier stored in Timestream as an 'external_id_property'
"""
property_name = self._row_as_dict['measure_name']
return IoTTwinMakerReference(ecp=EntityComponentPropertyRef(self._entity_id, self._component_name, property_name))
# overrides IoTTwinMakerDataRow.get_iso8601_timestamp abstractmethod
def get_iso8601_timestamp(self) -> str:
"""
This function extracts the timestamp from a Timestream row and returns in ISO8601 basic format
e.g. '2022-04-06 00:17:45.419000000' -> '2022-04-06T00:17:45.419000000Z'
"""
return self._row_as_dict['time'].replace(' ', 'T') + 'Z'
# overrides IoTTwinMakerDataRow.get_value abstractmethod
def get_value(self):
"""
This function extracts the value from a Timestream row
Only varchar and double types are currently supported. We return the value back as a native python type
"""
if 'measure_value::varchar' in self._row_as_dict and self._row_as_dict['measure_value::varchar'] is not None:
return self._row_as_dict['measure_value::varchar']
elif 'measure_value::double' in self._row_as_dict and self._row_as_dict['measure_value::double'] is not None:
return float(self._row_as_dict['measure_value::double'])
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unhandled type in timestream row: {self._row_as_dict}")
def _parse_row(self, column_schema, timestream_row):
"""
Utility function: parses a timestream row into a python dict for more convenient field access
Example:
column=[
{'Name': 'truck_id', 'Type': {'ScalarType': 'VARCHAR'}},
{'Name': 'measure_name', 'Type': {'ScalarType': 'VARCHAR'}},
{'Name': 'time', 'Type': {'ScalarType': 'TIMESTAMP'}},
{'Name': 'measure_value::double', 'Type': {'ScalarType': 'DOUBLE'}},
{'Name': 'measure_value::varchar', 'Type': {'ScalarType': 'VARCHAR'}}
]
row={'Data': [
{'ScalarValue': '12345678'},
{'ScalarValue': 'load'},
{'ScalarValue': '2021-10-15 20:45:43.287000000'},
{'NullValue': True},
{'ScalarValue': 'ACTIVE'}
]}
->
{
'truck_id': '12345678',
'measure_name': 'load',
'time': '2021-10-15 20:45:43.287000000',
'measure_value::double': None,
'measure_value::varchar': 'ACTIVE'
}
"""
data = timestream_row['Data']
result = {}
for i in range(len(data)):
info = column_schema[i]
datum = data[i]
key, val = self._parse_datum(info, datum)
result[key] = val
return result
@staticmethod
def _parse_datum(info, datum):
"""
Utility function: parses timestream datum entries into (key,value) tuples. Only ScalarTypes currently supported.
Example:
info={'Name': 'time', 'Type': {'ScalarType': 'TIMESTAMP'}}
datum={'ScalarValue': '2021-10-15 20:45:25.793000000'}
->
('time', '2021-10-15 20:45:25.793000000')
"""
if datum.get('NullValue', False):
return info['Name'], None
column_type = info['Type']
if 'ScalarType' in column_type:
return info['Name'], datum['ScalarValue']
else:
raise Exception(f"Unsupported columnType[{column_type}]")
SESSION = boto3.Session()
QUERY_CLIENT = SESSION.client('timestream-query')
# retrieve database name and table name from Lambda environment variables
# check if running on Lambda
if os.environ.get("AWS_EXECUTION_ENV") is not None:
DATABASE_NAME = os.environ['TIMESTREAM_DATABASE_NAME']
TABLE_NAME = os.environ['TIMESTREAM_TABLE_NAME']
else:
LOGGER.addHandler(logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout))
DATABASE_NAME = None
TABLE_NAME = None
TIMESTREAM_UDQ_READER = TimestreamReader(QUERY_CLIENT, DATABASE_NAME, TABLE_NAME)
# Main Lambda invocation entry point, use the TimestreamReader to process events
# noinspection PyUnusedLocal
def lambda_handler(event, context):
LOGGER.info('Event: %s', event)
result = TIMESTREAM_UDQ_READER.process_query(event)
LOGGER.info("result:")
LOGGER.info(result)
return result
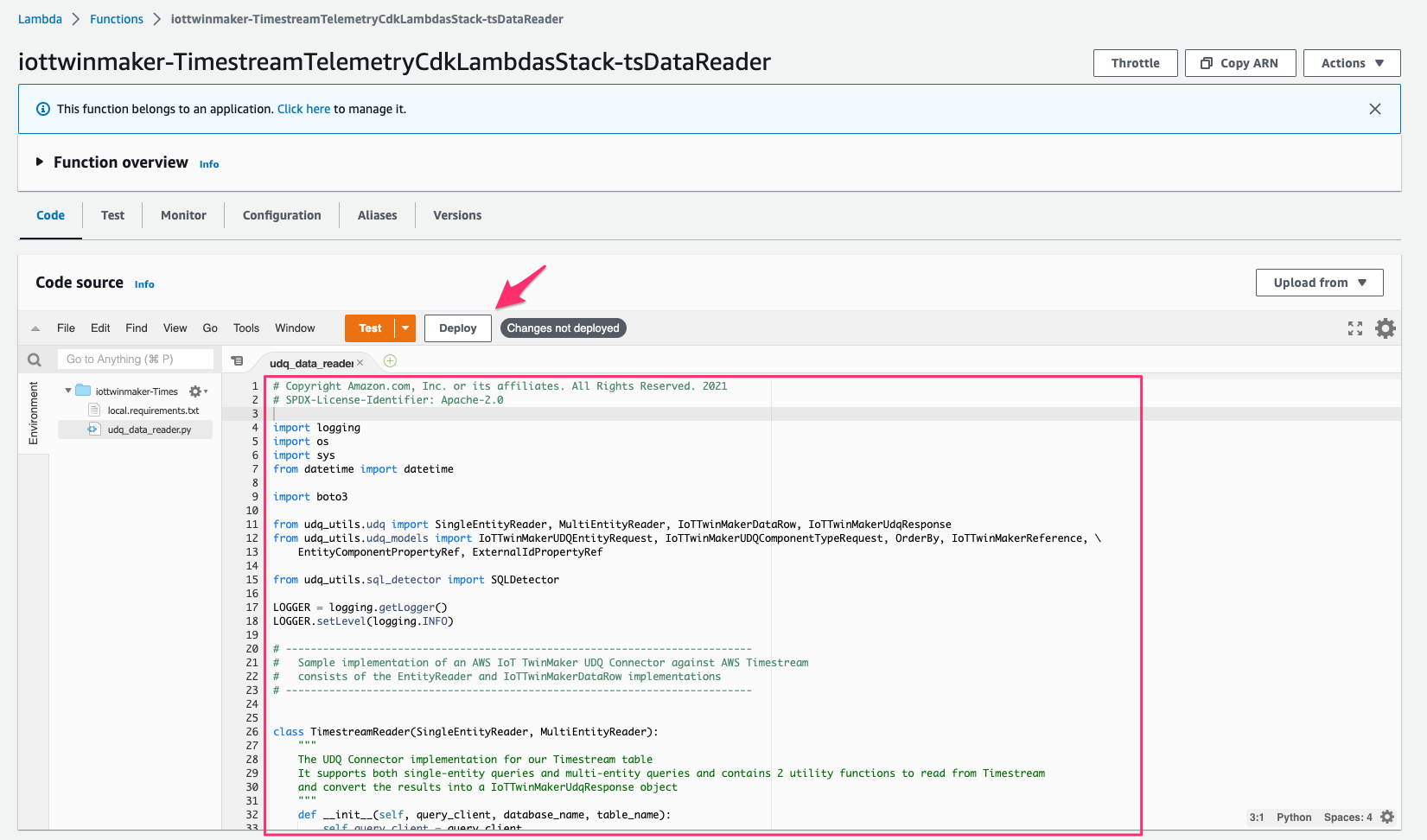
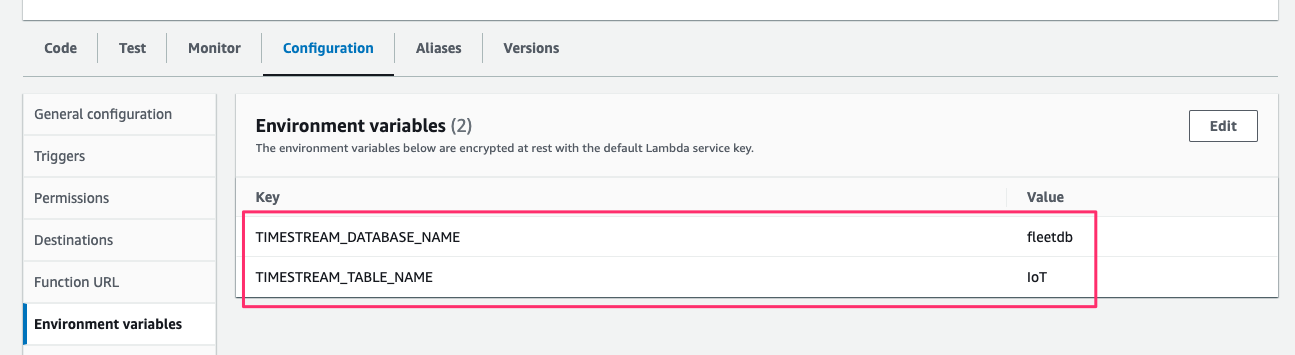
また[Configuration > Environment variables]で variable を次の通り変更します。
- TIMESTREAM_DATABASE_NAME:
fleetdb - TIMESTREAM_TABLE_NAME:
IoT
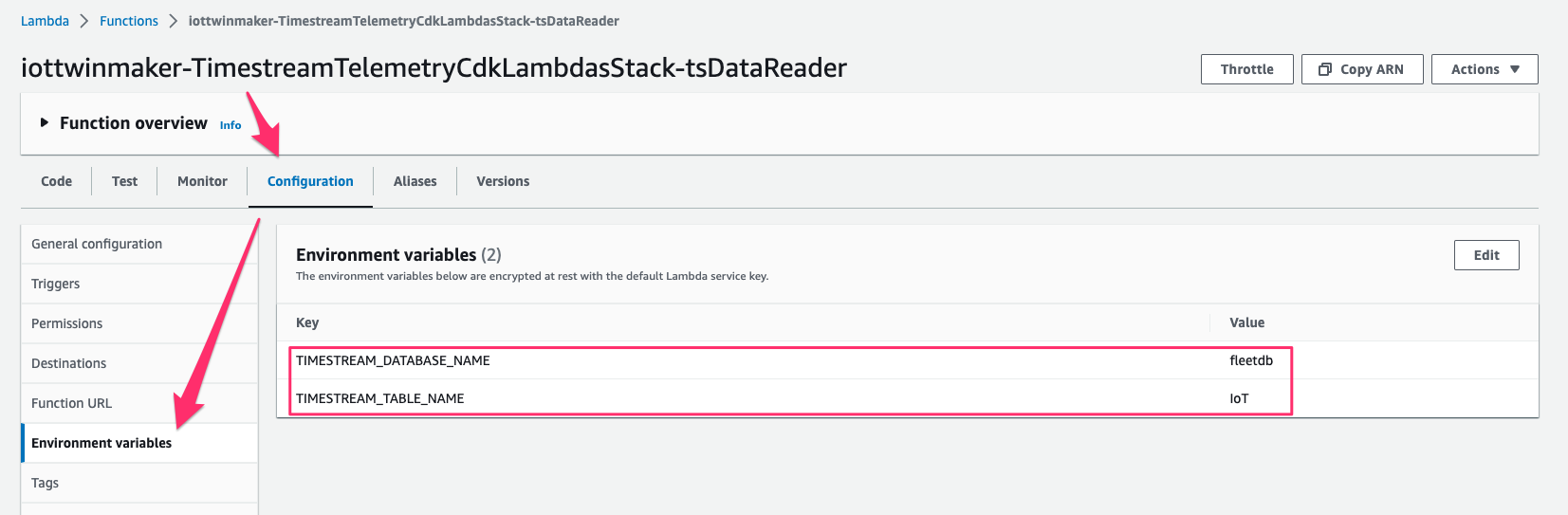
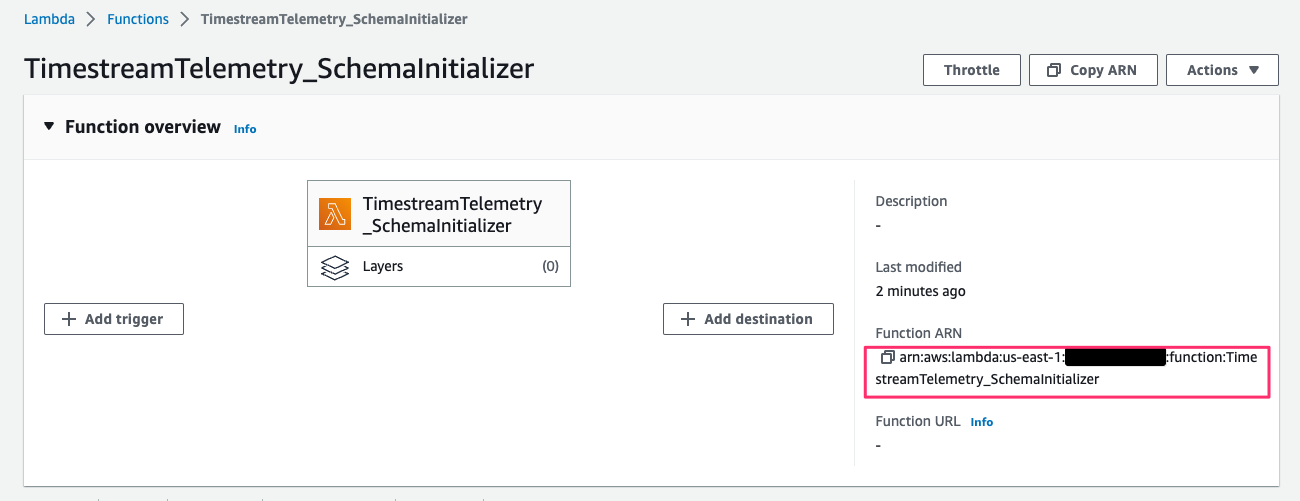
この Lambda function の ARN は後ほど workspace で component を作成する際に使用するので控えておきます。
Install Amazon TimeStream Schema Initializer Function
ここでは component の初期設定時に必要な property list をリターンする resource を作成します。
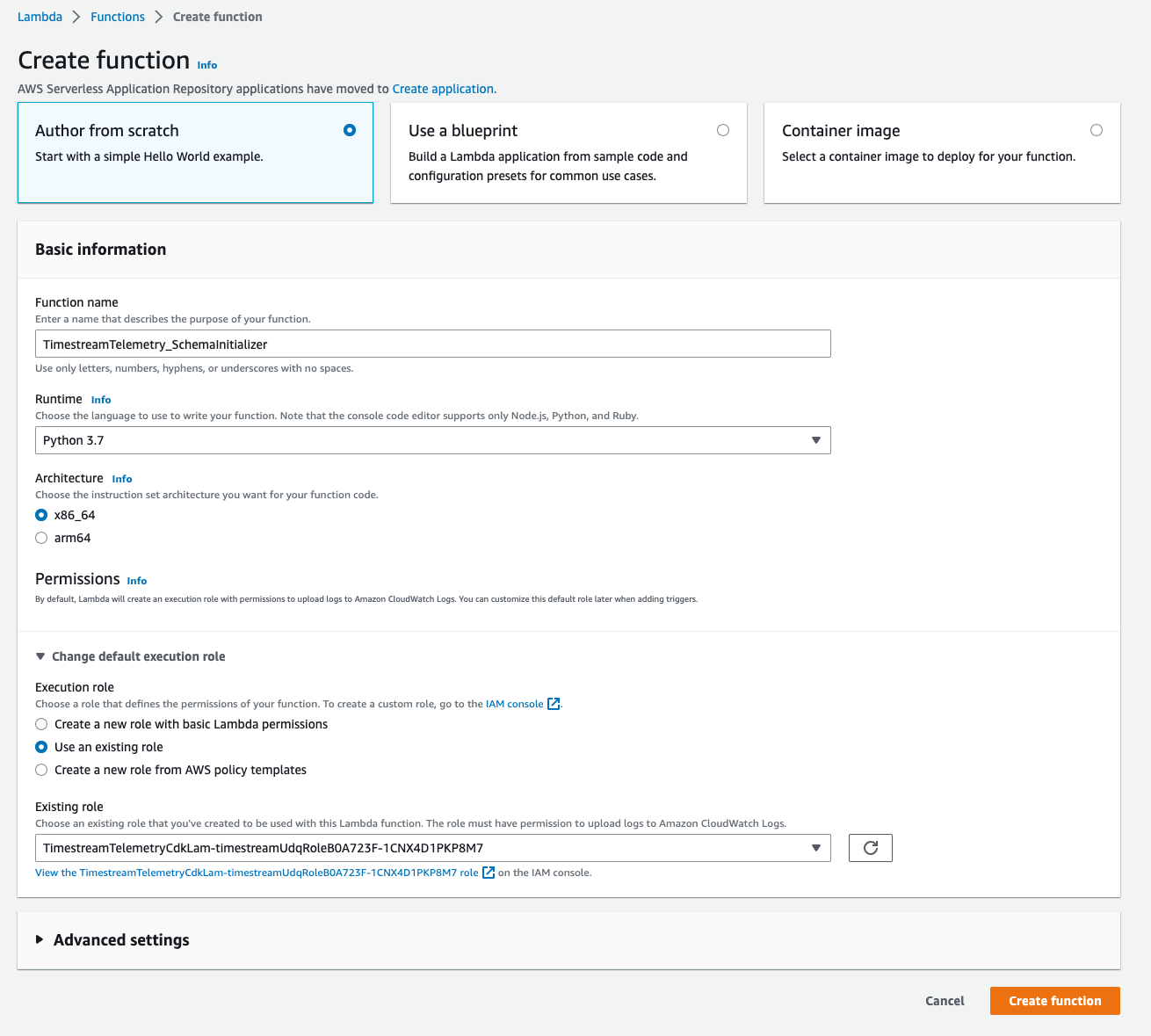
Lambda > Functions > Create functionにアクセスして、パラメータを次の通り指定して[Create function]をクリックし function の作成を完了します。
- Function name:
TimestreamTelemetry_SchemaInitializer - Runtime:
Python 3.7 - Execution role:
Use an existing role - Existing role:先程 CDK deploy により作成された
TimestreamTelemetryCdkLam-timestreamUdqRoleから始まる IAM role
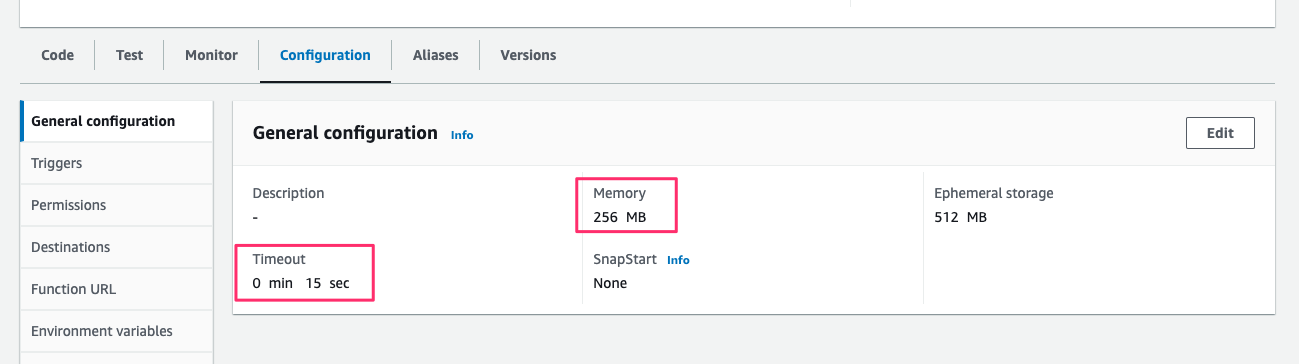
[Configuration > General configuration]で、[Memory]を256MB、[Timeout]を15secに変更します。
[Configuration > Environment variables]で、Data Reader Function と同じ environment を指定します。
[Code]より filelambda_function.pyを次のコードで書き換え、[Deploy]をクリックしてデプロイします。
# Copyright Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. 2021
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
import logging
import boto3
import os
import json
REQUEST_KEY_PROPERTIES = 'properties'
REQUEST_KEY_TRUCK_ID = 'truck_id'
REQUEST_KEY_VALUE = 'value'
REQUEST_KEY_VALUE_STRING = 'stringValue'
ILLEGAL_CHARACTERS = ['#', '(', ')', ' ']
# Configure logger
LOGGER = logging.getLogger()
LOGGER.setLevel(logging.INFO)
SESSION = boto3.Session()
QUERY_CLIENT = SESSION.client('timestream-query')
# retrieve database name and table name from Lambda environment variables
# check if running on Lambda
if os.environ.get("AWS_EXECUTION_ENV") is not None:
DATABASE_NAME = os.environ['TIMESTREAM_DATABASE_NAME']
TABLE_NAME = os.environ['TIMESTREAM_TABLE_NAME']
else:
LOGGER.addHandler(logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout))
DATABASE_NAME = None
TABLE_NAME = None
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Sample implementation of an AWS IoT TwinMaker control plane Connector against TimeStream
# queries property schema of a component
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print(event)
properties = {}
# Prepare and execute query statement to TimeStream
truck_id = event[REQUEST_KEY_PROPERTIES][REQUEST_KEY_TRUCK_ID][REQUEST_KEY_VALUE][REQUEST_KEY_VALUE_STRING]
try:
query_string = f"SELECT distinct measure_name, make, model" \
f" FROM {DATABASE_NAME}.{TABLE_NAME} " \
f" WHERE truck_id = '{truck_id}'"
LOGGER.info('truck_id: %s', truck_id)
query_result = QUERY_CLIENT.query(QueryString=query_string)
column_info = query_result['ColumnInfo']
for row in query_result['Rows']:
values = __parse_row(column_info, row)
attr_name = values["measure_name"]
current_property = {
'definition': {}
}
if(attr_name == "location"):
current_property['definition']['dataType'] = {
'type': 'STRING'
}
else:
current_property['definition']['dataType'] = {
'type': 'DOUBLE'
}
current_property['definition']['isTimeSeries'] = True
# Some characters are not allowed to present in property name
attr_name = replace_illegal_character(attr_name)
properties[attr_name] = current_property
# Add other properties that have static metadata
attr_name = "make"
current_property = {
'definition': {}
}
current_property['definition']['dataType'] = {
'type': 'STRING'
}
current_property['definition']['defaultValue'] = {
'stringValue': values["make"]
}
properties[attr_name] = current_property
attr_name = "model"
current_property = {
'definition': {}
}
current_property['definition']['dataType'] = {
'type': 'STRING'
}
current_property['definition']['defaultValue'] = {
'stringValue': values["model"]
}
properties[attr_name] = current_property
except Exception as e:
LOGGER.error("Query exception: %s", e)
raise e
return {
'properties': properties
}
def __parse_row(column_info, row):
data = row['Data']
row_output = {}
for j in range(len(data)):
info = column_info[j]
datum = data[j]
key,val = __parse_datum(info, datum)
row_output[key] = val
return row_output
def __parse_datum(info, datum):
column_type = info['Type']
return __parse_column_name(info), datum['ScalarValue']
def __parse_time_series(info, datum):
time_series_output = []
for data_point in datum['TimeSeriesValue']:
time_series_output.append("{time=%s, value=%s}"
% (data_point['Time'],
__parse_datum(info['Type']['TimeSeriesMeasureValueColumnInfo'],
data_point['Value'])))
return "[%s]" % str(time_series_output)
def __parse_column_name(info):
if 'Name' in info:
return info['Name']
else:
return ""
def __parse_array(array_column_info, array_values):
array_output = []
for datum in array_values:
array_output.append(__parse_datum(array_column_info, datum))
return "[%s]" % str(array_output)
def replace_illegal_character(attr_name):
for illegal_char in ILLEGAL_CHARACTERS:
attr_name = attr_name.replace(illegal_char, '_')
return attr_name.replace('__', '_')
この Lambda function の ARN は後ほど workspace で component を作成する際に使用するので控えておきます。
ここで、TwinMaker workspace の実行 role(twinmaker-workspace-vehiclefleetworkspace-<account id>-iad)に次の permission を追記します。
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "lambda:InvokeFunction",
"Resource": "arn:aws:lambda:*:*:function:TimestreamTelemetry_SchemaInitializer"
},
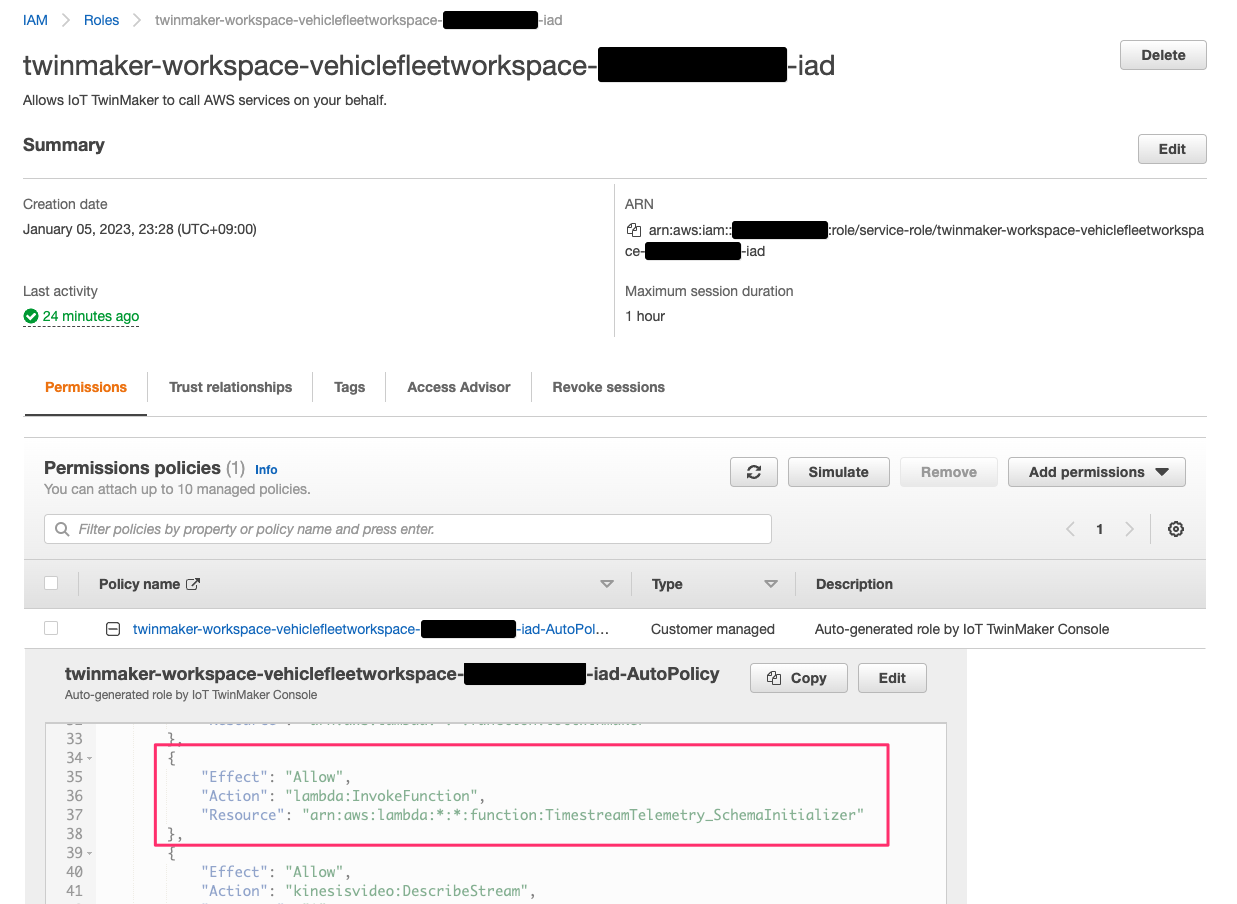
これをしなければ後続の手順[Import Ontology]で作成した entity が次のようにTimestreamTelemetry_SchemaInitializerfunction の実行権限が無い旨のエラーとなってしまいます。
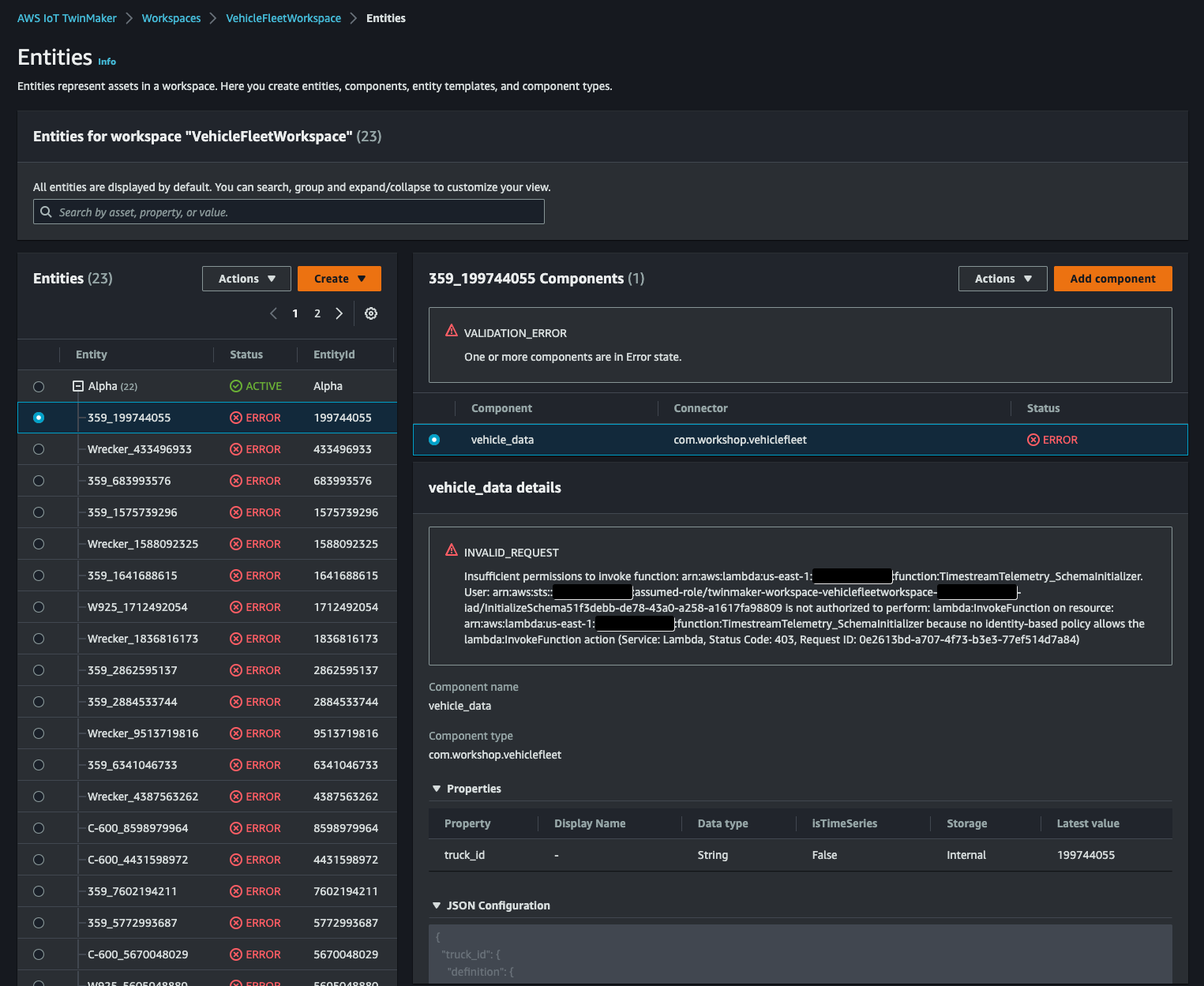
こうなるとエラーとなった entity を一度すべて削除する必要がありめんどうなので気をつけましょう。(workshop の手順にこの操作がなく少しハマりました)
Create AWS IoT TwinMaker Component
AWS IoT TwinMaker > Workspaces > VehicleFleetWorkspace > Component types > Create component typeにアクセスし、次の JSON を先程控えた Lambda function の ARN および使用している AWS 環境の情報で置き換えて[Request]に指定します。[Create component type]をクリックして componet の作成を完了します。
{
"workspaceId": "VehicleFleetWorkspace",
"isSingleton": true,
"componentTypeId": "com.workshop.vehiclefleet",
"propertyDefinitions": {
"truck_id": {
"dataType": {
"type": "STRING"
},
"isTimeSeries": false,
"isRequiredInEntity": true,
"isExternalId": false,
"isStoredExternally": false,
"isImported": false,
"isFinal": false,
"isInherited": false
}
},
"functions": {
"dataReader": {
"implementedBy": {
"lambda": {
"arn": "[ARN OF THE DATA READER LAMBDA]"
},
"isNative": false
},
"isInherited": false
},
"schemaInitializer": {
"implementedBy": {
"lambda": {
"arn": "[ARN OF THE SCHEMA INITIALIZER LAMBDA]"
},
"isNative": false
},
"isInherited": false
}
},
"arn": "arn:aws:iottwinmaker:[REGION]:[ACCOUNT-NUMBER]:workspace/VehicleFleetWorkspace/component-type/com.workshop.vehiclefleet",
"isAbstract": false,
"isSchemaInitialized": false
}
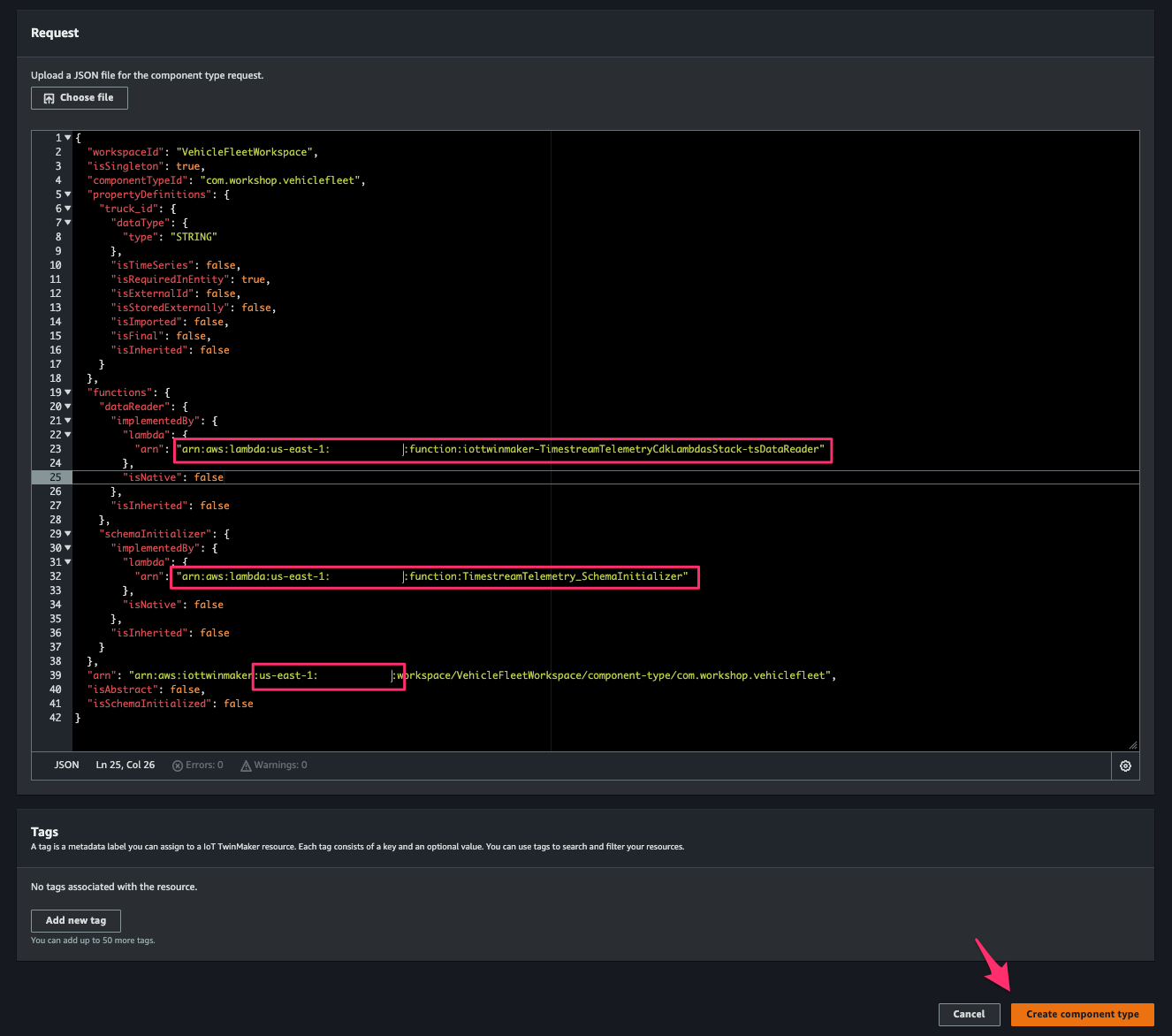
Import Ontology
ここでは TwinMaker workspace に entity を作成し、先程作成した component を entity に紐付けします。
Cloud9 environment に戻り、次の fileimport_ontology.pyを作成します。
# Copyright Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. 2021
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
# This is a sample importer that will gather a list of entities from a sample
# TimeStream database and create the entities in IoT TwinMaker
import argparse
import csv
import json
import os
import re
import logging
import boto3
import time
import sys
# Configure logger
LOGGER = logging.getLogger()
LOGGER.setLevel(logging.INFO)
def boto3_session(profile = 'default', region = 'us-east-1'):
s = boto3.Session(
#profile_name = profile if profile else os.environ.get('AWS_PROFILE'),
region_name = os.environ.get('AWS_REGION' ) if os.environ.get('AWS_REGION' ) else region)
#s = boto3.Session( profile_name = 'mykey', region_name = 'us-east-1')
return s
def get_iottwinmaker_client():
iottwinmaker = boto3_session().client('iottwinmaker')
return iottwinmaker
def get_timestream_client():
timestream = boto3_session().client('timestream-query')
return timestream
#SERVICE_ENDPOINT= os.environ.get('AWS_ENDPOINT')
timestream_client = get_timestream_client()
iottwinmaker_client = get_iottwinmaker_client()
## -f as the input iottwinmaker json file
def parse_arguments():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description='Load JSON entities into Iottwinmaker')
parser.add_argument('-w', '--workspace-id',
help='The workspace id to create components and entities in',
required=True)
parser.add_argument('-c', '--component-type-id',
help='The component id for timestream',
required=True)
parser.add_argument('-d', '--timestream-database',
help='The sample timestream database',
required=True)
parser.add_argument('-t', '--timestream-table',
help='The sample timestream table',
required=True)
parser.add_argument('-r', '--iottwinmaker-role-arn',
help='ARN of the role assumed by Iottwinmaker',
default=False,
required=False)
return parser
def log(isError, message):
if sys.stdin and sys.stdin.isatty():
print(message)
else:
if(isError):
LOGGER.error(message)
else:
LOGGER.info(message)
def populate_assets(entity, comp_id, workspace_id):
#create_properties_component(workspace_id, comp_id)
description = entity.get("description")
properties = entity.get("properties",{})
components = {
"vehicle_data": {
"componentTypeId" : comp_id,
"properties" : properties
}
}
return components
def entity_exists(workspace_id, entity_id):
try:
resp = iottwinmaker_client.get_entity(
workspaceId = workspace_id,
entityId = entity_id)
api_report(resp)
except:
return False
return True
def get_parent_from_input(input_entities, parent_id):
for entity in input_entities:
if parent_id == entity.get("entity_id"):
return entity
return None
def create_root(root_id, root_name, workspace_id):
if root_name == '$ROOT':
root_name = 'ROOT'
return {
"entityId": root_id,
"entityName": root_name,
"description": root_name,
"workspaceId": workspace_id
}
def create_iottwinmaker_entity(input_entities, entity, workspace_id, comps):
entity_id = entity.get("entity_id")
parent_id = entity.get("parent_entity_id")
entity_name = entity.get("entity_name")
parent_name = entity.get("parent_name")
comp_id = entity.get("component_type")
description = entity.get("description") if entity.get("description") else entity_name
log(False, f"Processing entity {entity_id}, parent {parent_id}")
if entity_exists(workspace_id, entity_id):
return
if parent_id is not None:
comps = populate_assets(entity, comp_id, workspace_id) if comp_id else comps
parent_exists = entity_exists(workspace_id, parent_id)
if not parent_exists:
parent = get_parent_from_input(input_entities, parent_id)
if parent is not None:
create_iottwinmaker_entity(input_entities, parent, workspace_id, None) # no component will be used for the parent in this sample
else:
root = create_root(parent_id, parent_name, workspace_id)
create_entity_api(None, root, workspace_id)
ntt = { "entityName": entity_name,
"entityId": entity_id,
"description": description,
"workspaceId": workspace_id }
if parent_id is not None:
ntt["parentEntityId"] = parent_id
create_entity_api(comps, ntt, workspace_id)
def create_entity_api(comps, ntt, workspace_id):
if comps:
resp = iottwinmaker_client.create_entity(
**ntt, components=comps)
else:
resp = iottwinmaker_client.create_entity(**ntt)
api_report(resp)
wait_over(iottwinmaker_client.get_entity,
{"entityId": ntt.get('entityId'), "workspaceId": workspace_id},
'status.state', 'ACTIVE')
# Log non 200 responses or non api responses
def api_report(response):
m = response.get('ResponseMetadata')
if m:
s = m.get('HTTPStatusCode')
if s:
c = int(s)
if c != 200:
log(True,"Error: " + str(response))
else:
log(False,str(response))
else:
log(False,str(response))
def wait_over(aws_api, api_params, nested_jq_path,
expected_value, timeout=30, hop=1):
if timeout <= 0:
#print("Timed out")
return False
## Start with sleep, just in case the original call has not yet gone through
time.sleep(hop)
resource = aws_api(**api_params)
keys = nested_jq_path.split(".")
for k in keys:
resource = resource.get(k)
if expected_value == resource:
return True
else:
#print("waiting.." + str(timeout) + " seconds")
return wait_over(aws_api, api_params, nested_jq_path,
expected_value, timeout-1, hop)
def show_entity(entity):
log(False,str(entity))
def queryTimeStreamOntology(DATABASE_NAME, TABLE_NAME):
entities = { "entities":[]}
try:
query_string = f"SELECT distinct fleet, make, model, truck_id" \
f" FROM {DATABASE_NAME}.{TABLE_NAME} "
query_result = timestream_client.query(QueryString=query_string)
column_info = query_result['ColumnInfo']
for row in query_result['Rows']:
values = __parse_row(column_info, row)
entity = {}
entity["entity_id"] = values["truck_id"]
entity["parent_entity_id"] = values["fleet"]
entity["entity_name"] = values["model"]+ "_" + values["truck_id"]
entity["parent_name"] = values["fleet"]
entity["component_type"] = "com.workshop.vehiclefleet"
entity["description"] = "A {} {} truck with ID {}".format(values["make"],values["model"],values["truck_id"])
entity["properties"] = {
"truck_id": {
"definition":{
"dataType":{
"type": "STRING"
},
"isRequiredInEntity": True,
},
"value": {
"stringValue": values["truck_id"]
}
}
}
entities["entities"].append(entity)
#### Add Root Parent
root = {}
root["entity_id"] = values["fleet"]
root["entity_name"] = values["fleet"]
root["description"] = "{} fleet of trucks".format(values["fleet"])
entities["entities"].append(root)
except Exception as e:
log(True,"Query exception: %s".format(str(e)))
raise e
return entities
def __parse_row(column_info, row):
data = row['Data']
row_output = {}
for j in range(len(data)):
info = column_info[j]
datum = data[j]
key,val = __parse_datum(info, datum)
row_output[key] = val
return row_output
def __parse_datum(info, datum):
column_type = info['Type']
return __parse_column_name(info), datum['ScalarValue']
def __parse_time_series(info, datum):
time_series_output = []
for data_point in datum['TimeSeriesValue']:
time_series_output.append("{time=%s, value=%s}"
% (data_point['Time'],
__parse_datum(info['Type']['TimeSeriesMeasureValueColumnInfo'],
data_point['Value'])))
return "[%s]" % str(time_series_output)
def __parse_column_name(info):
if 'Name' in info:
return info['Name']
else:
return ""
def __parse_array(array_column_info, array_values):
array_output = []
for datum in array_values:
array_output.append(__parse_datum(array_column_info, datum))
return "[%s]" % str(array_output)
def process_records(j_data, workspace_id, comp_id):
entities = j_data.get("entities")
for entity in entities:
comps = populate_assets(entity, comp_id, workspace_id)
#create_iottwinmaker_entity( entity, workspace_id )
create_iottwinmaker_entity( entities, entity, workspace_id, comps )
def create_iottwinmaker_entities(j_data, workspace_id, comp_id, iottwinmaker_role_arn):
process_records(j_data, workspace_id, comp_id)
def import_handler(event, context):
input = event.get('body')
database = input.get("timestream_database")
table = input.get("timestream_table")
workspace_id = input.get("workspaceId")
connector = input.get("componentTypeId")
iottwinmaker_role_arn = input.get("iottwinmakerRoleArn")
json_content = queryTimeStreamOntology(database, table)
create_iottwinmaker_entities(json_content, workspace_id, connector, iottwinmaker_role_arn)
def main():
if __name__ != '__main__':
return
parser = parse_arguments()
args = parser.parse_args()
log(False,"Starting import...")
import_handler( {'body':{
'timestream_database':args.timestream_database,
'timestream_table':args.timestream_table,
'workspaceId':args.workspace_id,
'componentTypeId':args.component_type_id,
'iottwinmakerRoleArn' : args.iottwinmaker_role_arn}}, None)
main()
# install boto3 pip3 install boto3 # Run the python script with the commands below. It may take up to 90 seconds to complete the import cd ~/environment export AWS_REGION=us-east-1 # Change to your region python3 import_ontology.py -w VehicleFleetWorkspace -c com.workshop.vehiclefleet -d fleetdb -t IoT
AWS IoT TwinMaker > Workspaces > VehicleFleetWorkspace > Entitiesにアクセスすると、Alphaの配下に先程作成した component が追加された entity が 40 個作成されているはずです。
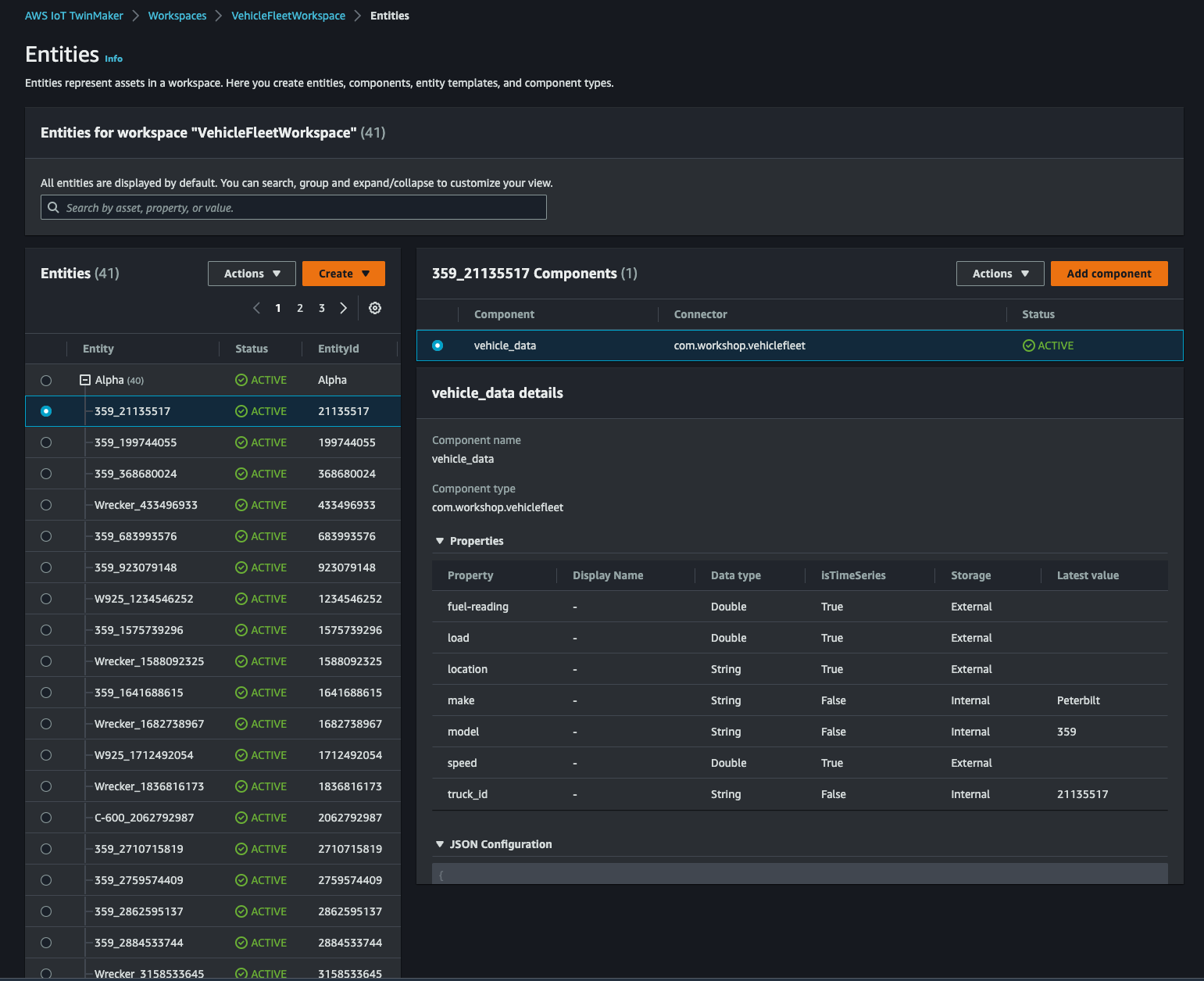
Upload 3D Model
トラックの 3D model をアップロードして workspace で使えるようにします。
こちらから glb 形式の 3D model をダウンロードします。
AWS IoT TwinMaker > Workspaces > VehicleFleetWorkspace > Resource Libraryにアクセスし、[Add resources]をクリックして 3D model をアップロードします。
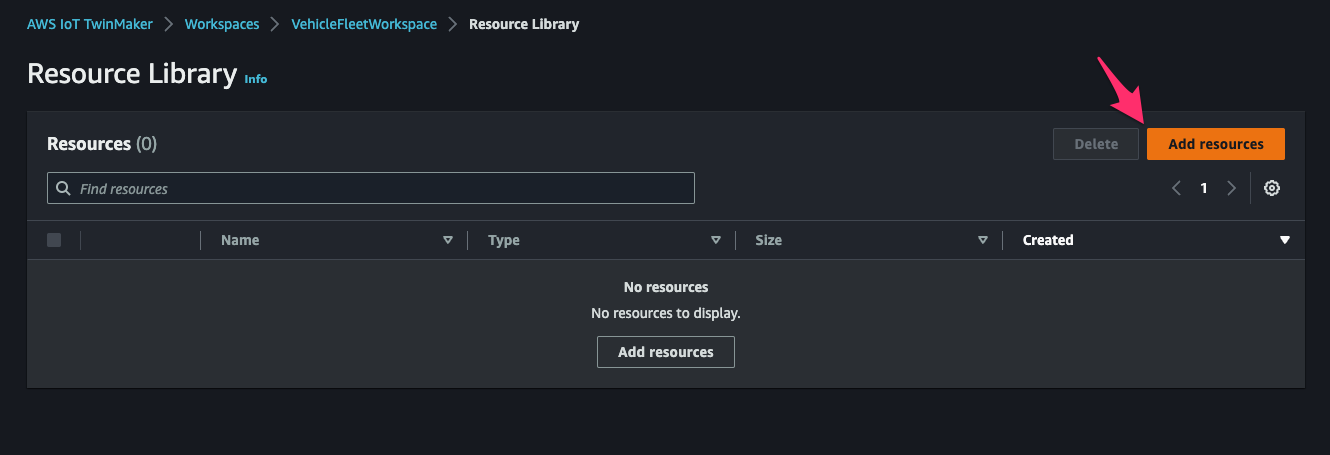
アップロードできました。
Create Scene
AWS IoT TwinMaker > Workspaces > VehicleFleetWorkspace > Scenesにアクセスし、[Create scene]をクリック。
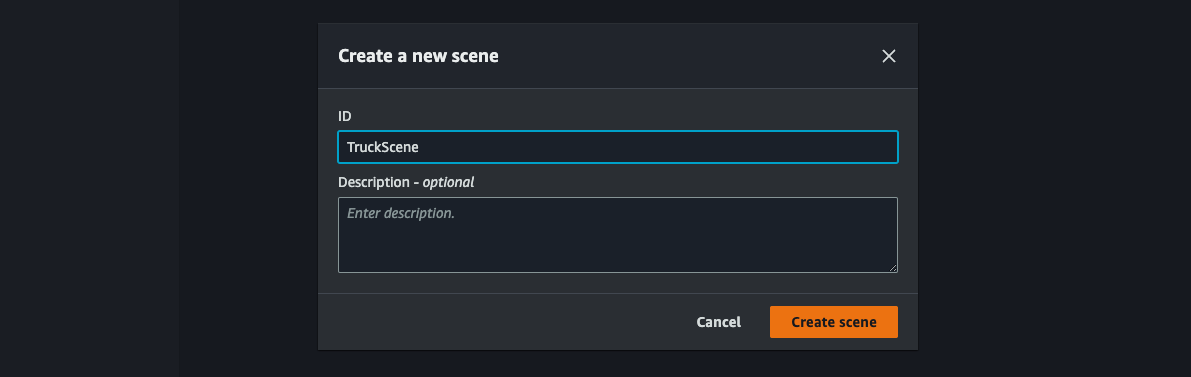
[ID]でTruckSceneと指定し[Create scene]をクリック。
[+ > Add 3D model]をクリック。
先程アップロードした resource を選択して[Add]をクリック。

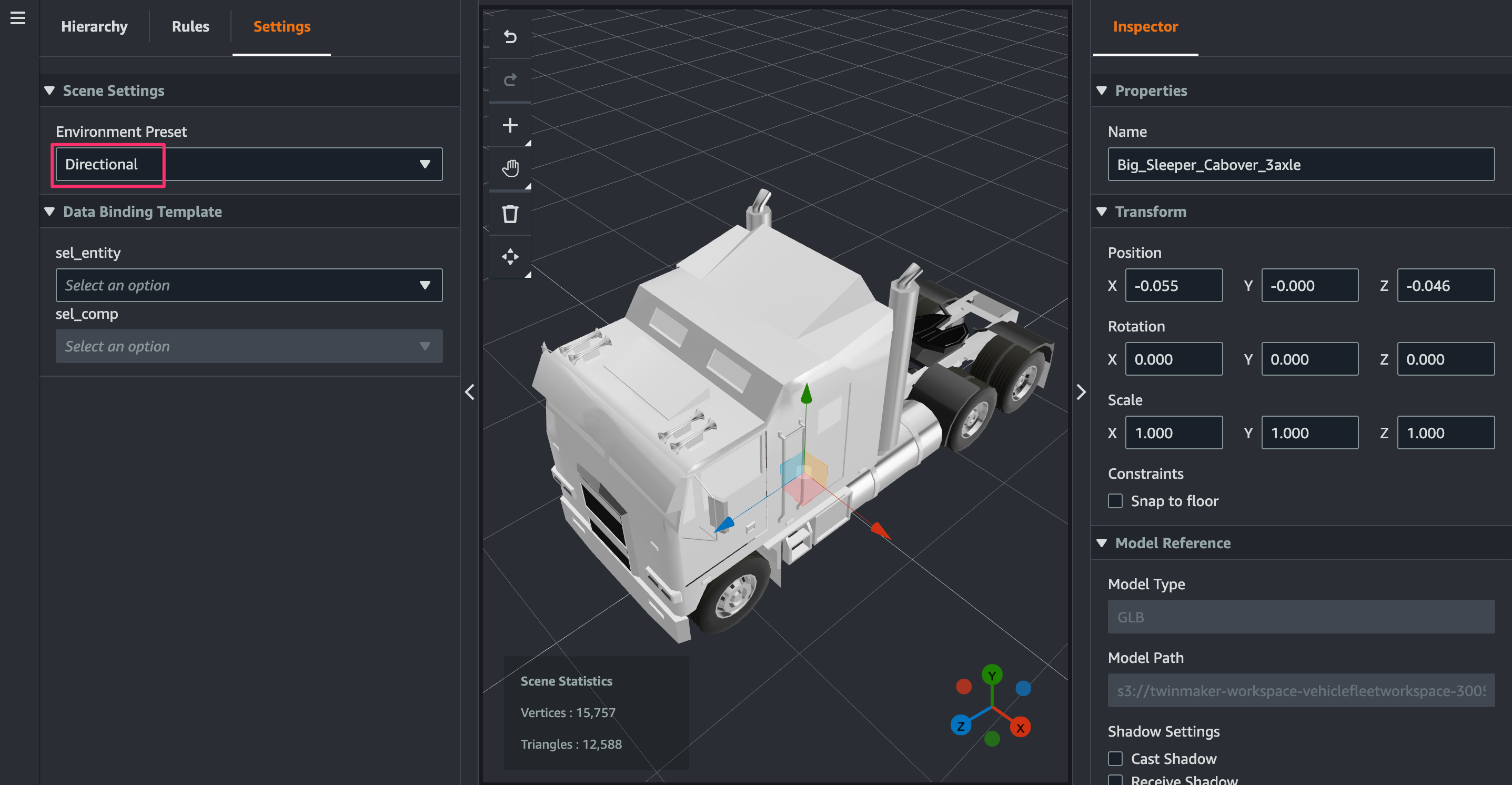
3D model が追加されたら、[Settings]タブの[Environment Preset]でDirectionalを選択します。すると 3D model に色が付くようになります。
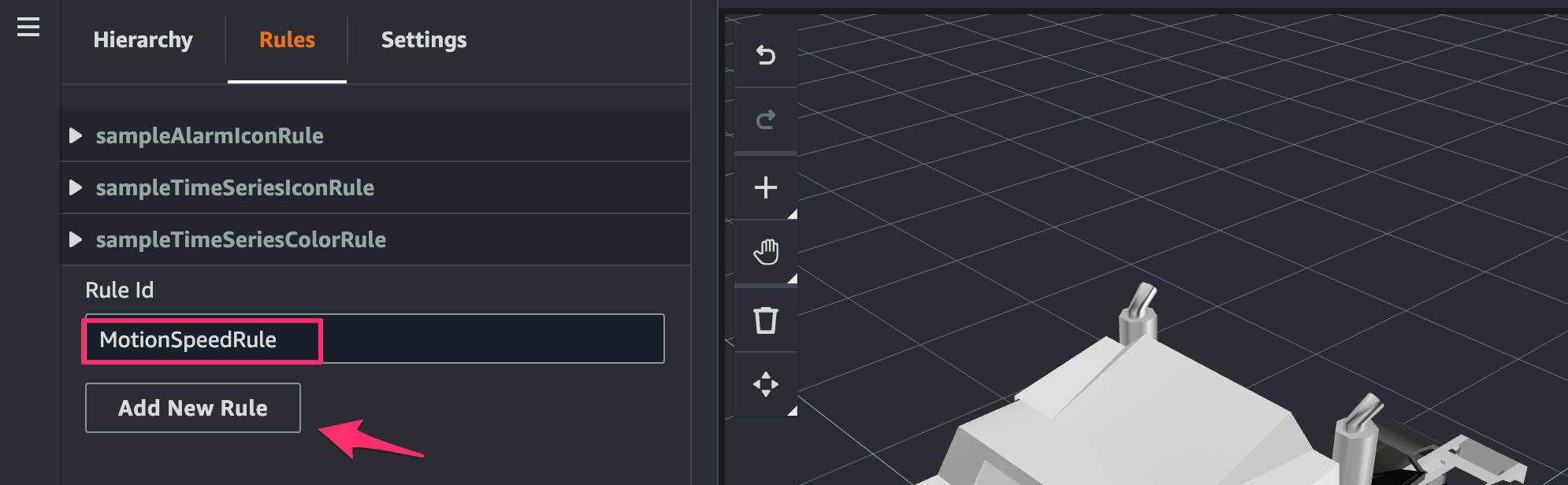
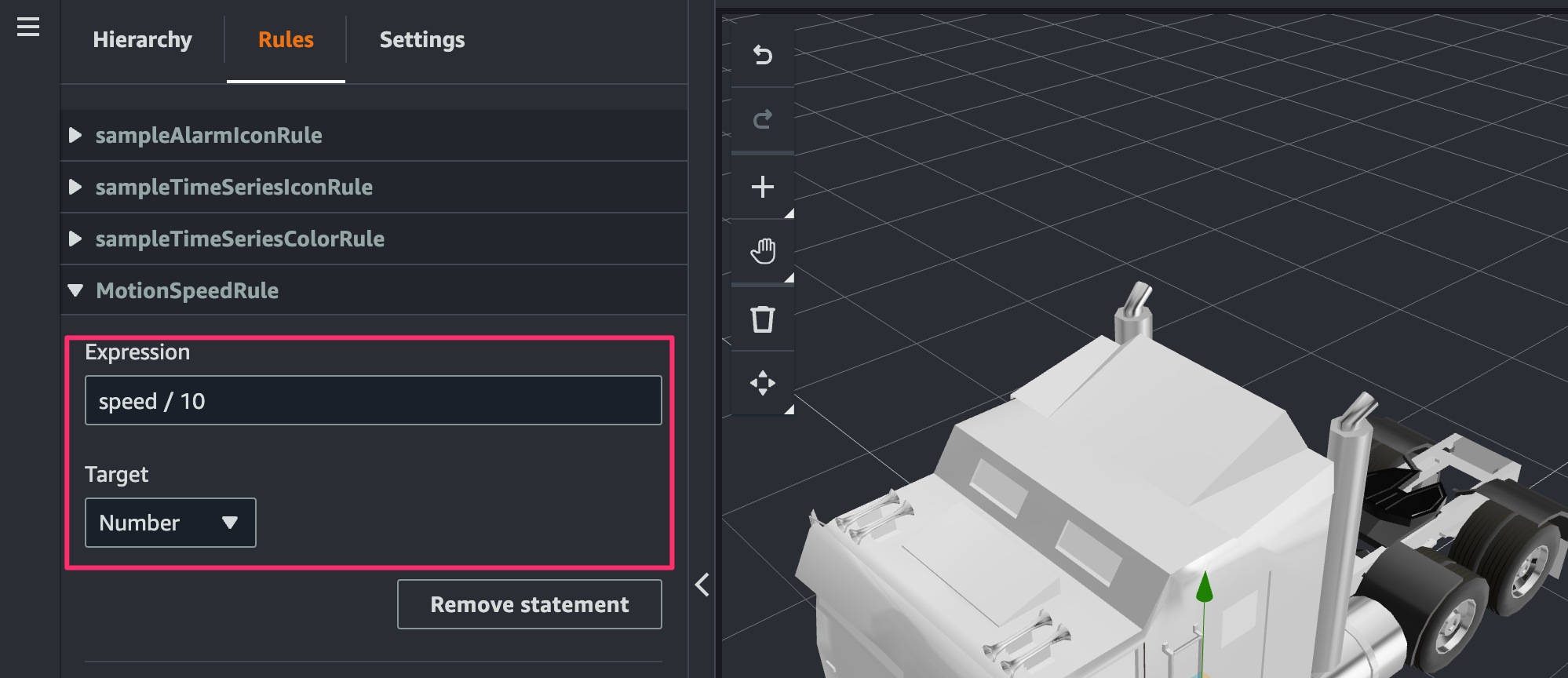
[Rules]で[Rule ID]にMotionSpeedRuleを指定し[Add New Rule]をクリック。
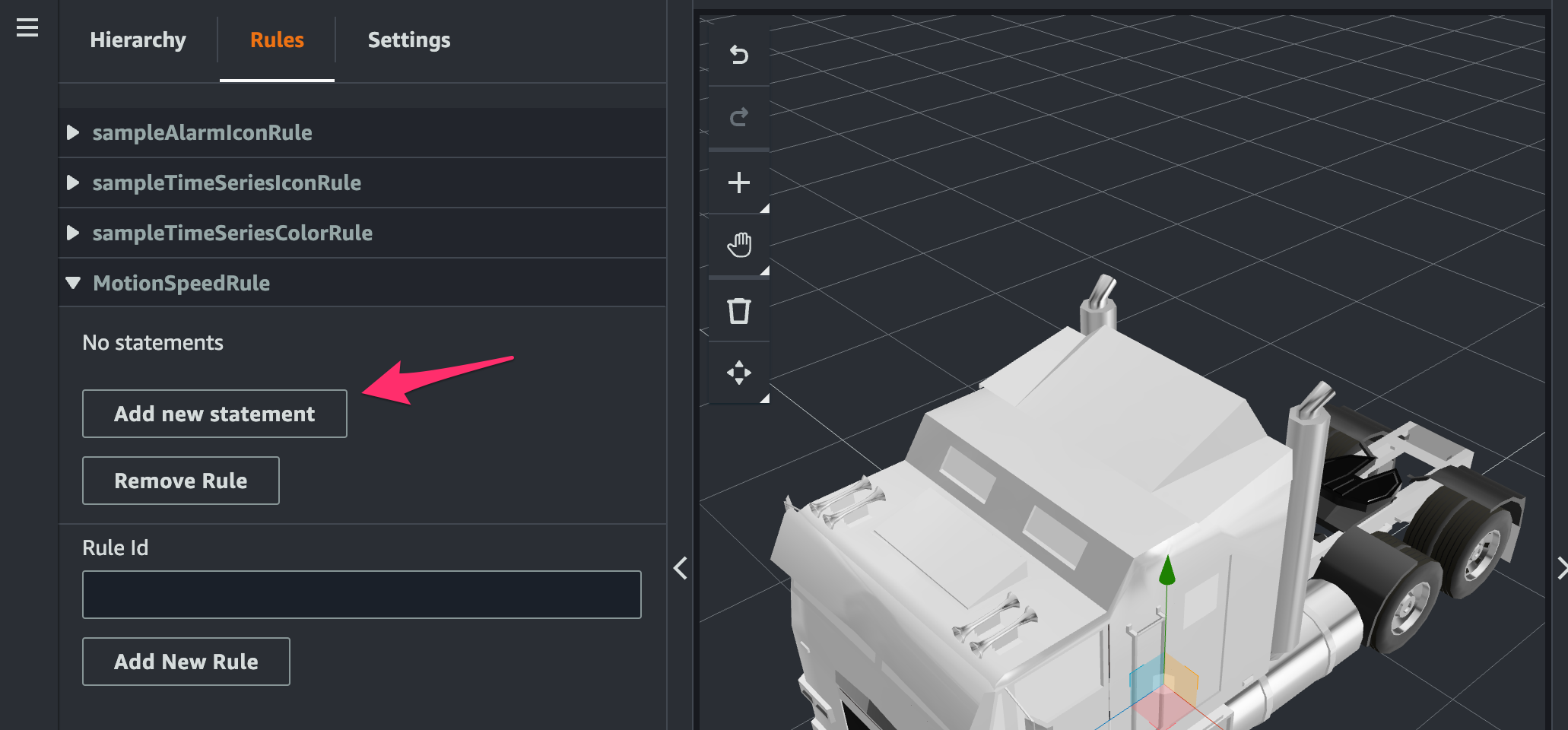
追加された rule の[Add new statement]をクリック。
statement を次のように指定します。
- Expression:
speed / 10 - Target:
Number
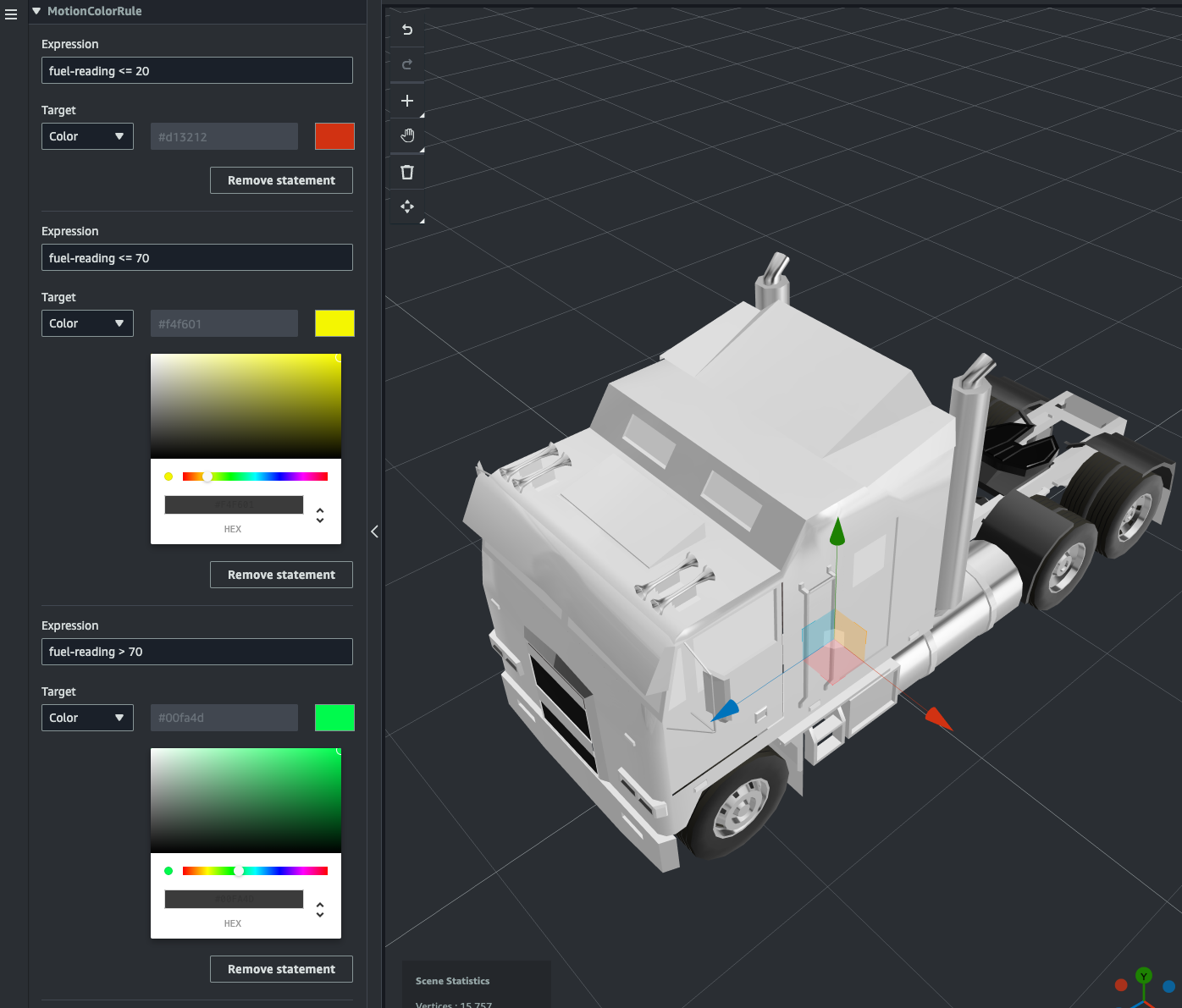
また同様にMotionColorRulerule を作成して次のように statement を設定します。
- 1:
- Expression:
fuel-reading <= 20 - Color:赤色
- Expression:
- 2:
- Expression:
fuel-reading <= 20 - Color:黄色
- Expression:
- 3:
- Expression:
fuel-reading > 70 - Color:緑色
- Expression:
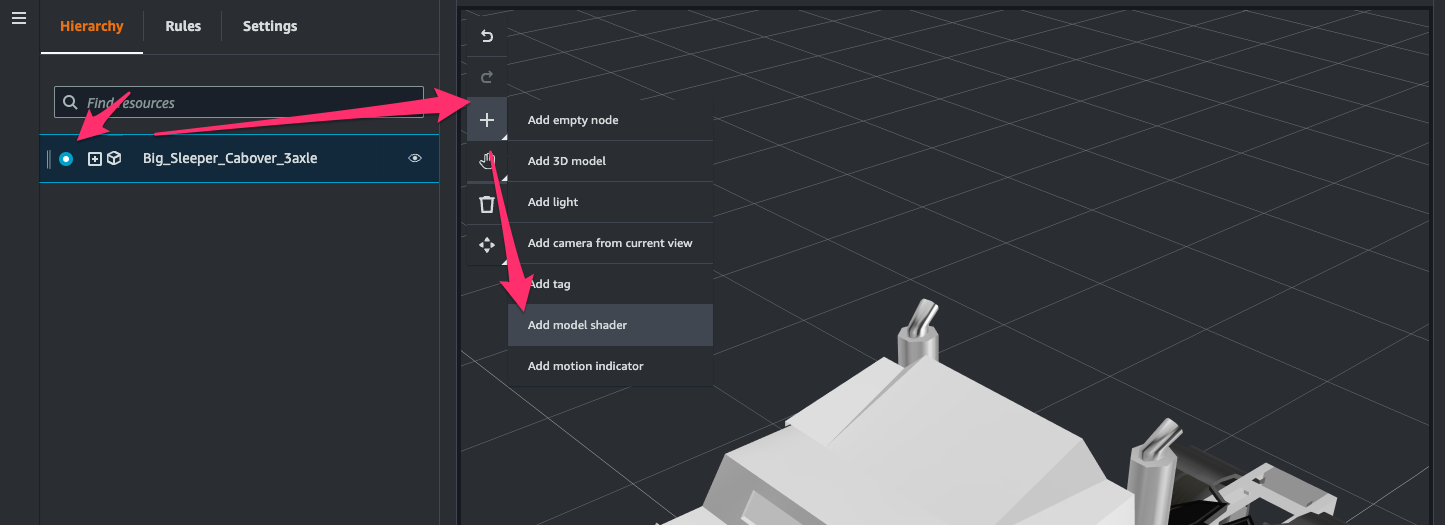
[Hierarchy]タブを開き 3D model の node を選択して[+ > Add model shader]をクリック。
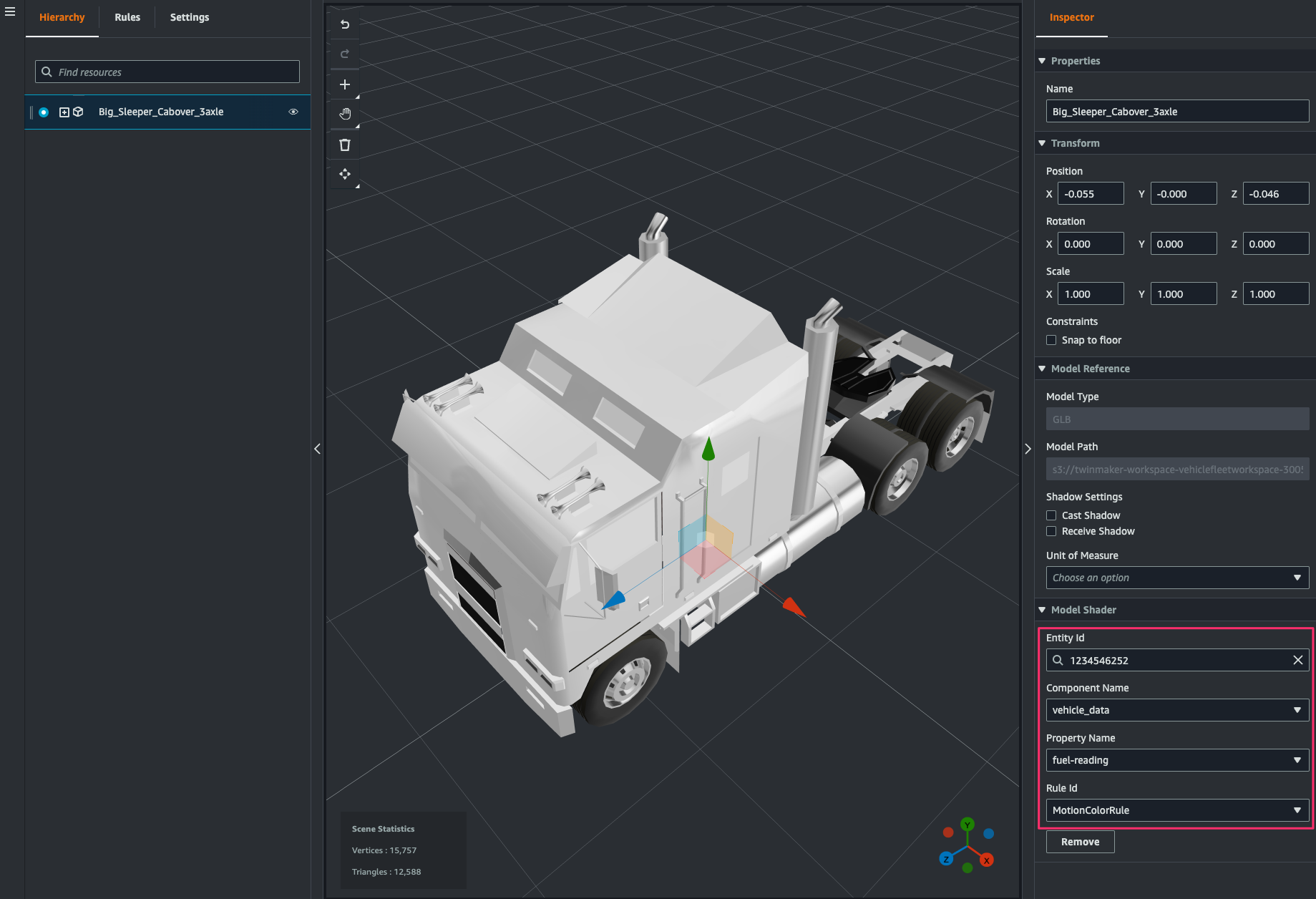
[Inspector > Model Shader]で次のように指定します。これにより component から取得したデータのfuel-readingの値に応じて 3D model の色が変わるようになります。
- Entity Id:
1234546252(W925_1234546252) - Component Name:
vehicle_data - Property Name:
fuel-reading - Rule Id:
MotionColorRule
同じ 3D model の node を選択して[+ > Add motion indicator]をクリック。
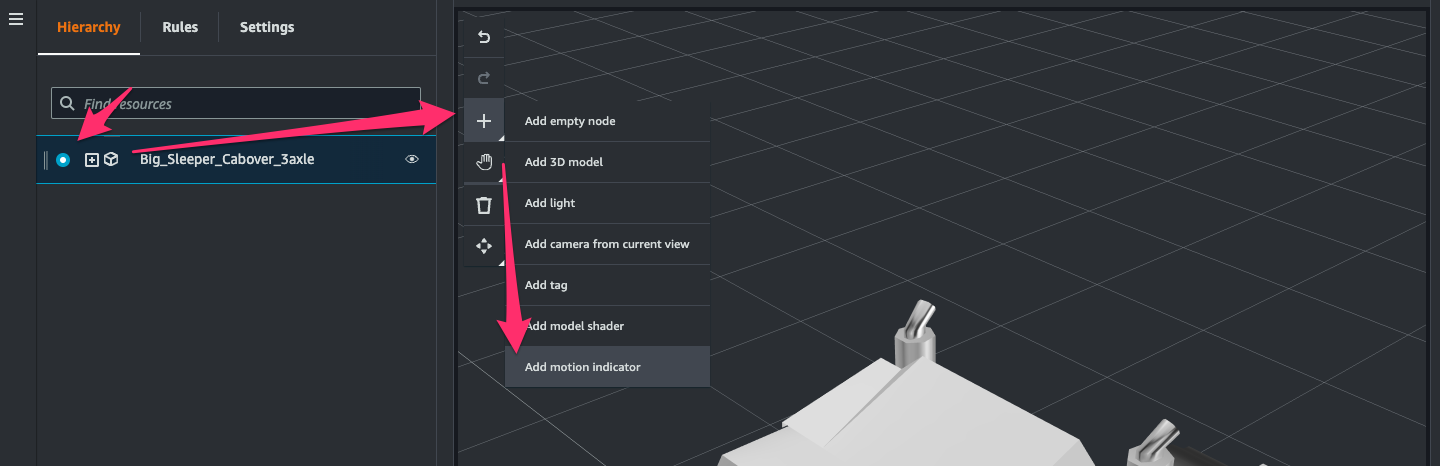
3D model の左前輪付近をクリック。
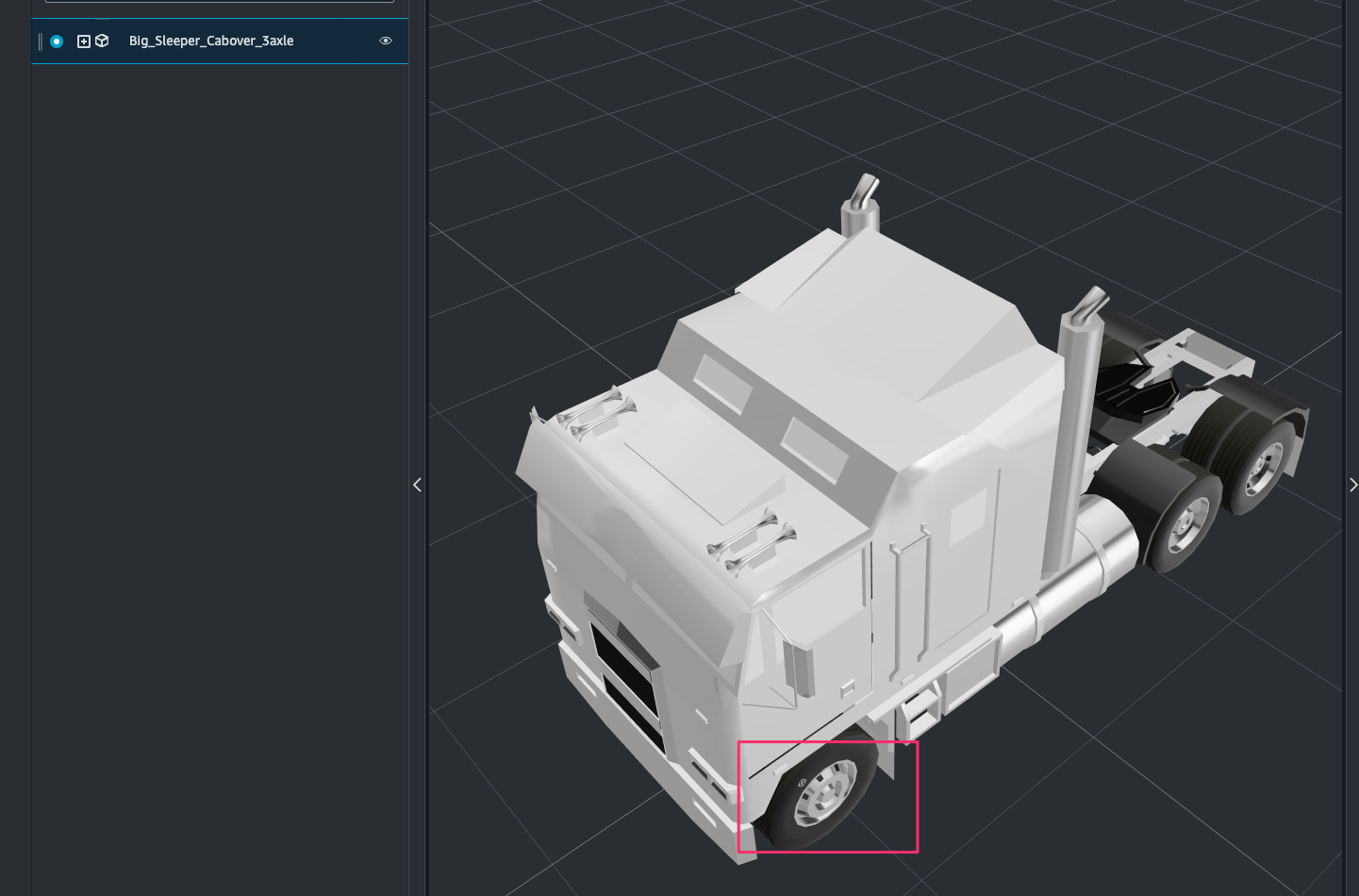
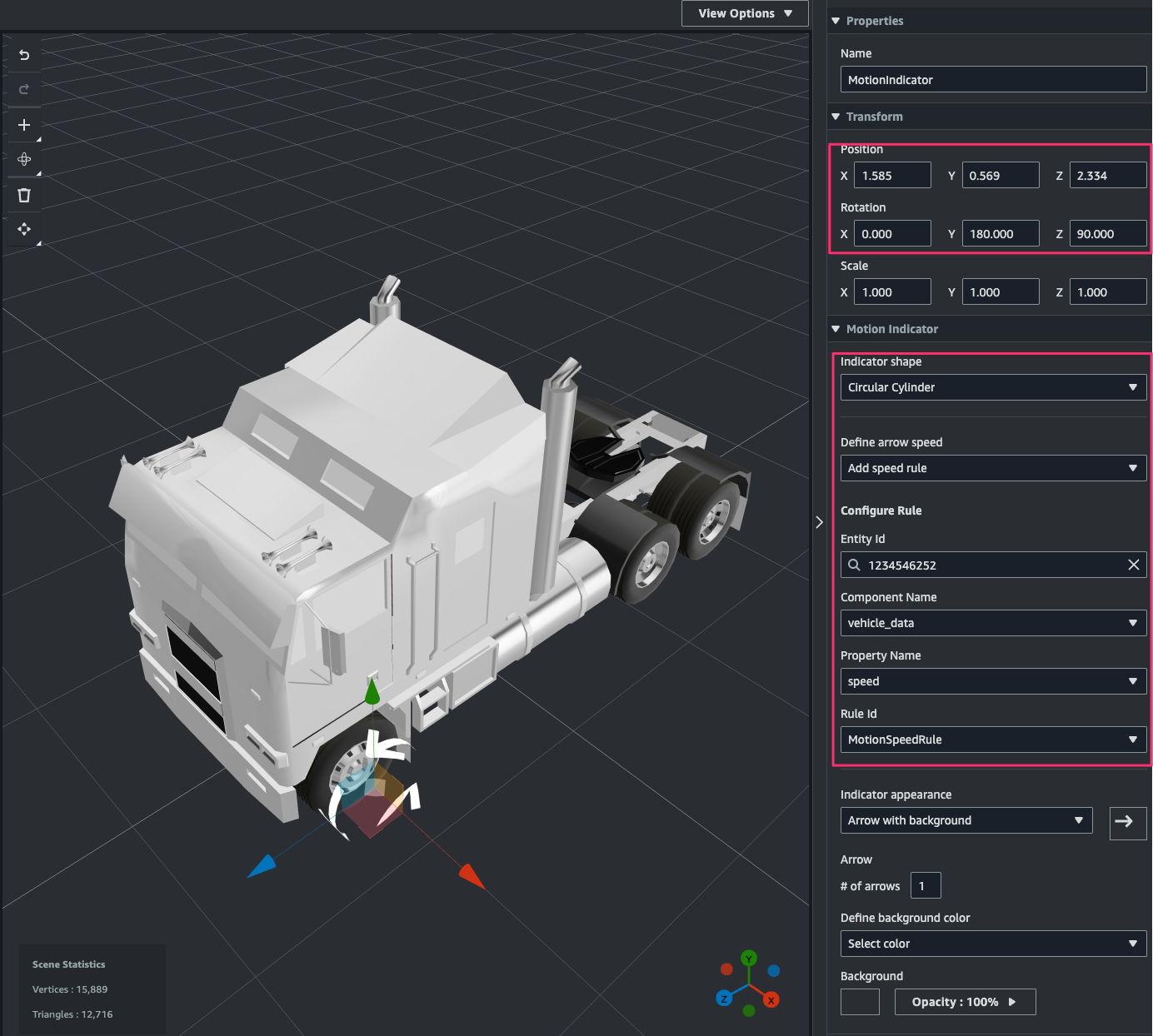
[Inspector]で次のように指定します。これにより component から取得したデータのspeedの値に応じて motion indicator の回転速度が変わるようになります。
- Transform
- Position:タイヤの左手前近くに位置を調整
- Rotation:
- Y:
180 - Z:
90
- Motion Indicator
- Indicator shape:
Circular Cylinder - Define arrow speed:
Add speed rule - Configure Rule:
- Entity Id:
1234546252(W925_1234546252) - Component Name:
vehicle_data - Property Name:
speed - Rule Id:
MotionSpeedRule
- Indicator shape:
Visualize in Grafana
Amazon Managed Grafana dashboard を設定して、ここまでで作成したトラックのデジタルツインを可視化します。
Configure Datasource in Amazon Managed Grafana
Grafana workspace に管理者ユーザーでアクセスしたら、[Configuration > Data sources]をクリック。
[Add data source]をクリック。
検索して表示されたAWS IoT TwinMakerをクリック。
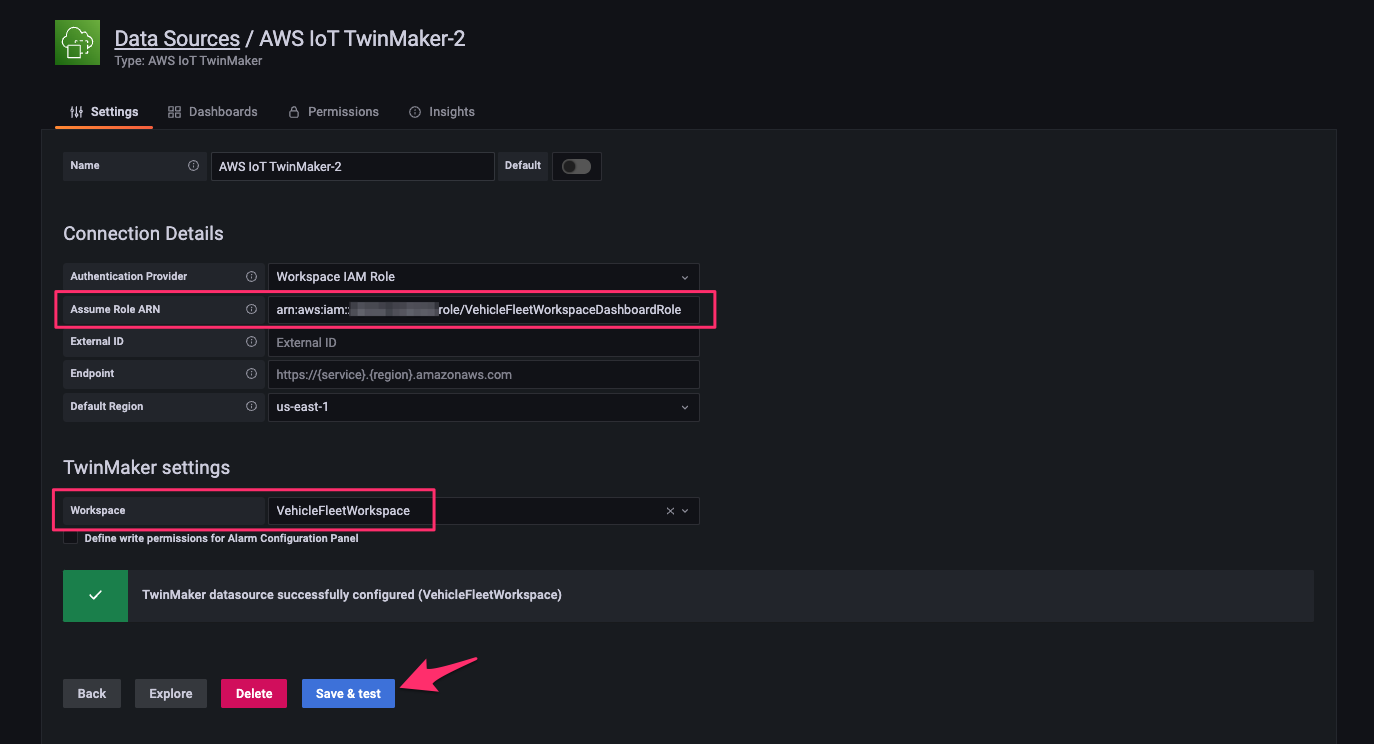
次のように指定して[Save & test]をクリックし、テストが成功することを確認します。
- Assume Role ARN:TwinMaker workspace に設定した dashboar role(
arn:aws:iam::<Account ID>:role/VehicleFleetWorkspaceDashboardRole) - Workspace:
VehicleFleetWorkspace
Create Dashboard
[+ > Dashboard]をクリック。
[Add a new panel]をクリック。
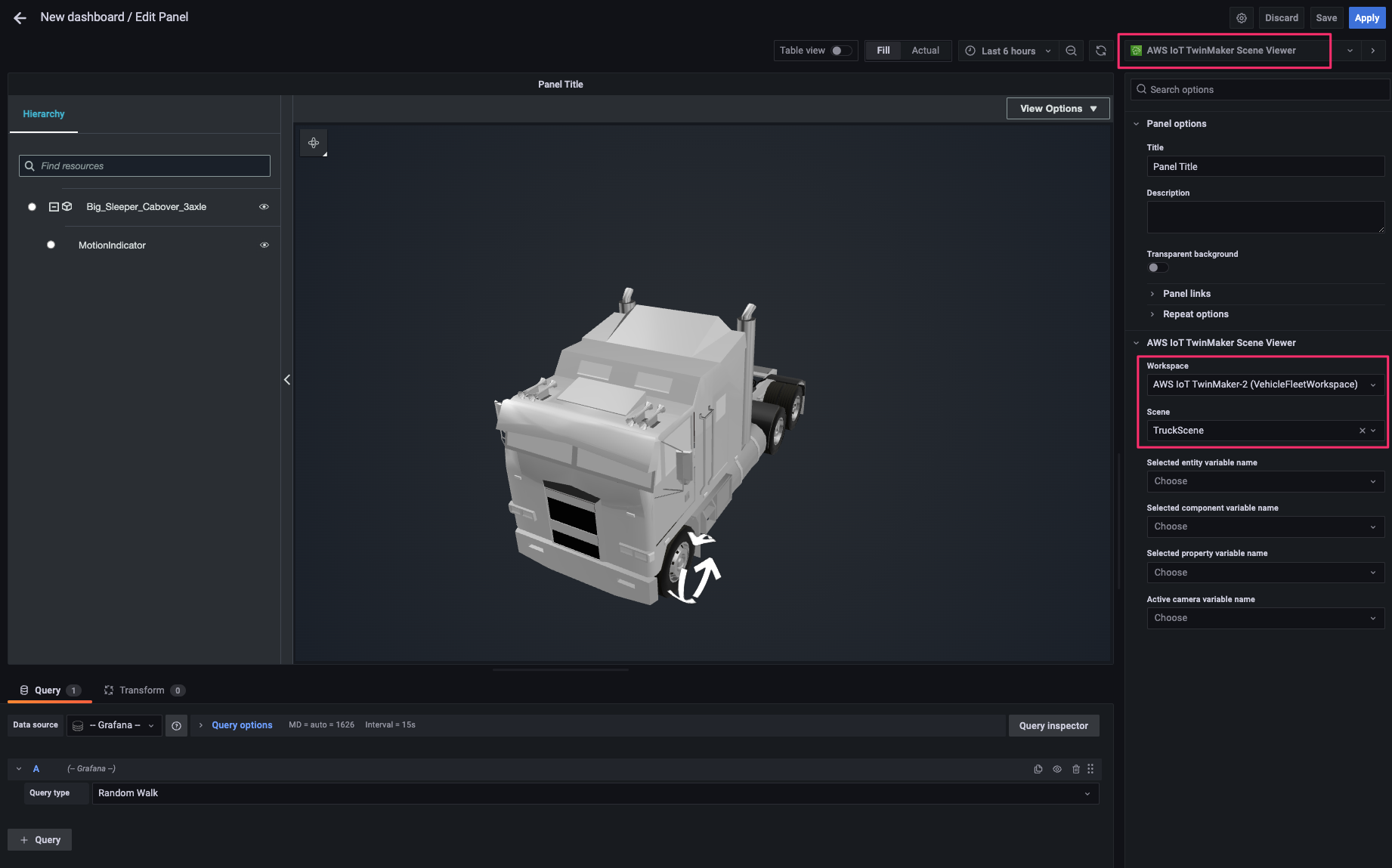
visualization を次の通り指定します。scene および 3D model が読み込まれます。
- visualization:
AWS IoT TwinMaker Scene Viewer - Workspace:
VehicleFleetWorkspace - Scene:
TruckScene
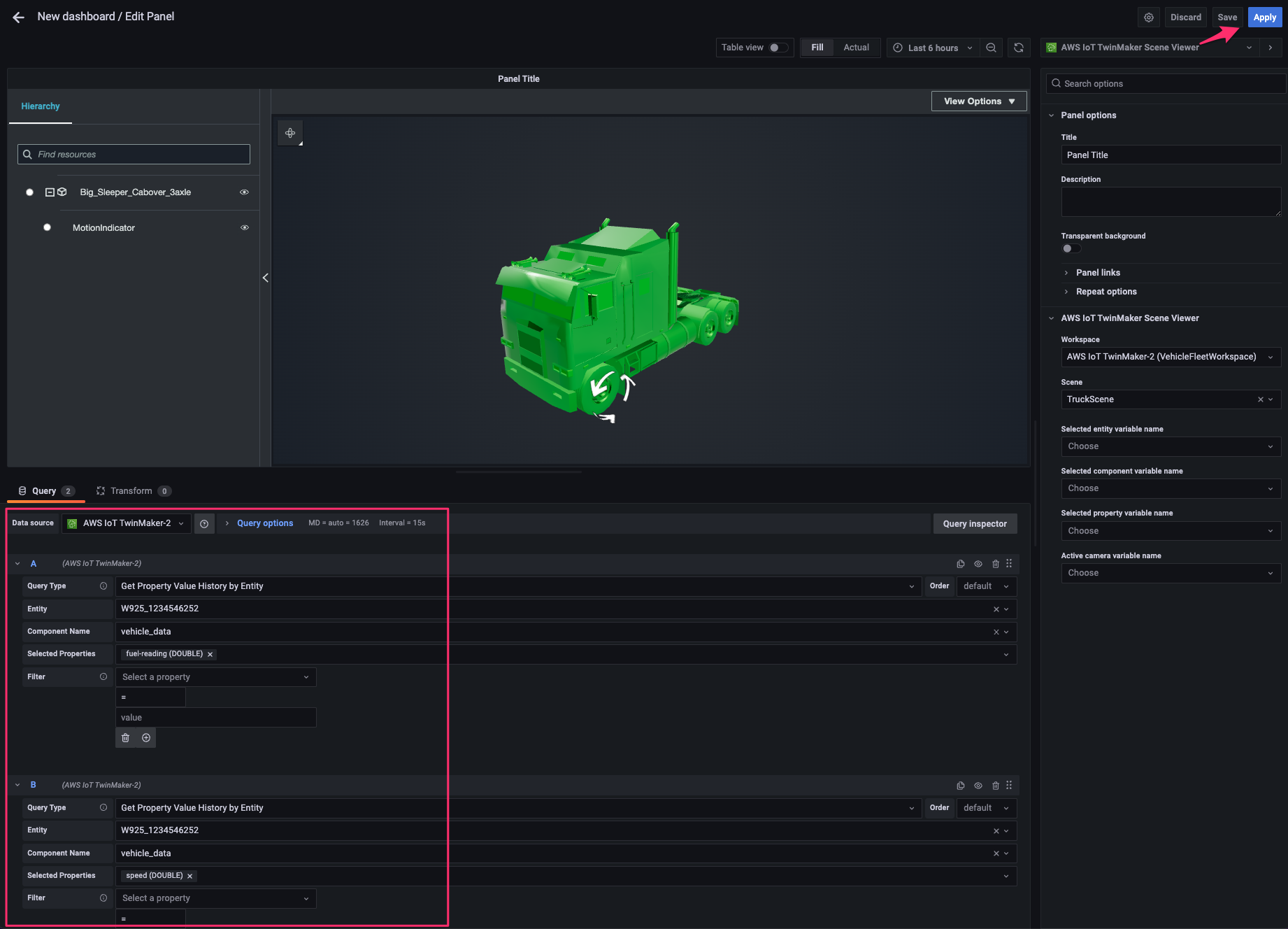
[data source]で先程追加した AWS IoT TwinMaker の data source を指定し、次の 2 つの query を追加します。すると 3D model 上の indicator が回転を開始するはずです。[Apply]をクリックして変更を適用します。
- A:
- Query Type:
Get Property Value History by Entity - Entity:
W925_1234546252 - Component Name:
vehicle_data - Selected Properties:
fuel-reading
- Query Type:
- B:
- Query Type:
Get Property Value History by Entity - Entity:
W925_1234546252 - Component Name:
vehicle_data - Selected Properties:
speed
- Query Type:
次に画面右上の panel 追加ボタンをクリックし、表示される[Add a new panel]をクリック。
同じ data source および query で time series のチャートを追加します。
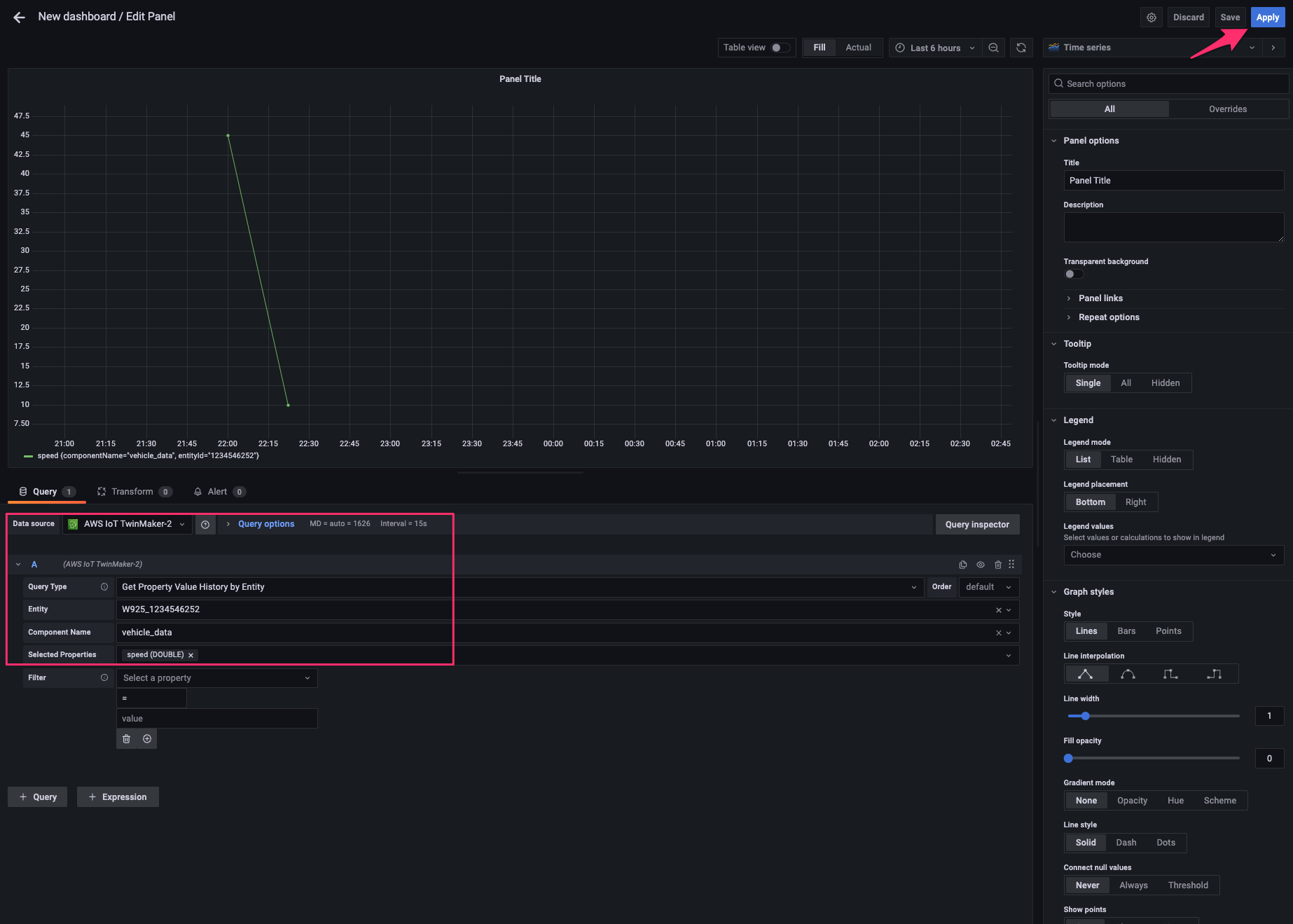
同じ要領で他の property の panel も追加し、配置を調整したら dashboard が出来上がりました。
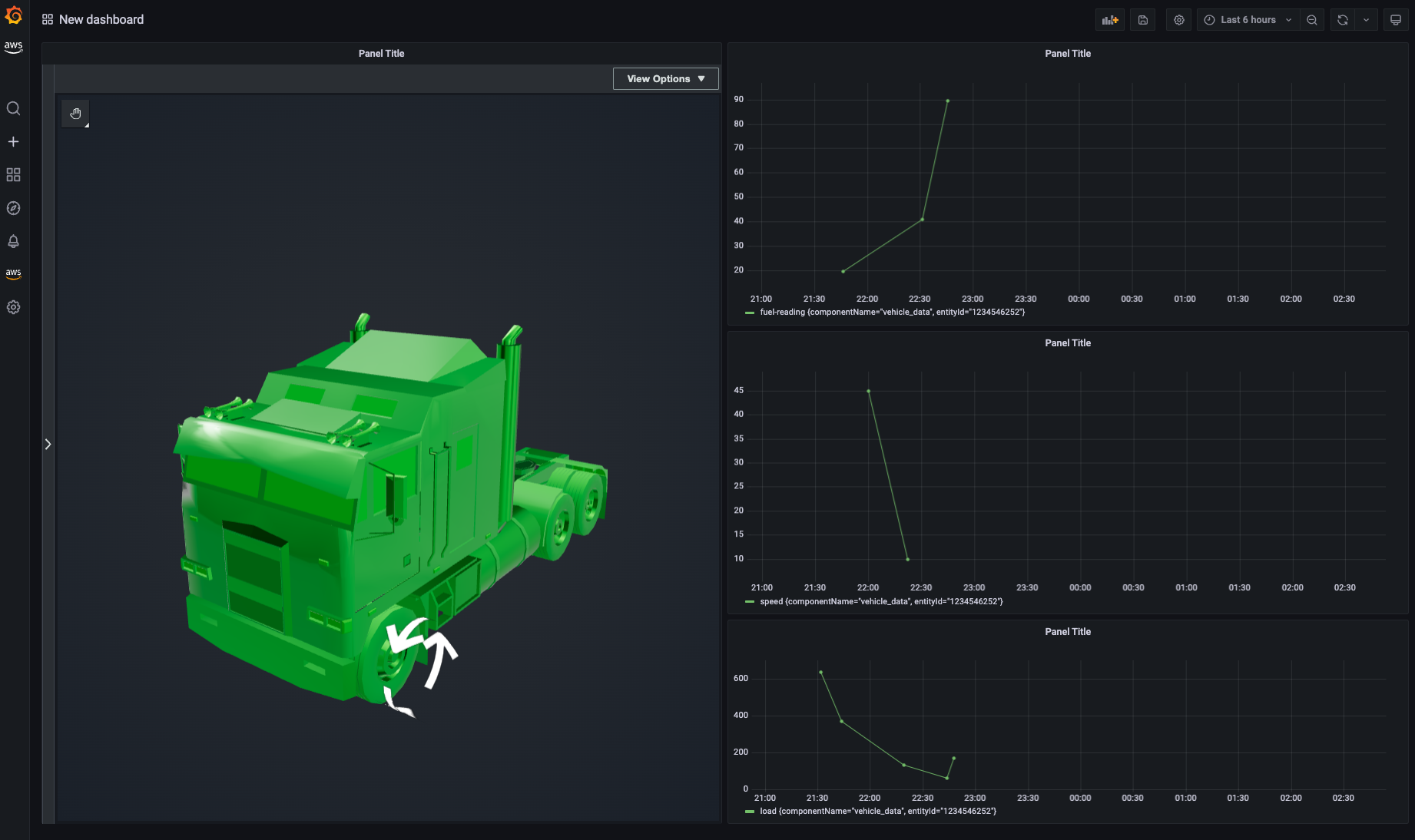
GIF だとこんな感じです。走行するトラックの速度に応じて motion indicator(矢印のシリンダー)の回転速度が変わるようになります。

おわりに
AWS IoT TwinMaker で走行するトラックのデジタルツインを作って可視化してみました。
現実の IoT データに応じてデジタルツイン上で動きが付けられるとより視覚に訴えた見える化ができるようになりますね。速度や進行方向などの動きがあるモノをデジタルツイン化する場合は是非とも設定をしてみたいです。
余談ですが、Schema initializerは今回初めて作ったのですが、その役割がまだいまいち理解できていないのでスクリプトを読み込むなりしてもう少し勉強します。
以上