
Service Brokerを利用してKubernetes(EKS)からAWSのリソースを作成する
この記事は公開されてから1年以上経過しています。情報が古い可能性がありますので、ご注意ください。
kubernetes好きのみなさん、Service Brokerは使っていますか?
Service Brokerを使えば、KubernetesのAPI経由でAWSやGCPなどの外部リソース(RDSやS3など)を管理することができます。なかなか面白い機能です。 ということで本日は、Service Broker(とService Catalog)を利用してAWSのリソースを作成する方法を紹介したいと思います。
現時点で管理できるAWSのリソースは以下になります。
- dynamodb AWS Service Broker - Amazon DynamoDB
- sqs AWS Servicebroker - Amazon SQS
- s3 AWS Service Broker - Amazon S3
- sns AWS Service Broker - Amazon SNS
- polly AWS Service Broker - Amazon Polly
- kinesis AWS Service Broker - Amazon Kinesis Data Stream
- elasticache AWS Service Broker - Amazon ElastiCache for memcached
- kms AWS Service Broker - KMS Key
- route53 AWS Service Broker - Amazon Route 53
- rdspostgresql AWS Service Broker - Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL
- emr AWS Service Broker - Amazon EMR
- rdsmariadb AWS Service Broker - Amazon RDS for MariaDB
- athena AWS Service Broker - Amazon Athena
- redshift AWS Service Broker - Amazon Redshift
- rekognition AWS Service Broker - Amazon Rekognition
- lex AWS Service Broker - Amazon Lex
- translate AWS Service Broker - Amazon Translate
- rdsmysql AWS Service Broker - Amazon RDS for MySQL
こちらのドキュメントを元に進めていきます。
今回構築する環境および実施内容のイメージ
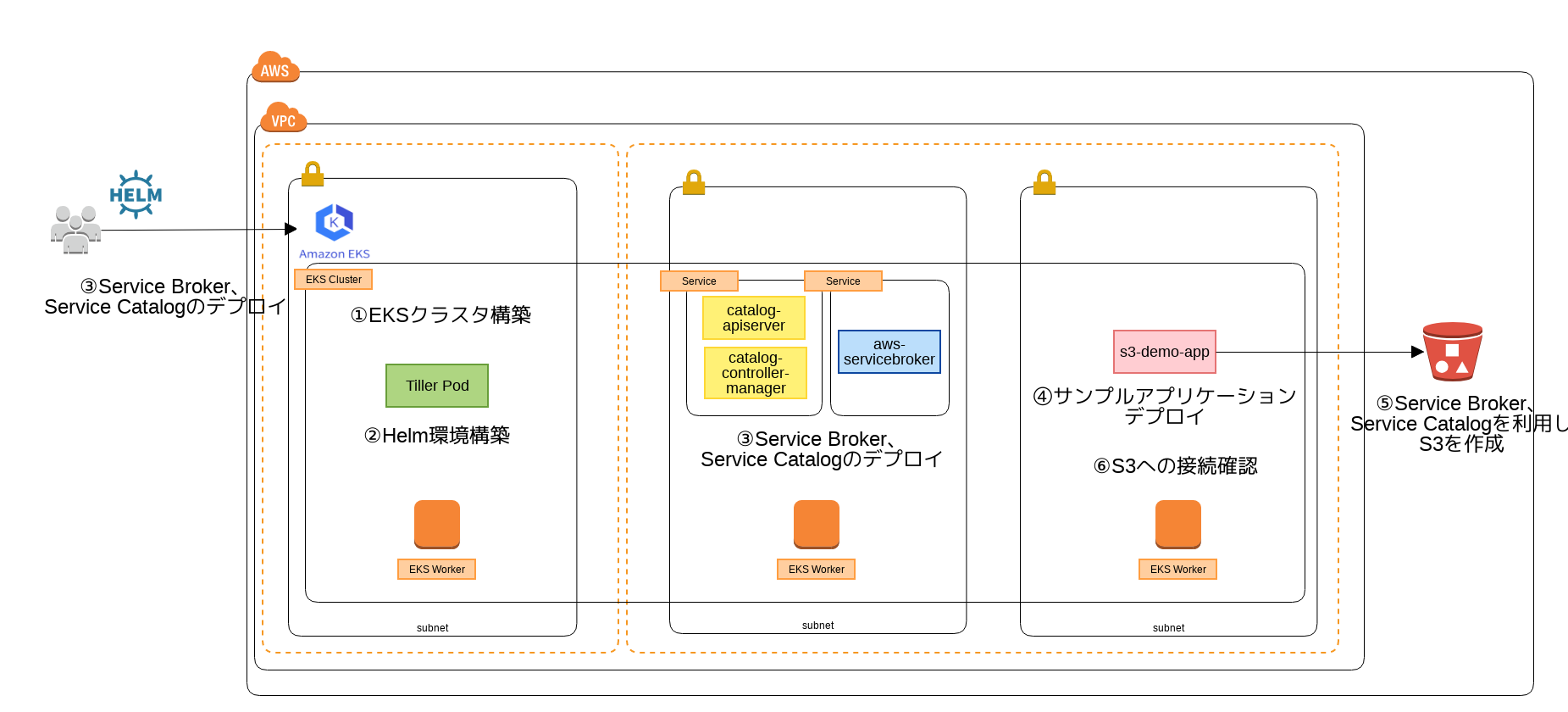
今回は以下の作業を実施します。
- EKSクラスタ構築
- Helm環境構築
- Service Broker、Service Catalogのデプロイ
- サンプルアプリケーションデプロイ
- Service Broker、Service Catalogを利用しS3を作成
- サンプルアプリケーションからのS3への接続確認
では早速やっていきましょう!
EKSクラスタを構築する
以下を参考に東京リージョンにEKSクラスタを構築します。
3つのWorkerノードをクラスタ化した状態からスタートします。 kubectlでの実行結果は以下のようになります。
$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION ip-192-168-168-64.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal NotReady <none> 0s v1.11.5 ip-192-168-176-167.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal NotReady <none> 1s v1.11.5 ip-192-168-220-213.ap-northeast-1.compute.internal NotReady <none> 1s v1.11.5 $ kubectl get all NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.100.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 19m
Helm環境構築
Service Broker、Service CatalogのデプロイにはHelmを利用します。まずはHelmを利用するため初期処理を行います。
#kube-systemにserviceaccountを作成 $ kubectl create serviceaccount tiller --namespace kube-system serviceaccount/tiller created #serviceaccountにRoleを紐付け $ kubectl create clusterrolebinding tiller \ --clusterrole=cluster-admin \ --serviceaccount=kube-system:tiller clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/tiller created #EKSクラスタ上にtillerをデプロイ $ helm init --service-account tiller $HELM_HOME has been configured at /Users/jogan.naoki/.helm. Tiller (the Helm server-side component) has been installed into your Kubernetes Cluster. Please note: by default, Tiller is deployed with an insecure 'allow unauthenticated users' policy. To prevent this, run `helm init` with the --tiller-tls-verify flag. For more information on securing your installation see: https://docs.helm.sh/using_helm/#securing-your-helm-installation Happy Helming!
デプロイが完了すると名前空間kube-systemにtillerのpodが作成されます。
$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system -l name=tiller NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE tiller-deploy-57f988f854-vdx6q 1/1 Running 0 1m
Service Broker、Service Catalogをデプロイする
次にEKSクラスタ上にService BrokerおよびServiceCatalogをデプロイします。
Service Brokerとは
Service Brokerは、開発者からの要求を受けてAWSやGCPなどの各種リソース(RDSやS3など)を作成するAPIサーバーです。Service Brokerは各プロバイダー毎に用意されています。AWSの場合、Service BrokerはCloudFormationにより必要なリソースを作成します。
Service Brokerは大きく分けて以下2つのリソースを作成します。
- Service Instance
- 対象のリソースを作成(RDSやS3など)
- k8sのマニュフェスト(kind: ServiceInstance)として定義
- Service Binding
- Service Instanceへの接続情報を作成
- k8sのマニュフェスト(kind: ServiceBinding)として定義
Service Catalogとは
Service Catalogは、KubernetesのAPIサーバーからの要求を受けてService Brokerを実行するAPIサーバーです。 KubernetesのAPIからリソースを作成する際には、Service Catalogを経由してService Brokerが呼び出されます。
Service Catalogのデプロイ
まずはService Catalogの方からデプロイしていきます。
#リポジトリを追加
$ helm repo add svc-cat https://svc-catalog-charts.storage.googleapis.com
#Service Catalogをデプロイ
$ helm install svc-cat/catalog \
--name catalog --namespace catalog --wait
NAME: catalog
LAST DEPLOYED: Wed Dec 26 04:59:51 2018
NAMESPACE: catalog
STATUS: DEPLOYED
RESOURCES:
==> v1beta1/APIService
NAME AGE
v1beta1.servicecatalog.k8s.io 2s
==> v1/RoleBinding
servicecatalog.k8s.io:apiserver-authentication-reader 2s
service-catalog-controller-manager-cluster-info 2s
service-catalog-controller-manager-leader-election 2s
==> v1/Role
servicecatalog.k8s.io:cluster-info-configmap 2s
servicecatalog.k8s.io:leader-locking-controller-manager 2s
==> v1/ServiceAccount
service-catalog-apiserver 2s
service-catalog-controller-manager 2s
==> v1/Pod(related)
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
catalog-catalog-apiserver-58dd7744c5-bshgk 0/2 ContainerCreating 0 1s
catalog-catalog-controller-manager-755b8b54d4-nsj86 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 2s
==> v1/Secret
NAME AGE
catalog-catalog-apiserver-cert 2s
==> v1/Service
catalog-catalog-apiserver 2s
==> v1beta1/Deployment
catalog-catalog-apiserver 2s
catalog-catalog-controller-manager 2s
==> v1/ClusterRole
servicecatalog.k8s.io:apiserver 2s
servicecatalog.k8s.io:controller-manager 2s
==> v1/ClusterRoleBinding
servicecatalog.k8s.io:apiserver 2s
servicecatalog.k8s.io:apiserver-auth-delegator 2s
servicecatalog.k8s.io:controller-manager 2sデプロイが完了すると名前空間catalogにapi-serverとcontroller-managerのpodが作成されます。
$ kubectl get pods -n catalog NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE catalog-catalog-apiserver-58dd7744c5-bshgk 2/2 Running 0 2m catalog-catalog-controller-manager-755b8b54d4-nsj86 1/1 Running 2 2m
Service Brokerのデプロイ
Service BrokerもService Catalogと同様にHelmを利用してデプロイを行います。 Service Brokerを利用するためにはService Broker用のIAMユーザーとDynamoDBのテーブルが必要になるため、CloudFormationを利用しそれらのリソースを作成します。
$ REGION=ap-northeast-1
# テンプレートのダウンロード
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/awslabs/aws-servicebroker/master/setup/prerequisites.yaml
# スタックの作成
$ STACK_ID=$(aws cloudformation create-stack \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_IAM \
--template-body file://prerequisites.yaml \
--stack-name aws-service-broker-prerequisites \
--output text --query "StackId" \
--region ${REGION})
$ until \
ST=$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks \
--region ${REGION} \
--stack-name ${STACK_ID} \
--query "Stacks[0].StackStatus" \
--output text); \
echo $ST; echo $ST | grep "CREATE_COMPLETE"
do sleep 5
done
# BrokerUserの名前を取得
$ BUSERNAME=$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks \
--region ${REGION} \
--stack-name ${STACK_ID} \
--query "Stacks[0].Outputs[0].OutputValue" \
--output text)
# BrokerUserのアクセスキー、シークレットアクセスキーを作成
$ aws iam create-access-key \
--user-name ${BUSERNAME} \
--output json \
--query 'AccessKey.{KEY_ID:AccessKeyId,SECRET_ACCESS_KEY:SecretAccessKey}'Helmを使用してService Brokerをデプロイします。
#リポジトリを追加
$ helm repo add aws-sb https://awsservicebroker.s3.amazonaws.com/charts
#アクセスキー、シークレットアクセスキーを指定しService Brokerをデプロイ
$ helm install aws-sb/aws-servicebroker \
--wait \
--name aws-servicebroker \
--namespace aws-sb \
--version 1.0.0-beta.3 \
--set aws.region=${REGION} \
--set aws.accesskeyid=<ACCESS_KEY_ID> \
--set aws.secretkey=<SECRET_ACCESS_KEY>
NAME: aws-servicebroker
LAST DEPLOYED: Wed Dec 26 05:11:06 2018
NAMESPACE: aws-sb
STATUS: DEPLOYED
RESOURCES:
==> v1/Service
NAME AGE
aws-servicebroker 3s
==> v1beta1/Deployment
aws-servicebroker 3s
==> v1beta1/ClusterServiceBroker
aws-servicebroker 2s
==> v1/Pod(related)
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
aws-servicebroker-6cc7d9cbb8-rwwb9 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 3s
==> v1/Secret
NAME AGE
aws-servicebroker-credentials 3s
aws-servicebroker-cert 3s
==> v1/ServiceAccount
aws-servicebroker-service 3s
aws-servicebroker-client 3s
==> v1beta1/ClusterRole
access-aws-servicebroker 3s
aws-servicebroker 3s
==> v1beta1/ClusterRoleBinding
aws-servicebroker 3s
aws-servicebroker-client 3s
NOTES:
For more information on usage, see https://github.com/awslabs/aws-servicebroker/docs/デプロイが完了すると名前空間aws-sbにservicebrokerのpodが作成されます。
$ kubectl get ClusterServiceBrokers NAME URL STATUS AGE aws-servicebroker https://aws-servicebroker.aws-sb.svc.cluster.local Ready 47s $ kubectl get pods -n aws-sb NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE aws-servicebroker-6cc7d9cbb8-rwwb9 1/1 Running 0 56s
利用可能なサービスは以下のコマンドにて確認することができます。
kubectl get ClusterServiceClasses -o=custom-columns=NAME:.spec.externalName,DESCRIPTION:.spec.description NAME DESCRIPTION dynamodb AWS Service Broker - Amazon DynamoDB sqs AWS Servicebroker - Amazon SQS s3 AWS Service Broker - Amazon S3 sns AWS Service Broker - Amazon SNS polly AWS Service Broker - Amazon Polly kinesis AWS Service Broker - Amazon Kinesis Data Stream elasticache AWS Service Broker - Amazon ElastiCache for memcached kms AWS Service Broker - KMS Key route53 AWS Service Broker - Amazon Route 53 rdspostgresql AWS Service Broker - Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL emr AWS Service Broker - Amazon EMR rdsmariadb AWS Service Broker - Amazon RDS for MariaDB athena AWS Service Broker - Amazon Athena redshift AWS Service Broker - Amazon Redshift rekognition AWS Service Broker - Amazon Rekognition lex AWS Service Broker - Amazon Lex translate AWS Service Broker - Amazon Translate rdsmysql AWS Service Broker - Amazon RDS for MySQL
サンプルアプリケーションをデプロイする
S3へ接続するアプリケーションをデプロイします。後ほどS3への接続情報を環境変数から取得するようにマニュフェストを変更しますが、まずはS3のリソースがない状態で接続確認をします。接続エラーになることが期待値です。
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: s3-demo
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: s3-demo
namespace: s3-demo
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: s3-demo
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: s3-demo
spec:
containers:
- name: s3-demo
image: awsservicebroker/s3-demo:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8080デプロイが完了すると名前空間s3-demoにs3-demoのpodが作成されます。
$ kubectl apply -f sample.yaml namespace/s3-demo created deployment.apps/s3-demo created $ kubectl get pods -n s3-demo NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE s3-demo-c755848dd-xxmqr 1/1 Running 0 2m
サンプルアプリケーション内でローカルホストにアクセスします。
$ kubectl exec \
$(kubectl get pods -o name --namespace s3-demo | awk -F '/' '{print $2}') \
--namespace s3-demo -- \
curl -s http://127.0.0.1:8080 | jq .
{
"data": {
"delete": {
"data": [
"skipped"
],
"success": false
},
"put": {
"data": [
"skipped"
],
"success": false
},
"describe": {
"data": [
"skipped"
],
"success": false
},
"list": {
"data": [
"skipped"
],
"success": false
},
"cleanup": {
"data": [
"<class 'AssertionError'> Required secrets are not present in environment variables. ENVIRONMENT: environ({'X_SCLS': 'rh-python35 ', 'KUBERNETES_PORT': 'tcp://10.100.0.1:443', 'KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT_HTTPS': '443', 'XDG_DATA_DIRS': '/opt/rh/rh-python35/root/usr/share:/usr/local/share:/usr/share', 'HOSTNAME': 's3-demo-c755848dd-xxmqr', 'PKG_CONFIG_PATH': '/opt/rh/rh-python35/root/usr/lib64/pkgconfig', '_': '/opt/rh/rh-python35/root/usr/bin/python', 'KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP_ADDR': '10.100.0.1', 'KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP_PORT': '443', 'KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST': '10.100.0.1', 'KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP': 'tcp://10.100.0.1:443', 'LD_LIBRARY_PATH': '/opt/rh/rh-python35/root/usr/lib64', 'MANPATH': '/opt/rh/rh-python35/root/usr/share/man:', 'KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP_PROTO': 'tcp', 'SHLVL': '1', 'KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT': '443', 'PATH': '/opt/rh/rh-python35/root/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin', 'PWD': '/usr/src/sample-app/src', 'HOME': '/', 'BOTTLE_LOCKFILE': '/tmp/bottle.u1e4h9oe.lock', 'BOTTLE_CHILD': 'true'})\n\nTraceback (most recent call last):\n File \"app.py\", line 56, in test_method\n assert items['success'], items['error']\nAssertionError: Required secrets are not present in environment variables. ENVIRONMENT: environ({'X_SCLS': 'rh-python35 ', 'KUBERNETES_PORT': 'tcp://10.100.0.1:443', 'KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT_HTTPS': '443', 'XDG_DATA_DIRS': '/opt/rh/rh-python35/root/usr/share:/usr/local/share:/usr/share', 'HOSTNAME': 's3-demo-c755848dd-xxmqr', 'PKG_CONFIG_PATH': '/opt/rh/rh-python35/root/usr/lib64/pkgconfig', '_': '/opt/rh/rh-python35/root/usr/bin/python', 'KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP_ADDR': '10.100.0.1', 'KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP_PORT': '443', 'KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST': '10.100.0.1', 'KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP': 'tcp://10.100.0.1:443', 'LD_LIBRARY_PATH': '/opt/rh/rh-python35/root/usr/lib64', 'MANPATH': '/opt/rh/rh-python35/root/usr/share/man:', 'KUBERNETES_PORT_443_TCP_PROTO': 'tcp', 'SHLVL': '1', 'KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT': '443', 'PATH': '/opt/rh/rh-python35/root/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin', 'PWD': '/usr/src/sample-app/src', 'HOME': '/', 'BOTTLE_LOCKFILE': '/tmp/bottle.u1e4h9oe.lock', 'BOTTLE_CHILD': 'true'})\n"
],
"success": false
},
"idempotency": {
"data": [
"skipped"
],
"success": false
}
},
"success": false
}S3への接続情報がなく接続エラーになっていることが確認できます。
Service BrokerでS3を作成する
長くなりましたが、ここからが本題です。
Service Instanceを作成する
Service BrokerでAWSリソース(今回はS3)を作成していきます。マニュフェストのkindにはServiceInstanceを指定します。
--- apiVersion: servicecatalog.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: ServiceInstance metadata: name: s3-bucket namespace: s3-demo spec: clusterServiceClassExternalName: s3 clusterServicePlanExternalName: production
$ kubectl apply -f s3-instance.yaml
applyコマンドを実行するとService BrokerによりCloudFormationのスタックが作成されます。
$ aws cloudformation list-stacks \
--region ${REGION} \
--query 'StackSummaries[?starts_with(StackName,`aws-service-broker-s3-`)]'リソースとしてS3接続用のIAMユーザー、アプリケーションから利用するバケット、ログ出力用バケットなどが作成されていることが確認できます。
$ aws cloudformation list-stack-resources --stack-name aws-service-broker-s3-fea82c42-0886-11e9-b9da-d64a8ddc537f
{
"StackResourceSummaries": [
{
"LogicalResourceId": "AWSSBInjectedIAMUser",
"PhysicalResourceId": "aws-service-broker-s3-fea82c4-AWSSBInjectedIAMUser-157F7JFDXYBJZ",
"ResourceType": "AWS::IAM::User",
"LastUpdatedTimestamp": "2018-12-25T20:53:16.723Z",
"ResourceStatus": "CREATE_COMPLETE",
"DriftInformation": {
"StackResourceDriftStatus": "NOT_CHECKED"
}
},
{
"LogicalResourceId": "AWSSBInjectedIAMUserCreator",
"PhysicalResourceId": "8yjQMzE60v2VTKci",
"ResourceType": "AWS::CloudFormation::CustomResource",
"LastUpdatedTimestamp": "2018-12-25T20:53:24.276Z",
"ResourceStatus": "CREATE_COMPLETE",
"DriftInformation": {
"StackResourceDriftStatus": "NOT_CHECKED"
}
},
{
"LogicalResourceId": "AWSSBInjectedIAMUserLambda",
"PhysicalResourceId": "aws-service-broker-s3-fea-AWSSBInjectedIAMUserLamb-15ZFO1CIXQ4E3",
"ResourceType": "AWS::Lambda::Function",
"LastUpdatedTimestamp": "2018-12-25T20:53:04.306Z",
"ResourceStatus": "CREATE_COMPLETE",
"DriftInformation": {
"StackResourceDriftStatus": "NOT_CHECKED"
}
},
{
"LogicalResourceId": "AWSSBInjectedIAMUserPolicy1",
"PhysicalResourceId": "aws-s-AWSS-ZHLYW6ND0HON",
"ResourceType": "AWS::IAM::Policy",
"LastUpdatedTimestamp": "2018-12-25T20:53:40.185Z",
"ResourceStatus": "CREATE_COMPLETE",
"DriftInformation": {
"StackResourceDriftStatus": "NOT_CHECKED"
}
},
{
"LogicalResourceId": "AWSSBInjectedIAMUserRole",
"PhysicalResourceId": "aws-service-broker-s3-fea-AWSSBInjectedIAMUserRole-EZ05D6ALCNE0",
"ResourceType": "AWS::IAM::Role",
"LastUpdatedTimestamp": "2018-12-25T20:53:00.581Z",
"ResourceStatus": "CREATE_COMPLETE",
"DriftInformation": {
"StackResourceDriftStatus": "NOT_CHECKED"
}
},
{
"LogicalResourceId": "LoggingBucket",
"PhysicalResourceId": "aws-service-broker-s3-fea82c42-0886-loggingbucket-1t7a125eh3wok",
"ResourceType": "AWS::S3::Bucket",
"LastUpdatedTimestamp": "2018-12-25T20:53:03.125Z",
"ResourceStatus": "CREATE_COMPLETE",
"DriftInformation": {
"StackResourceDriftStatus": "NOT_CHECKED"
}
},
{
"LogicalResourceId": "S3bucket",
"PhysicalResourceId": "aws-service-broker-s3-fea82c42-0886-11e9-s3bucket-1nz2ok59ku2mi",
"ResourceType": "AWS::S3::Bucket",
"LastUpdatedTimestamp": "2018-12-25T20:53:27.871Z",
"ResourceStatus": "CREATE_COMPLETE",
"DriftInformation": {
"StackResourceDriftStatus": "NOT_CHECKED"
}
}
]
}また、以下のコマンドよりEKSクラスタでの状態も確認することができます。
$ kubectl get ServiceInstance/s3-bucket -n s3-demo -o yaml
apiVersion: servicecatalog.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ServiceInstance
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"servicecatalog.k8s.io/v1beta1","kind":"ServiceInstance","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"s3-bucket","namespace":"s3-demo"},"spec":{"clusterServiceClassExternalName":"s3","clusterServicePlanExternalName":"production"}}
creationTimestamp: "2018-12-25T20:52:30Z"
finalizers:
- kubernetes-incubator/service-catalog
generation: 1
name: s3-bucket
namespace: s3-demo
resourceVersion: "69"
selfLink: /apis/servicecatalog.k8s.io/v1beta1/namespaces/s3-demo/serviceinstances/s3-bucket
uid: fea82ca2-0886-11e9-b9da-d64a8ddc537f
spec:
clusterServiceClassExternalName: s3
clusterServiceClassRef:
name: 19b87923-2c60-5381-aac5-5d86196c3d21
clusterServicePlanExternalName: production
clusterServicePlanRef:
name: 362c5420-aa86-506a-8f31-1aa8a92375b8
externalID: fea82c42-0886-11e9-b9da-d64a8ddc537f
updateRequests: 0
userInfo:
groups:
- system:masters
- system:authenticated
uid: ""
username: kubernetes-admin
status:
asyncOpInProgress: true
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2018-12-25T20:52:30Z"
message: The instance is being provisioned asynchronously
reason: Provisioning
status: "False"
type: Ready
currentOperation: Provision
deprovisionStatus: Required
inProgressProperties:
clusterServicePlanExternalID: 362c5420-aa86-506a-8f31-1aa8a92375b8
clusterServicePlanExternalName: production
userInfo:
groups:
- system:masters
- system:authenticated
uid: ""
username: kubernetes-admin
observedGeneration: 1
operationStartTime: "2018-12-25T20:52:30Z"
orphanMitigationInProgress: false
provisionStatus: ""
reconciledGeneration: 0Service Bindingを作成する
EKSクラスタからS3にアクセスできるように認証情報をバインドします。
---
apiVersion: servicecatalog.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ServiceBinding
metadata:
name: s3-binding
namespace: s3-demo
spec:
instanceRef:
name: s3-bucket$ kubectl apply -f s3-binding.yaml
コマンドが正常に終了するとSercretにS3への接続情報が保存されます。
$ kubectl describe secrets/s3-binding -n s3-demo Name: s3-binding Namespace: s3-demo Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Type: Opaque Data ==== BUCKET_ARN: 76 bytes BUCKET_NAME: 63 bytes LOGGING_BUCKET_NAME: 63 bytes S3_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: 20 bytes S3_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: 40 bytes S3_REGION: 14 bytes
最後にPodからS3へ接続できることを確認するためサンプルアプリケーションを変更していきます。
まずは環境変数にSecretの値を設定するようマニュフェストを修正します。
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: s3-demo
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: s3-demo
namespace: s3-demo
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: s3-demo
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: s3-demo
spec:
containers:
- name: s3-demo
image: awsservicebroker/s3-demo:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: S3_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
valueFrom: { secretKeyRef: { name: s3-binding, key: S3_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID } }
- name: S3_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
valueFrom: { secretKeyRef: { name: s3-binding, key: S3_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY } }
- name: S3_REGION
valueFrom: { secretKeyRef: { name: s3-binding, key: S3_REGION } }
- name: BUCKET_ARN
valueFrom: { secretKeyRef: { name: s3-binding, key: BUCKET_ARN } }
- name: BUCKET_NAME
valueFrom: { secretKeyRef: { name: s3-binding, key: BUCKET_NAME } }
- name: LOGGING_BUCKET_NAME
valueFrom: { secretKeyRef: { name: s3-binding, key: LOGGING_BUCKET_NAME } }再度、サンプルアプリケーションをapplyします。
$ kubectl apply -f sample.yaml
先ほどと同様にサンプルアプリケーション内でローカルホストにアクセスします。
$ kubectl exec \
$(kubectl get pods -o name --namespace s3-demo | awk -F '/' '{print $2}') \
--namespace s3-demo -- \
curl -s http://127.0.0.1:8080 | jq .
{
"success": true,
"data": {
"idempotency": {
"success": true,
"data": [
"Put an additional item with duplicate item_id",
"Verified describe has updated content",
"Verified list does not contain duplicates",
"Successfully tested idempotency"
]
},
"put": {
"success": true,
"data": [
"Successfully put item"
],
"response": null
},
"delete": {
"success": true,
"data": [
"Successfully deleted item"
],
"response": null
},
"cleanup": {
"success": true,
"data": [
"Successfully cleaned up all items"
]
},
"list": {
"success": true,
"data": [
"Successfully listed items"
],
"response": [
"test"
]
},
"describe": {
"success": true,
"data": [
"Successfully described item"
],
"response": {
"content": "test_content",
"item_id": "test"
}
}
}
}サンプルアプリケーションからS3へ接続できていることが確認できました!!
さいごに
Service Brokerを利用してKubernetes(EKS)からAWSのリソースを作成する方法を紹介しました。
Service BrokerによるAWSのリソースの作成は、Kubernetesのマニュフェストの書き方さえ理解できれば誰でも簡単に実施することができます。この仕組みをうまく利用すれば、アプリケーションエンジニアがインフラエンジニアに頼らず解決できることが増えるのではないでしょうか。










