![[AWS CDK] AWS Step FunctionsからのAmazon Athenaクエリの実行でIntegrationPatternを指定して同期実行/非同期実行を使い比べてみる](https://devio2023-media.developers.io/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/amazon-athena.png)
[AWS CDK] AWS Step FunctionsからのAmazon Athenaクエリの実行でIntegrationPatternを指定して同期実行/非同期実行を使い比べてみる
この記事は公開されてから1年以上経過しています。情報が古い可能性がありますので、ご注意ください。
こんにちは、CX事業本部 IoT事業部の若槻です。
Amazon Athenaでクエリを実行するためのStartQueryExecution APIは、クエリ実行時に同期的な実行(Run a Job (.sync))とするか非同期実行(Request Response)とするかをオプションで指定することができます。既定は非同期実行です。
そしてAWS Step FunctionsのAWS CDK実装でAthenaクエリ実行を実装する場合だと、クエリを同期/非同期のいずれで実行するかをIntegrationPatternで制御することが可能です。
今回は、AWS Step FunctionsからのAmazon Athenaクエリの実行でIntegrationPatternを指定して際の同期実行/非同期実行を使い比べてみました。
やってみた
AWS CDK v2(TypeScript)で次のようなCDKスタックを作成します。
import { Construct } from 'constructs';
import {
aws_stepfunctions,
aws_stepfunctions_tasks,
Stack,
StackProps,
} from 'aws-cdk-lib';
export class AwsAppStack extends Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props: StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
// Athenaクエリを同期実行するタスク
const syncExecuteAthenaQueryTask =
new aws_stepfunctions_tasks.AthenaStartQueryExecution(
this,
'syncExecuteAthenaQueryTask',
{
queryString: aws_stepfunctions.JsonPath.stringAt(
'$.input.queryString'
),
integrationPattern: aws_stepfunctions.IntegrationPattern.RUN_JOB,
resultPath: '$.syncExecuteAthenaQueryTaskOutPut',
}
);
// 同期実行クエリの取得
const getAthenaQuerySyncExecutionTask =
new aws_stepfunctions_tasks.AthenaGetQueryExecution(
this,
'getAthenaQuerySyncExecutionTask',
{
queryExecutionId: aws_stepfunctions.JsonPath.stringAt(
'$.syncExecuteAthenaQueryTaskOutPut.QueryExecution.QueryExecutionId'
),
}
);
// Athenaクエリを同期実行するStateMachine
new aws_stepfunctions.StateMachine(this, 'syncExecuteAthenaQuery', {
stateMachineName: 'syncExecuteAthenaQuery',
definition: syncExecuteAthenaQueryTask.next(
getAthenaQuerySyncExecutionTask
),
});
// Athenaクエリを非同期実行するタスク
const asyncExecuteAthenaQueryTask =
new aws_stepfunctions_tasks.AthenaStartQueryExecution(
this,
'asyncExecuteAthenaQueryTask',
{
queryString: aws_stepfunctions.JsonPath.stringAt(
'$.input.queryString'
),
integrationPattern:
aws_stepfunctions.IntegrationPattern.REQUEST_RESPONSE,
resultPath: '$.asyncExecuteAthenaQueryTaskOutPut',
}
);
// 非同期実行クエリの取得
const getAthenaQueryAsyncExecutionTask =
new aws_stepfunctions_tasks.AthenaGetQueryExecution(
this,
'getAthenaQueryAsyncExecutionTask',
{
queryExecutionId: aws_stepfunctions.JsonPath.stringAt(
'$.asyncExecuteAthenaQueryTaskOutPut.QueryExecutionId'
),
}
);
// Athenaクエリを非同期実行するStateMachine
new aws_stepfunctions.StateMachine(this, 'asyncExecuteAthenaQuery', {
stateMachineName: 'asyncExecuteAthenaQuery',
definition: asyncExecuteAthenaQueryTask.next(
getAthenaQueryAsyncExecutionTask
),
});
}
}
Atheaクエリを同期実行するState Machineと非同期実行するState Machineの2つを作成しています。
上記をCDK Deployしてスタックをデプロイします。以下、作成されたそれぞれの定義です。
State MachinesyncExecuteAthenaQueryの定義では、Resourceの指定がarn:aws:states:::athena:startQueryExecution.syncとなっており(.syncが付いている)、クエリが同期的に実行されるようになっています。
{
"StartAt": "syncExecuteAthenaQueryTask",
"States": {
"syncExecuteAthenaQueryTask": {
"Next": "getAthenaQuerySyncExecutionTask",
"Type": "Task",
"ResultPath": "$.syncExecuteAthenaQueryTaskOutPut",
"Resource": "arn:aws:states:::athena:startQueryExecution.sync",
"Parameters": {
"QueryString.$": "$.input.queryString",
"ResultConfiguration": {}
}
},
"getAthenaQuerySyncExecutionTask": {
"End": true,
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "arn:aws:states:::athena:getQueryExecution",
"Parameters": {
"QueryExecutionId.$": "$.syncExecuteAthenaQueryTaskOutPut.QueryExecution.QueryExecutionId"
}
}
}
}
一方State MachineasyncExecuteAthenaQueryの定義では、Resourceの指定がarn:aws:states:::athena:startQueryExecutionとなっており(.syncが付いていない)、クエリが非同期で実行されるようになっています。
{
"StartAt": "asyncExecuteAthenaQueryTask",
"States": {
"asyncExecuteAthenaQueryTask": {
"Next": "getAthenaQueryAsyncExecutionTask",
"Type": "Task",
"ResultPath": "$.asyncExecuteAthenaQueryTaskOutPut",
"Resource": "arn:aws:states:::athena:startQueryExecution",
"Parameters": {
"QueryString.$": "$.input.queryString",
"ResultConfiguration": {}
}
},
"getAthenaQueryAsyncExecutionTask": {
"End": true,
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "arn:aws:states:::athena:getQueryExecution",
"Parameters": {
"QueryExecutionId.$": "$.asyncExecuteAthenaQueryTaskOutPut.QueryExecutionId"
}
}
}
}
動作確認
作成したクエリ同期実行/非同期実行State Machineをそれぞれ実行して、クエリが成功する場合と失敗する場合の動作を比べてみます。
同期実行クエリが成功の場合
実行が成功するクエリ文字列をInputに指定してsyncExecuteAthenaQueryState Machineを実行します。
{
"input": {
"queryString": "SELECT 'hoge';"
}
}
State Machine実行中の様子です。syncExecuteAthenaQueryTaskではTaskSubmittedEventの後はクエリ実行が完了するまで待機が行われています。
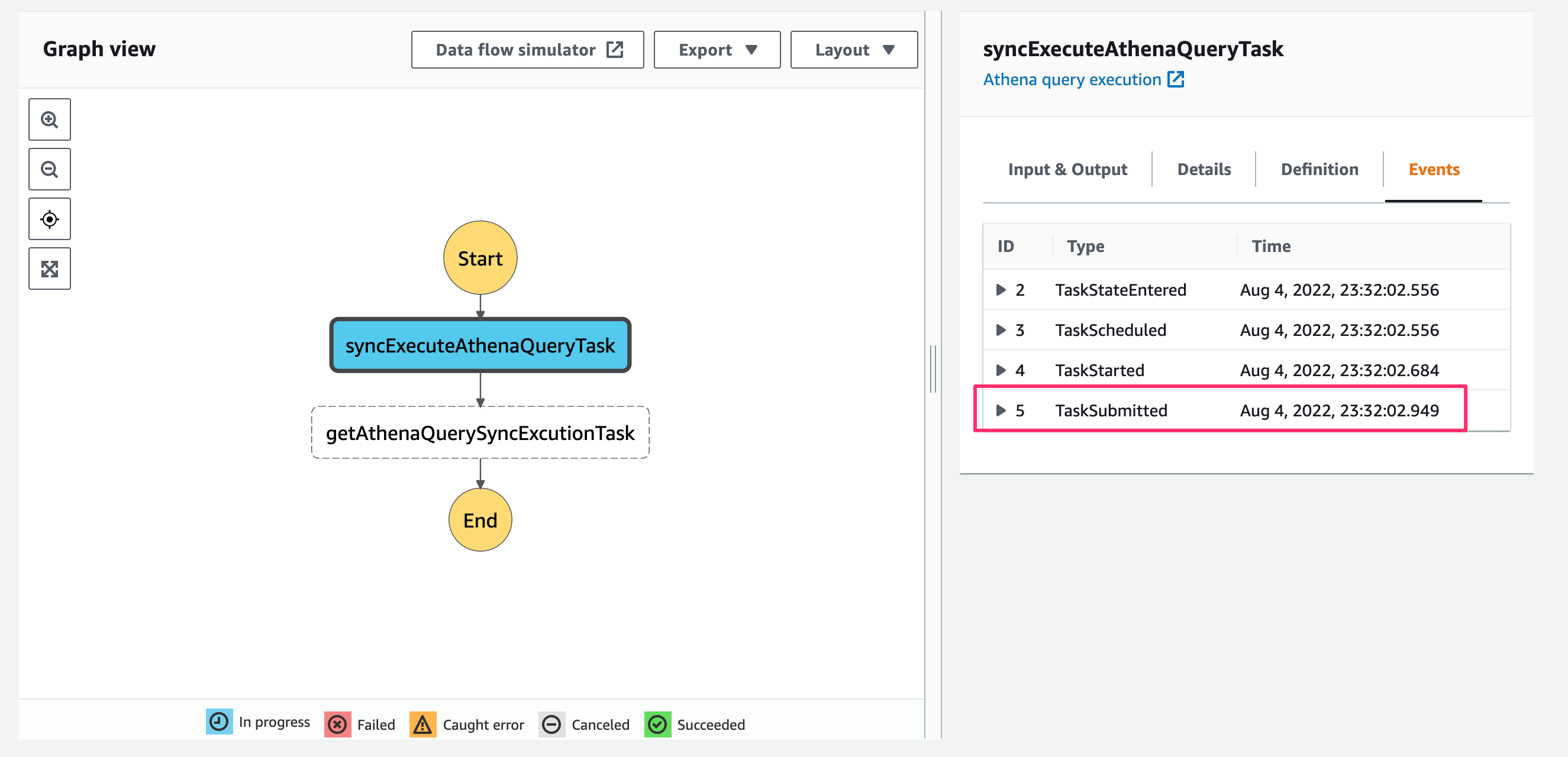
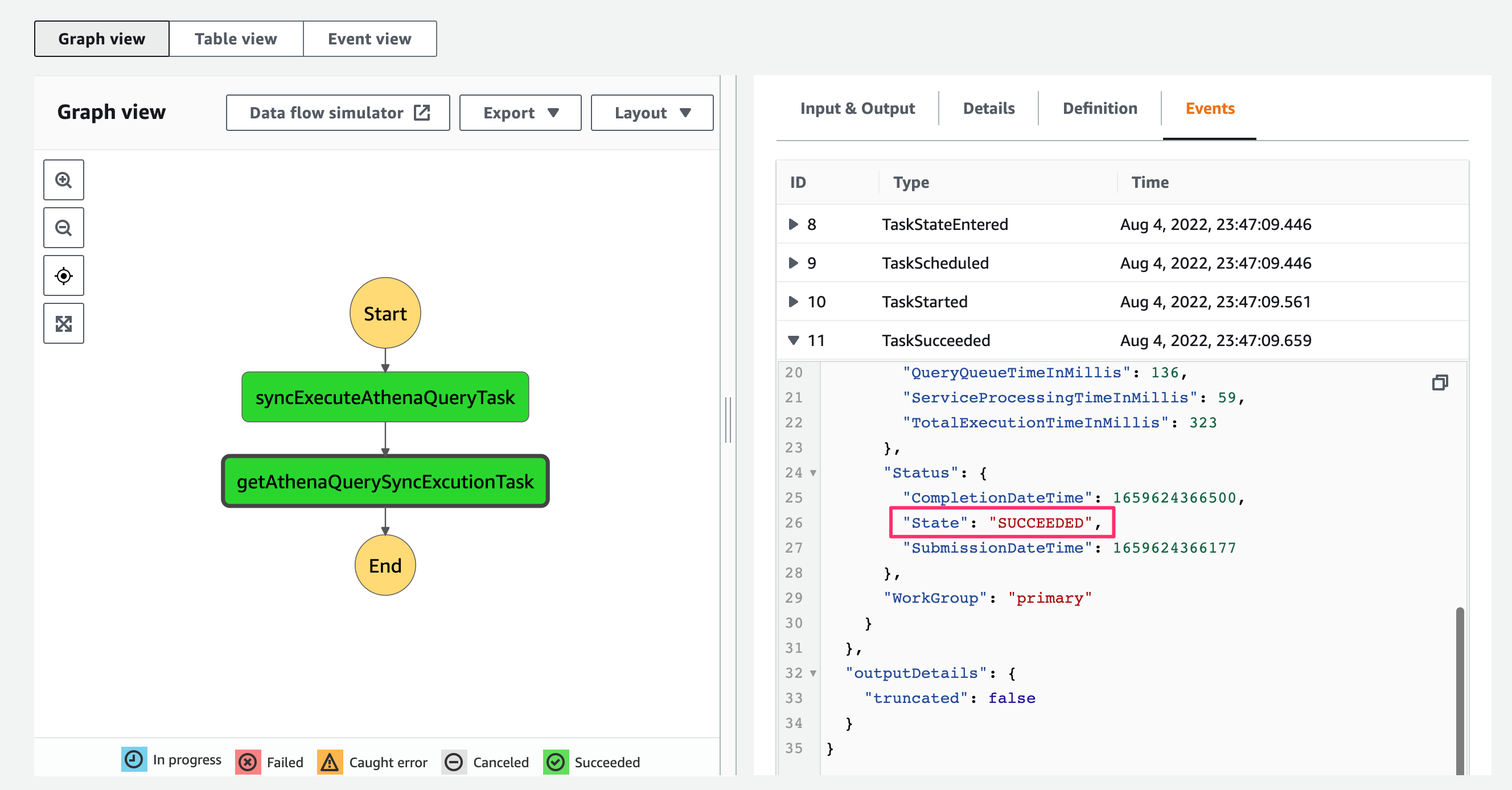
State Machine実行が完了し成功しました。取得したクエリのStatusはSUCCEEDEDとなっており、前段のクエリ実行タスクが完了後に次のStateに遷移したことが分かります。
非同期実行クエリが成功の場合
実行が成功するクエリ文字列をInputに指定してasyncExecuteAthenaQueryState Machineを実行します。
{
"input": {
"queryString": "SELECT 'hoge';"
}
}
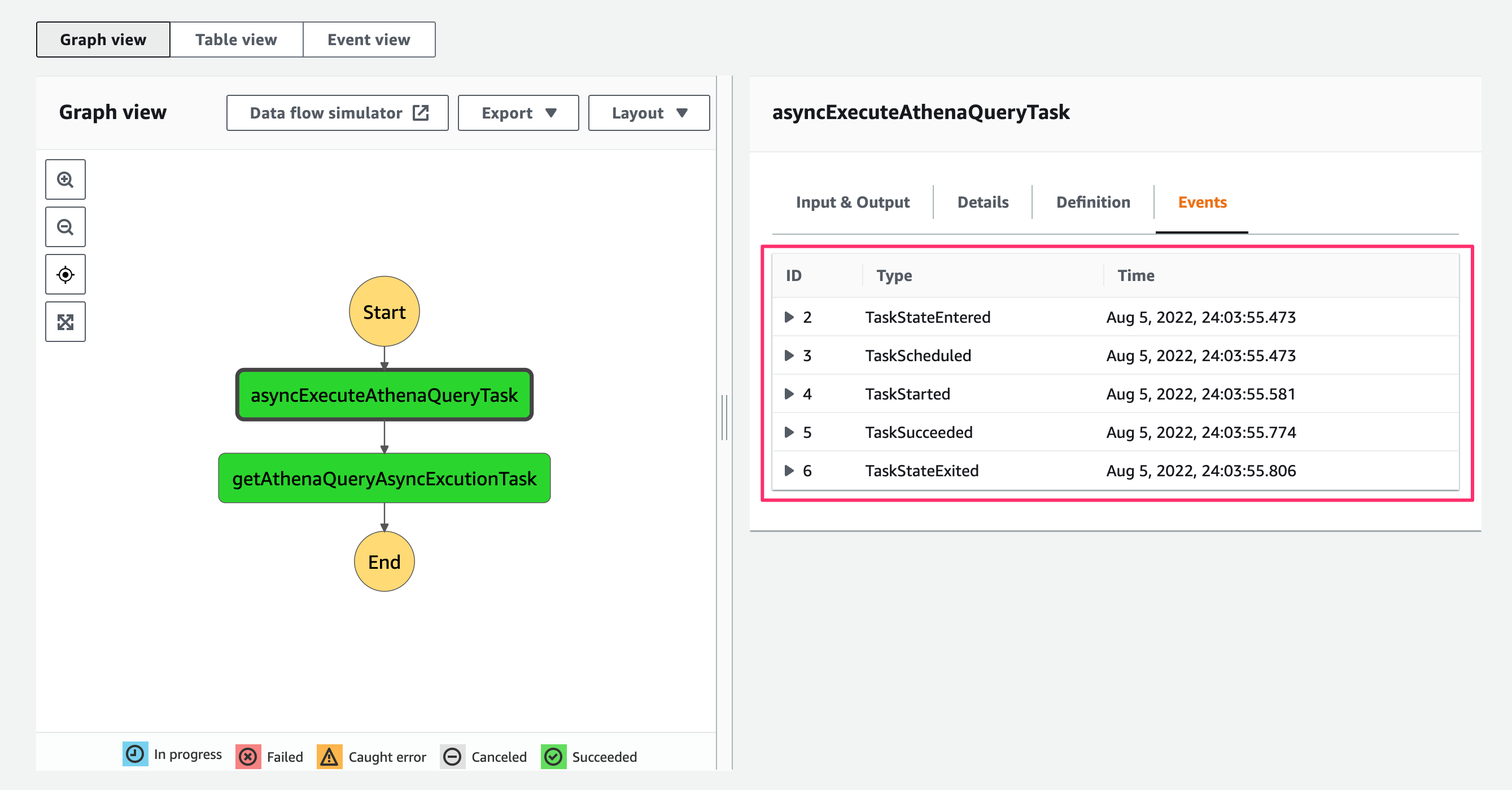
State Machine実行が成功し完了しました。asyncExecuteAthenaQueryTaskタスクのEventを見るとTaskSubmittedがスキップされてTaskが完了しています。
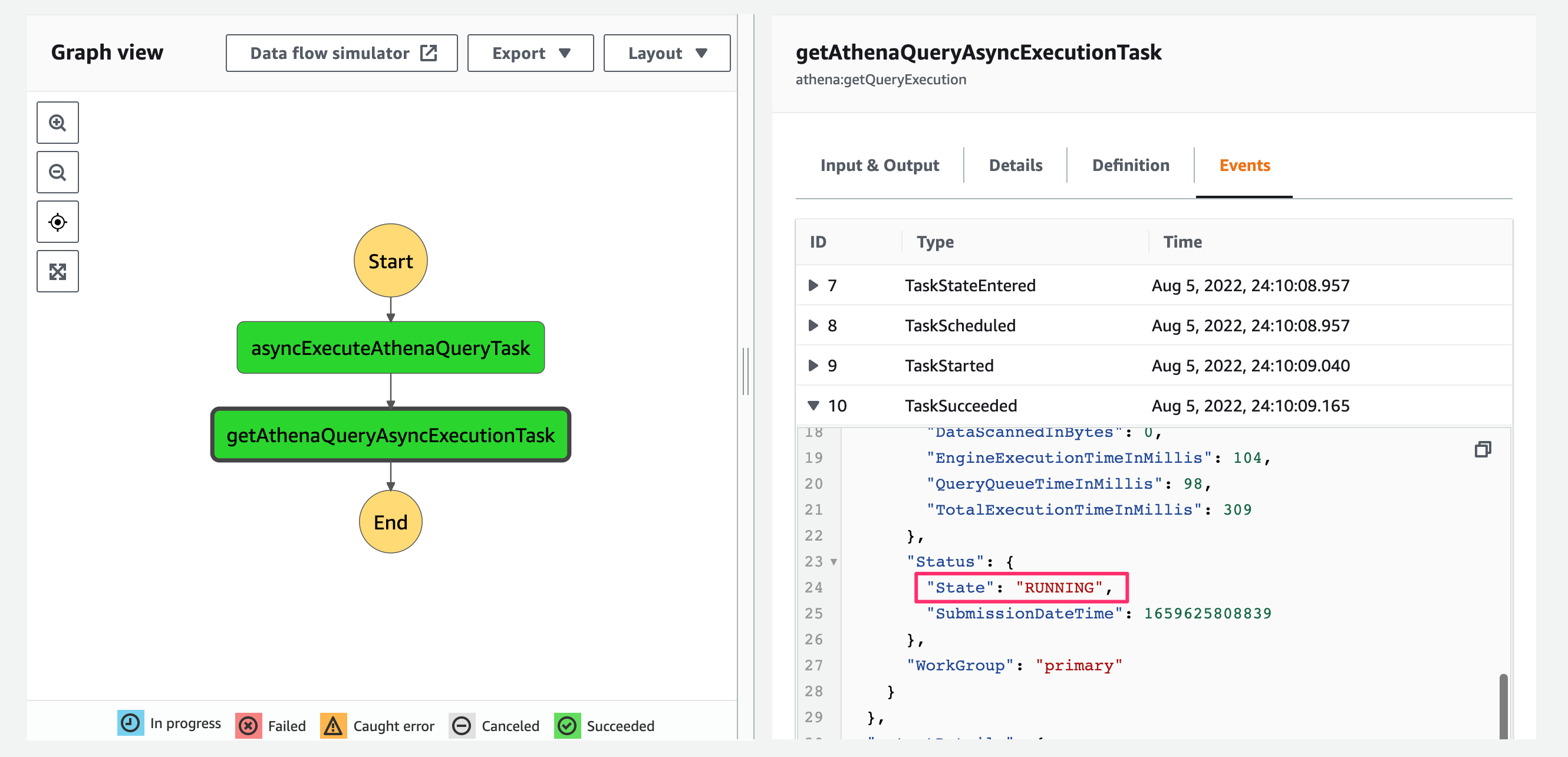
そして取得したクエリのStatusはRUNNINGとなっており、前段のクエリ実行タスクが完了前に次のStateに遷移したことが分かります。
同期実行クエリが失敗の場合
実行が失敗するクエリ文字列をInputに指定してsyncExecuteAthenaQueryState Machineを実行します。
{
"input": {
"queryString": "SELECT fuga;"
}
}
するとsyncExecuteAthenaQueryTaskタスクでクエリ実行が失敗し、タスクも失敗となりました。
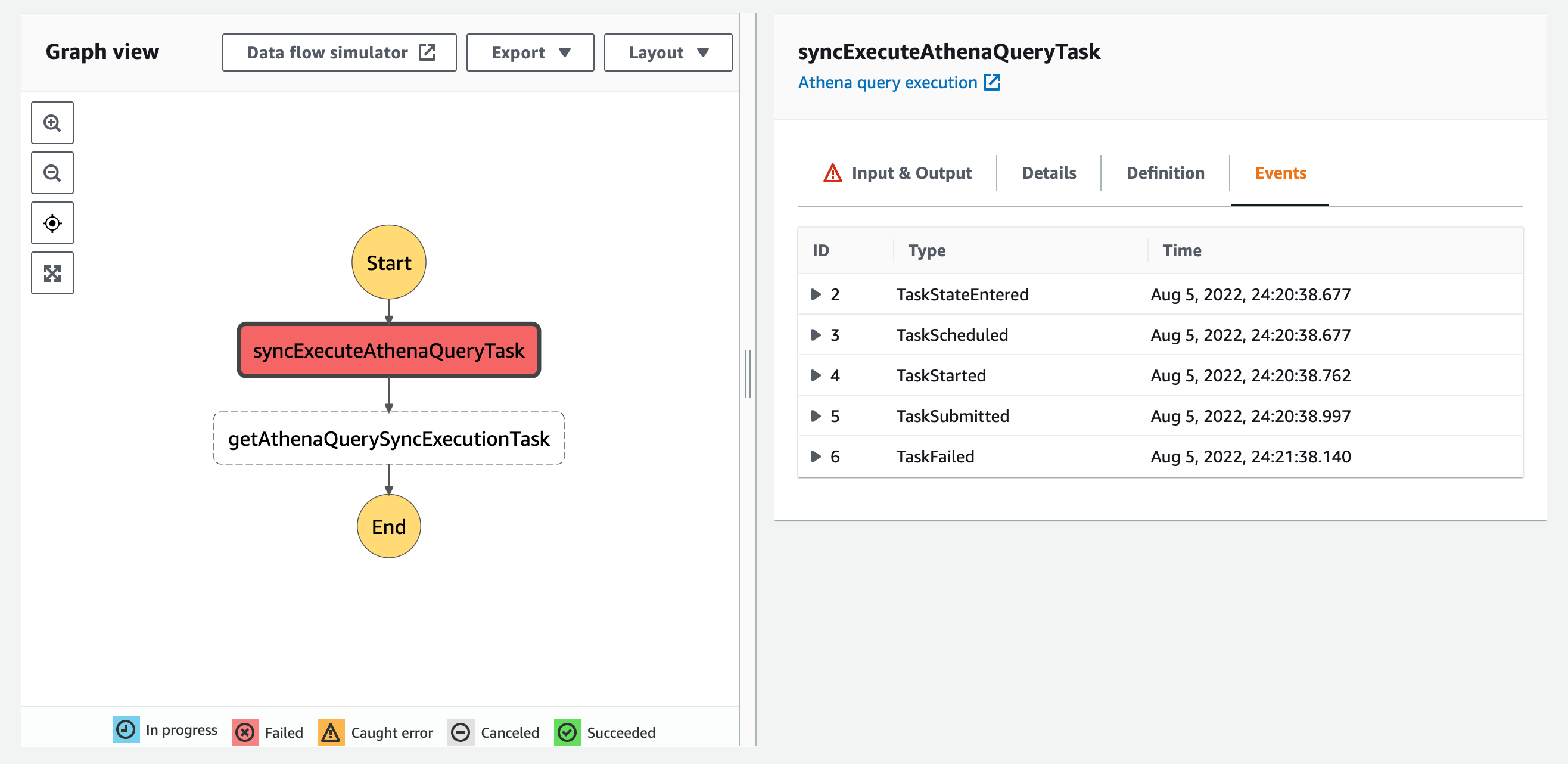
非同期実行クエリが失敗の場合
実行が失敗するクエリ文字列をInputに指定してasyncExecuteAthenaQueryState Machineを実行します。
{
"input": {
"queryString": "SELECT fuga;"
}
}
こちらの場合だとasyncExecuteAthenaQueryTaskタスクおよびState Machine自体の実行は成功しましたが、クエリ実行は失敗しています。
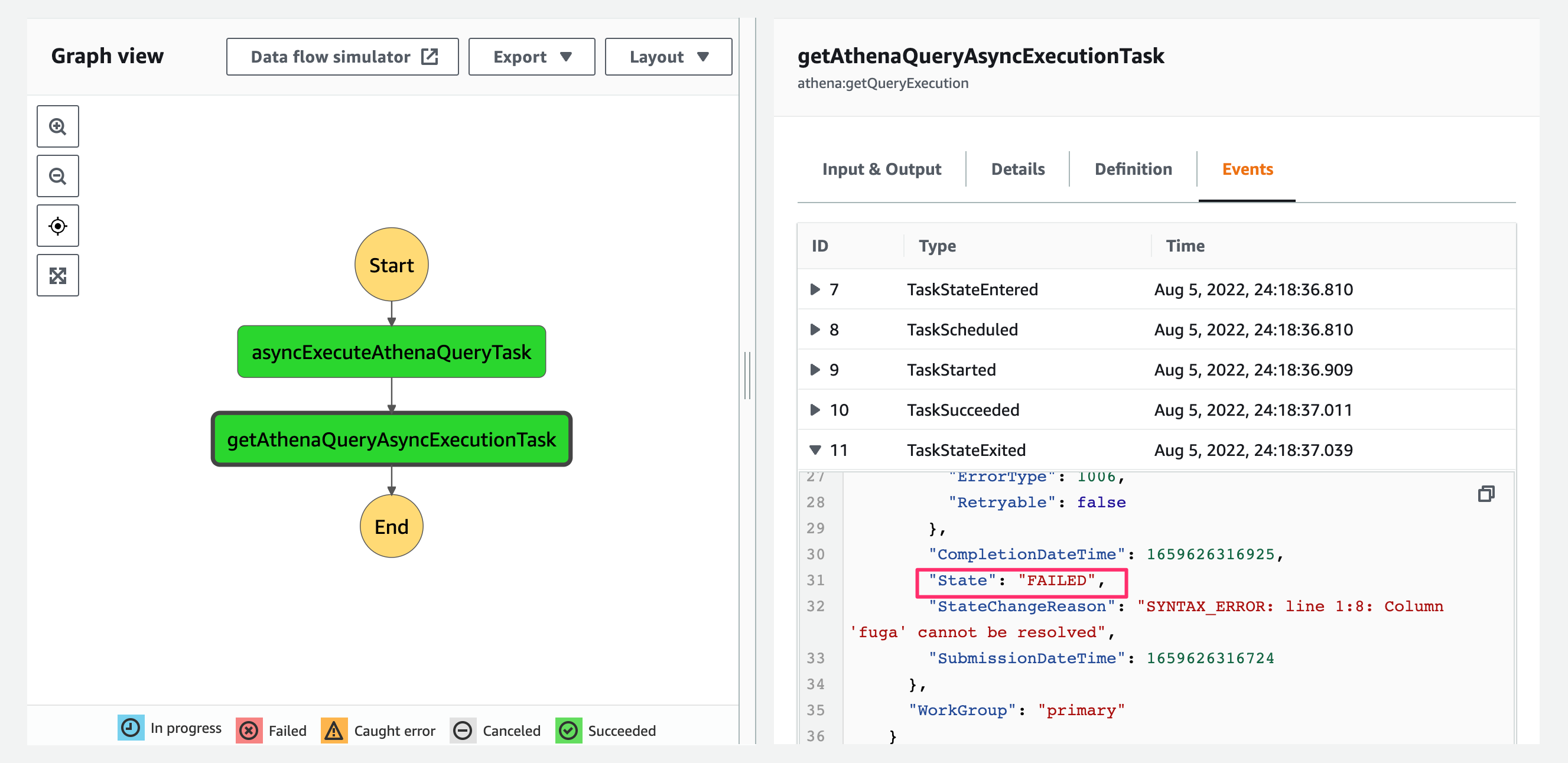
まとめ
ここまでAthenaクエリ実行の同期実行/非同期実行を使い比べてみて、次の結論を得ることができました。
- 同期的な実行(Run a Job (.sync)):クエリの成否がタスクの成否となる
- 非同期実行(Request Response):クエリ成否に関わらずタスクは成功し次のStateに遷移する
想定通りの結論となりました。おおよそのユースケースでは前者の同期実行で良いのではないでしょうか。
おわりに
AWS Step FunctionsからのAmazon Athenaクエリの実行でIntegrationPatternを指定して際の同期実行/非同期実行を使い比べてみました。
そもそもAthenaクエリを同期実行できることを今日初めて知りました。私の過去のブログを見て教えてくださった@yagi-yusei さんには感謝です!
以上









