
【小ネタ】100万レコードにアクセスするSQLでDSQLのDPUがどれだけ消費されるか確認してみた
リテールアプリ共創部@大阪の岩田です。
Aurora DSQLの料金体系の特徴としてDPU(分散処理ユニット)に対する課金が挙げられます。公式ドキュメントではDPUについて以下のように説明されています。
You can think of a DPU as a measure of how much work the system does to run your SQL workload. This includes compute resources used to execute query logic (e.g., joins, functions, aggregations) as well as the input/output (I/O) required to read from and write to storage.
この説明からすると、DPUはあくまで論理的な値であって、何行を処理したから何DPUと計算できるようなものでは無さそうです。CPUをどれだけ消費したとか、何ページにアクセスしたとか、そういった指標から計算されるのだとは思いますが、ユーザー側で正確に事前に見積もれるものでも無さそうです。
以下のブログですでに検証結果が公開されていましたが、自分でもいくつか別パターンを検証してみたので結果についてご紹介します。
なお、今回の検証は全てシングルリージョンクラスタにて実施しています。
1.CTEで100万レコード生成して最大値を集計するSQL
まずは以下のSQLを試してみます。
EXPLAIN ANALYZE
WITH RECURSIVE v1 (n) AS (
SELECT
1
UNION ALL
SELECT
n + 1
FROM
v1
WHERE
n < 1000000
)
SELECT
max(n)
FROM
v1;
SQLはこちで紹介されていたSQLを流用させて頂きました。
日々の覚書: テンポラリーテーブルがストレージを埋め尽くした時のエラー番号の違い on MySQL 8.0.32
実行結果は以下のとおりでした。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Aggregate (cost=3.34..3.35 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=750.832..750.833 rows=1 loops=1)
CTE v1
-> Recursive Union (cost=0.00..2.65 rows=31 width=4) (actual time=0.005..490.542 rows=1000000 loops=1)
-> Result (cost=0.00..0.01 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.004..0.004 rows=1 loops=1)
-> WorkTable Scan on v1 v1_1 (cost=0.00..0.23 rows=3 width=4) (actual time=0.000..0.000 rows=1 loops=1000000)
Filter: (n < 1000000)
Rows Removed by Filter: 0
-> CTE Scan on v1 (cost=0.00..0.62 rows=31 width=4) (actual time=0.007..685.521 rows=1000000 loops=1)
Planning Time: 0.393 ms
Execution Time: 755.357 ms
(10 rows)
該当時間帯の各種DPUの合計値をCloudWatchから確認すると結果は以下の通りでした。
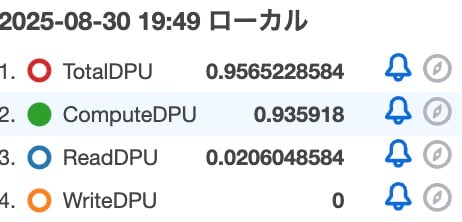
| メトリクス | 値 |
|---|---|
| TotalDPU | 0.9565228584 |
| ComputeDPU | 0.935918 |
| ReadDPU | 0.0206048584 |
| WriteDPU | 0 |
2.CTEで100万レコード生成&ハッシュ値を計算して最大値を集計するSQL
お次のSQLはこちらです。
EXPLAIN ANALYZE
WITH RECURSIVE v1 (n) AS (
SELECT
1
UNION ALL
SELECT
n + 1
FROM
v1
WHERE
n < 1000000
),
v2 AS (
SELECT
n,
MD5(n::text) AS m
FROM
v1
)
SELECT
max(m)
FROM
v2;
先程のSQLと同様CTEで100万レコードを生成したのち、MD5で100万レコード分のハッシュ値を計算しています。
実行結果は以下の通りです。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Aggregate (cost=3.58..3.58 rows=1 width=32) (actual time=1644.433..1644.435 rows=1 loops=1)
CTE v1
-> Recursive Union (cost=0.00..2.65 rows=31 width=4) (actual time=0.003..496.009 rows=1000000 loops=1)
-> Result (cost=0.00..0.01 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.002..0.002 rows=1 loops=1)
-> WorkTable Scan on v1 v1_1 (cost=0.00..0.23 rows=3 width=4) (actual time=0.000..0.000 rows=1 loops=1000000)
Filter: (n < 1000000)
Rows Removed by Filter: 0
-> CTE Scan on v1 (cost=0.00..0.62 rows=31 width=4) (actual time=0.005..695.582 rows=1000000 loops=1)
Planning Time: 0.427 ms
Execution Time: 1649.016 ms
(10 rows)
実行計画としては同じですね。textにキャストする処理とMD5の処理でCPUリソースの使用量は変わりそうですがDPUはどうでしょう?メトリクスは以下の通りでした。

| メトリクス | 値 |
|---|---|
| TotalDPU | 1.78309889063 |
| ComputeDPU | 1.775511 |
| ReadDPU | 0.00758789062 |
| WriteDPU | 0 |
先ほどと比較するとComputeDPUが2倍近くに増えています。
3-1.CROSS JOINで100万レコード生成して最大値を集計するSQL
次はpgbenchで生成されたテスト用テーブルpgbench_accountsを使ってCROSS JOINで100万レコード生成、最大値を取得してみます。ちなみにpgbench_accountsテーブルの定義は以下の通りです。
CREATE TABLE public.pgbench_accounts (
aid int4 NOT NULL,
bid int4 NULL,
abalance int4 NULL,
filler bpchar(84) NULL,
CONSTRAINT pgbench_accounts_pkey PRIMARY KEY (aid)
)
実行するSQLはこちら。
EXPLAIN ANALYZE
SELECT
MAX(aid)
FROM
(SELECT * FROM pgbench_accounts LIMIT 100) a
CROSS JOIN
(SELECT * FROM pgbench_accounts LIMIT 100) b
CROSS JOIN
(SELECT * FROM pgbench_accounts LIMIT 100) c
実行結果はこうなりました。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Aggregate (cost=46285.83..46285.84 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=214.686..214.689 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Nested Loop (cost=31150.25..43785.83 rows=1000000 width=4) (actual time=6.010..164.826 rows=1000000 loops=1)
-> Nested Loop (cost=20766.83..20898.81 rows=10000 width=0) (actual time=4.789..7.871 rows=10000 loops=1)
-> Limit (cost=10383.42..10385.78 rows=100 width=352) (actual time=1.392..2.213 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Index Only Scan using pgbench_accounts_pkey on pgbench_accounts (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual time=1.391..2.202 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Storage Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=100 loops=1)
Projections:
-> B-Tree Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=143 loops=1)
-> Materialize (cost=10383.42..10387.28 rows=100 width=0) (actual time=0.034..0.047 rows=100 loops=100)
-> Subquery Scan on b (cost=10383.42..10386.78 rows=100 width=0) (actual time=3.391..4.118 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Limit (cost=10383.42..10385.78 rows=100 width=352) (actual time=3.391..4.106 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Index Only Scan using pgbench_accounts_pkey on pgbench_accounts pgbench_accounts_1 (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual time=3.390..4.096 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Storage Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=100 loops=1)
Projections:
-> B-Tree Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=155 loops=1)
-> Materialize (cost=10383.42..10387.28 rows=100 width=4) (actual time=0.000..0.006 rows=100 loops=10000)
-> Subquery Scan on c (cost=10383.42..10386.78 rows=100 width=4) (actual time=1.216..1.949 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Limit (cost=10383.42..10385.78 rows=100 width=352) (actual time=1.215..1.939 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Index Only Scan using pgbench_accounts_pkey on pgbench_accounts pgbench_accounts_2 (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual time=1.215..1.928 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Storage Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=100 loops=1)
Projections: aid
-> B-Tree Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=167 loops=1)
Planning Time: 27.866 ms
Execution Time: 214.788 ms
(24 rows)
先程までとは異なり、実際にテーブルのデータにアクセスしていることが分かります。Index Only Scanが出ていますが、DSQLのテーブルは通常のPostgreSQLと異なりクラスター化インデックスと同じような形式でストレージに保存することによるものですね
(参考)
メトリクスも確認してみましょう。
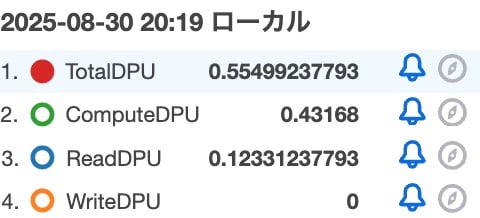
| メトリクス | 値 |
|---|---|
| TotalDPU | 0.55499237793 |
| ComputeDPU | 0.43168 |
| ReadDPU | 0.12331237793 |
| WriteDPU | 0 |
ReadDPUは増えましたが、ハッシュ値を計算していない分先ほどの検証パターン2よりComputeDPUは減りました。さらに、検証パターン1との比較でもComputeDPUが小さいのもポイントですね。検証パターン1だとn + 1 の計算があるので、これが影響しているのでしょうか?
3-2.CROSS JOINで100万レコード生成して最大値を集計するSQLに1加算する処理を追加
CTEの方がCompute DPUが大きくなったので、先程のSQLにも+ 1する処理を追加して再確認してみました。
EXPLAIN ANALYZE
SELECT
MAX(c.aid)
FROM
(SELECT aid + 1 as aid,bid,abalance,filler FROM pgbench_accounts LIMIT 100) a
CROSS JOIN
(SELECT aid + 1 as aid,bid,abalance,filler FROM pgbench_accounts LIMIT 100) b
CROSS JOIN
(SELECT aid + 1 as aid,bid,abalance,filler FROM pgbench_accounts LIMIT 100) c
実行結果はこうなりました。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Aggregate (cost=46286.08..46286.09 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=214.528..214.531 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Nested Loop (cost=31150.25..43786.08 rows=1000000 width=4) (actual time=3.705..164.101 rows=1000000 loops=1)
-> Nested Loop (cost=20766.83..20898.81 rows=10000 width=0) (actual time=2.546..5.693 rows=10000 loops=1)
-> Limit (cost=10383.42..10385.78 rows=100 width=352) (actual time=1.262..2.108 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Index Only Scan using pgbench_accounts_pkey on pgbench_accounts (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual time=1.261..2.097 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Storage Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=100 loops=1)
Projections:
-> B-Tree Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=196 loops=1)
-> Materialize (cost=10383.42..10387.28 rows=100 width=0) (actual time=0.013..0.026 rows=100 loops=100)
-> Subquery Scan on b (cost=10383.42..10386.78 rows=100 width=0) (actual time=1.275..2.008 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Limit (cost=10383.42..10385.78 rows=100 width=352) (actual time=1.274..1.996 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Index Only Scan using pgbench_accounts_pkey on pgbench_accounts pgbench_accounts_1 (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual time=1.274..1.986 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Storage Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=100 loops=1)
Projections:
-> B-Tree Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=196 loops=1)
-> Materialize (cost=10383.42..10387.53 rows=100 width=4) (actual time=0.000..0.006 rows=100 loops=10000)
-> Subquery Scan on c (cost=10383.42..10387.03 rows=100 width=4) (actual time=1.153..1.876 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Limit (cost=10383.42..10386.03 rows=100 width=352) (actual time=1.153..1.865 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Index Only Scan using pgbench_accounts_pkey on pgbench_accounts pgbench_accounts_2 (cost=10383.42..12530.69 rows=82267 width=352) (actual time=1.152..1.855 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Storage Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12530.69 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=100 loops=1)
Projections: aid
-> B-Tree Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12530.69 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=196 loops=1)
Planning Time: 29.143 ms
Execution Time: 214.646 ms
(24 rows)
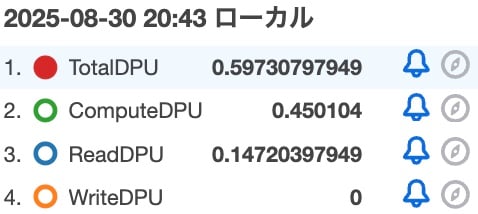
| メトリクス | 値 |
|---|---|
| TotalDPU | 0.59730797949 |
| ComputeDPU | 0.450104 |
| ReadDPU | 0.14720397949 |
| WriteDPU | 0 |
検証パターン3-1よりComputeDPUは増えましたが、それでも検証パターン1よりは小さくなっています。CTEの方は100万レコードに対して加算を実行するのに対してCROSS JOINだとサブクエリの中身100件×3に対してしか加算処理を実行しないからでしょうかね?
4.CROSS JOINで100万レコード生成後にハッシュ値を計算して最大値を集計するSQL
CROSS JOINするパターンにもMD5のハッシュ値計算処理を追加し、さらに計算対象が100万レコードになるようSQLを再調整してみました。
EXPLAIN ANALYZE
SELECT max_aid FROM
(
SELECT
MAX(MD5((c.aid + 1)::text)) as max_aid
FROM
(SELECT * FROM pgbench_accounts LIMIT 100) a
CROSS JOIN
(SELECT * FROM pgbench_accounts LIMIT 100) b
CROSS JOIN
(SELECT * FROM pgbench_accounts LIMIT 100) c
) d
実行結果です。
Aggregate (cost=56285.83..56285.84 rows=1 width=32) (actual time=1094.924..1094.928 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Nested Loop (cost=31150.25..43785.83 rows=1000000 width=4) (actual time=4.575..175.501 rows=1000000 loops=1)
-> Nested Loop (cost=20766.83..20898.81 rows=10000 width=0) (actual time=3.662..7.352 rows=10000 loops=1)
-> Limit (cost=10383.42..10385.78 rows=100 width=352) (actual time=1.118..2.397 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Index Only Scan using pgbench_accounts_pkey on pgbench_accounts (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual time=1.117..2.384 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Storage Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=100 loops=1)
Projections:
-> B-Tree Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=131 loops=1)
-> Materialize (cost=10383.42..10387.28 rows=100 width=0) (actual time=0.025..0.039 rows=100 loops=100)
-> Subquery Scan on b (cost=10383.42..10386.78 rows=100 width=0) (actual time=2.532..3.290 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Limit (cost=10383.42..10385.78 rows=100 width=352) (actual time=2.531..3.278 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Index Only Scan using pgbench_accounts_pkey on pgbench_accounts pgbench_accounts_1 (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual time=2.531..3.267 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Storage Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=100 loops=1)
Projections:
-> B-Tree Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=155 loops=1)
-> Materialize (cost=10383.42..10387.28 rows=100 width=4) (actual time=0.000..0.006 rows=100 loops=10000)
-> Subquery Scan on c (cost=10383.42..10386.78 rows=100 width=4) (actual time=0.908..1.664 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Limit (cost=10383.42..10385.78 rows=100 width=352) (actual time=0.907..1.653 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Index Only Scan using pgbench_accounts_pkey on pgbench_accounts pgbench_accounts_2 (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual time=0.907..1.642 rows=100 loops=1)
-> Storage Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=100 loops=1)
Projections: aid
-> B-Tree Scan on pgbench_accounts_pkey (cost=10383.42..12325.02 rows=82267 width=352) (actual rows=167 loops=1)
Planning Time: 23.531 ms
Execution Time: 1095.048 ms
(24 rows)
メトリクスはこちら。
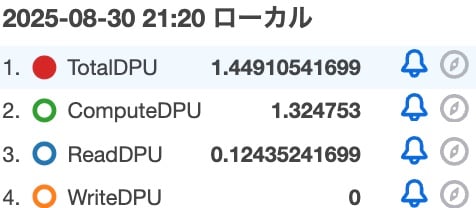
ComputeDPUが増えたのは想定通りですが、CTEを使うパターンの方が0.45程度ComputeDPUの消費が大きいという結果になりました。これまでの検証結果をまとめると以下のようになります。※WriteDPUはすべて0だったので省略しています。
| 検証パターン | TotalDPU | ComputeDPU | ReadDPU |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.CTEで100万レコード生成 | 0.9565228584 | 0.935918 | 0.0206048584 |
| 2.CTEで100万レコード生成&ハッシュ値を計算 | 1.78309889063 | 1.775511 | 0.00758789062 |
| 3-1.CROSS JOINで100万レコード生成 | 0.55499237793 | 0.43168 | 0.12331237793 |
| 3-2.CROSS JOINで100万レコード生成 &1を加算 | 0.59730797949 | 0.450104 | 0.14720397949 |
| 4.CROSS JOINで100万レコード生成後に1加算&ハッシュ値を計算 | 1.44910541699 | 1.324753 | 0.12435241699 |
おまけ pgbenchのテストデータをリストアした時のメトリクス
おまけとして検証パターン3,4で利用したpgbenchのテストデータを投入した際のメトリクスも紹介しておきます。外部キーやCOPYコマンドの非互換から、pgbenchコマンドで初期データが作成できないため、ローカル環境にテストデータを生成してからDSQLにリストアする形でデータを投入しました。
pg_dumpを使ってデータをINSERT文の形式でダンプしており、ダンプファイルは以下のような形式になります。
--
-- Data for Name: pgbench_accounts; Type: TABLE DATA; Schema: public; Owner: postgres
--
INSERT INTO public.pgbench_accounts VALUES (1, 1, 0, ' ');
INSERT INTO public.pgbench_accounts VALUES (2, 1, 0, ' ');
INSERT INTO public.pgbench_accounts VALUES (3, 1, 0, ' ');
INSERT INTO public.pgbench_accounts VALUES (4, 1, 0, ' ');
...略
これをpsqlでまとめてINSERTした際のメトリクスはこんな感じでした。
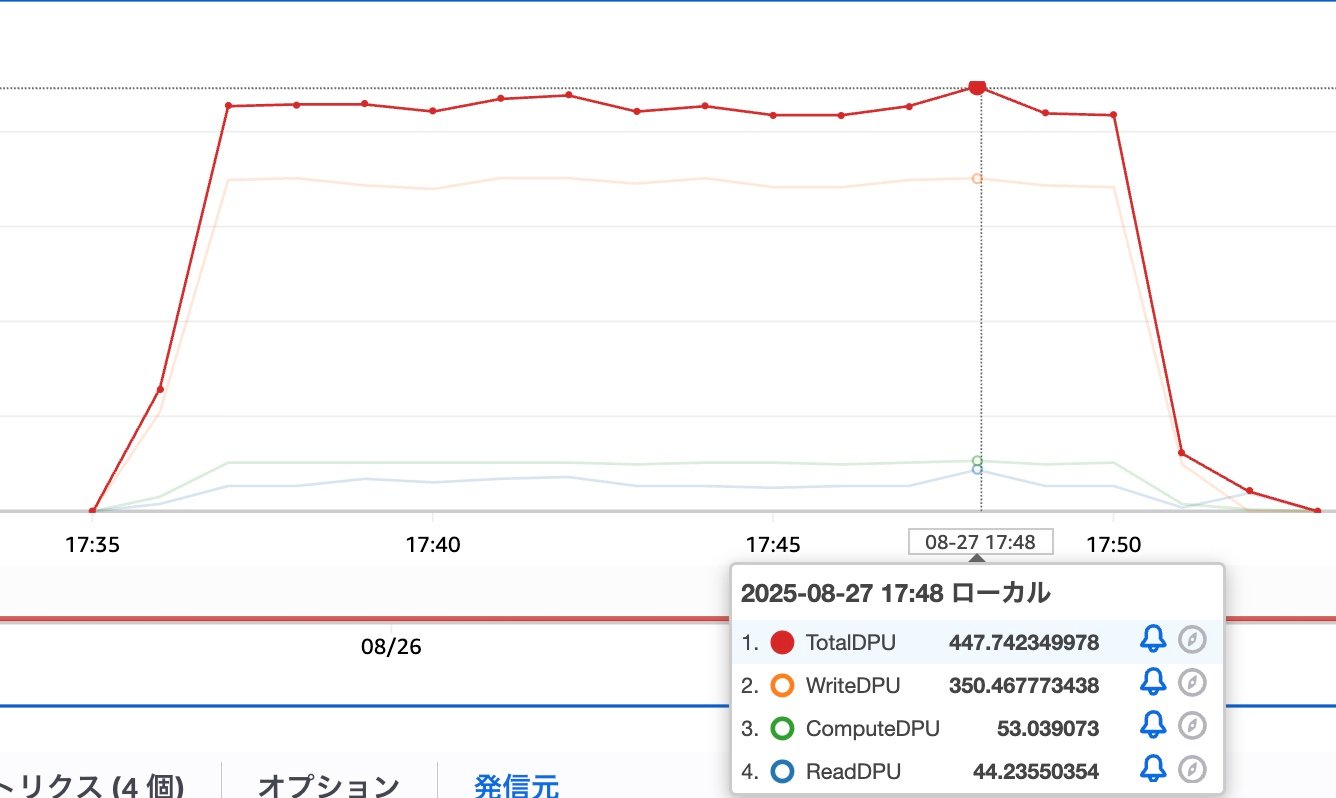
WriteDPUが大きくなるのは想定どおりですが、意外とReadDPUも消費してますね。
まとめ
DSQLのDPUについていくつかのパターンで検証してみました。検証で大量に請求されないか少し不安だったのですが、100万レコード程度であれば全然大したDPU消費になりませんでした。良かった!!








